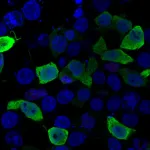
(Press-News.org) Cancer, which affects millions every year, requires proteins to spread through the body. In a new strategy to beat the wide-ranging disease, scientists are sabotaging its protein factories.
In a new forum paper published in Trends in Biology, researchers from the University of North Carolina at Charlotte encapsulated the young field of nucleolar DNA damage response (DDR) pathways. The review highlights six mechanisms by which cells repair DNA damage, including one which was published five months ago in Nucleic Acids Research by the same authors. By attacking these mechanisms, future applied researchers will be able to trip up cancer’s reproduction and growth.
“The whole purpose of the Trends paper is to bring attention to scientists in the field and trigger their research,” says Shan Yan, the main author. “I did not realize the significance of this field, which is only fifteen years old, until a couple of years ago.”
In a groundbreaking 2007 paper published in Nature, researchers began the field by unveiling the first pathway within the nucleolus, an area within an organelle, or room, within the cell. Inside the nucleolus, different molecules help copy DNA, which contains the plans for cells. Different factors can cause glitches, such as strand breaks, in the copies. These researchers found a way to help heal glitches when copying ribosomal DNA, or the plans for the protein factories of the cell.
By studying these mechanisms, researchers can target cancer, which relies on ribosomal DNA to make the proteins they need to attack the human body. For instance, a Phase I clinical trial is already underway for a drug that targets the second mechanism listed in the paper—if the cancer cells can’t heal glitches, then they can’t make new factories and hence can’t make new proteins.
While the first four mechanisms take place inside the nucleolus, which is in a room cordoned off within the watery cell, the last two mechanisms use a new cellular process which won the 2023 Breakthrough Prize in Life Sciences. In the process, called liquid-liquid phase transition, proteins pop up their own liquid ‘tents’ to do their work instead of staying inside a room.
Before working on the nucleolar DDR, Yan researched a protein called APE1. When he discovered that APE1 could locate the nucleolus within a cell and could also pop up these liquid tents to do work, it launched his investigation into these pathways and ultimately to the review paper.
“What's new is that APE1 acts like a GPS or a first responder,” Yan said. “It says there’s a problem here, we need a police car, a medic, and others to come and be concentrated here.”
Basic researchers like Yan will continue to better define these mechanisms, while more applied scientists can then use those mechanisms as points of attack in the war on cancer.
“This is an exciting and emerging area,” Yan said. “By testing this idea, and if the clinical trial is successful, then these mechanisms will be tickets into new clinical trials and treatments.”
###
“Molecular mechanisms of nucleolar DNA damage checkpoint response” by Jia Li and Shan Yan in Trends in Cell Biology.
“APE1 assembles biomolecular condensates to promote the ATR-Chk1 DNA damage response in nucleolus” by Jia Li, Haichao Zhao, Anne McMahon, and Shan Yan in Nucleic Acids Research online October 6, 2022 (https://academic.oup.com/nar/article/50/18/10503/6749544).
The Yan laboratory is supported in part by grants from the NIH/NCI (R01CA225637 and R03CA270663) and the NIH/NIEHS (R21ES032966) and funds from the University of North Carolina at Charlotte.
END
A new tool that can be used to forecast the prevalence of individuals within a country that may have insufficient access to food — known as food insecurity — up to 30 days into the future is presented in a study published in Scientific Reports. The authors suggest that the tool could aid decision makers in countries at risk of food insecurity and help facilitate more timely responses.
Elisa Omodei and colleagues developed the tool using food consumption data from Burkina Faso, Cameroon, Mali, Nigeria, Syria and Yemen — all countries that have recently ...
Most immunotherapies, which aim to boost T cell activity, work poorly in treating estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancer. Targeting a different type of immune cell called macrophages could be a more effective approach, suggests a comprehensive new analysis of invasive ER+ breast cancers led by University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine scientists.
Published today in Nature Cancer, the study found that macrophages were the dominant immune cell infiltrating ER+ invasive lobular carcinoma (ILC) and invasive ductal carcinoma ...
New York, NY (March 16, 2023) – Using a new computational approach they developed to analyze large genetic datasets from rare disease cohorts, researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai and colleagues have discovered previously unknown genetic causes of three rare conditions: primary lymphedema (characterized by tissue swelling), thoracic aortic aneurysm disease, and congenital deafness. The work was done in collaboration with colleagues at the University of Bristol, UK; KU Leuven, Belgium; the University of Tokyo; the University of Maryland; Imperial College London, and others from around the world.
An enhanced understanding of the functions ...
Fast facts:
The global shortage of fresh water currently affects hundreds of millions of people around the world, and it is estimated that by 2025, 1.8 billion people will experience severe water scarcity and hunger due to loss of fertile farming lands caused by droughts.
The discovery of alternative water-harvesting technologies holds the potential to alleviate the foreseeable socioeconomic impacts of severe water scarcity.
Abu Dhabi, UAE, March 16 2023: Researchers of the Smart Materials Lab (SML) and the Center for Smart Engineering Materials (CSEM) at NYU Abu Dhabi (NYUAD) have reported a novel method of harvesting water from ...
HOUSTON ― In a Phase II trial led by researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center, adding ipilimumab to a neoadjuvant, or pre-surgical, combination of nivolumab plus platinum-based chemotherapy, resulted in a major pathologic response (MPR) in half of all treated patients with early-stage, resectable non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
New findings from the NEOSTAR trial, published today in Nature Medicine, provide further support for neoadjuvant immunotherapy-based treatment as an approach to reduce viable tumor at surgery and to improve outcomes in NSCLC. The combination also was associated with an increase in immune cell infiltration and a favorable gut microbiome ...
Leipzig. Intense fishing and overexploitation have led to evolutionary changes in fish stocks like cod, reducing both their productivity and value on the market. These changes can be reversed by more sustainable and far-sighted fisheries management. The new study by researchers from the German Centre for Integrative Biodiversity Research (iDiv), Leipzig University and the Institute of Marine Research in Tromsø, which was published in Nature Sustainability, shows that reversal of evolutionary change would only slightly reduce the profit of fishing, but would help regain and conserve natural genetic diversity.
The impact of global fisheries on marine ecosystems ...
A research team from the University of Cologne (Germany) and the University of St Andrews (Scotland) has shown in a new study how a fundamental physical concept can be used to boost the colour brilliance of smartphone, computer or TV screens without cutbacks in energy efficiency. The results have been published in Nature Photonics.
Organic light-emitting diodes (OLEDs) have conquered the market for displays in recent years – from high-resolution smartphone to wall-sized television screens. However, industry and science face several challenges in creating the next generation of devices ...
Hot topic – how heat flow affects the Earth’s magnetic field
Compass readings that do not show the direction of true north and interference with the operations of satellites are a few of the problems caused by peculiarities of the Earth’s magnetic field.
The magnetic field radiates around the world and far into space, but it is set by processes that happen deep within the Earth’s core, where temperatures exceed 5,000-degress C.
New research from geophysicists at the University of Leeds suggests that ...
A new method to cure HIV—by transplanting HIV-resistant stem cells from umbilical cord blood—has yielded long-term successful results, say scientists. The approach was successfully used to treat the “New York patient,” a middle-aged woman with leukemia and HIV who self-identifies as mixed race, who has been without HIV since 2017. Using stem cells from cord blood rather than from compatible adult donors, as has been done previously, increases the potential to cure HIV via stem cell transplantation ...
The Ashaninka are the most numerous Indigenous people living in the rainforests of Peru and Brazil where they inhabit a crucial area between the Andes and sources of the Amazon River. And yet, despite the size of the population and their importance in the past and present, their genetic history has remained understudied.
Now a team of researchers reporting in the journal Current Biology on March 16 has analyzed the genomes of more than 50 individuals to clarify the group’s interactions with nearby South American regions, including Central America and the Caribbean. ...