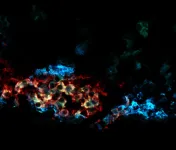
(Press-News.org) The common commensal gut bacterium Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron uses phase separation of the transcription termination factor Rho to colonize and thrive in the mammalian gut, according to a new study in mice. The findings suggest that phase separation may also be vital for other important gut microbes and relevant for novel microbiome-based clinical applications. The gut microbiota plays a critical role in human health. Manipulating gut commensal communities could provide promising therapeutic pathways for treating a host of diseases. However, this goal requires understanding mechanisms that enable beneficial bacteria to colonize the gut – a complex process that includes successful competition for scarce nutrients and resistance to the host’s immune system. Here, Emilia Krypotou and colleagues evaluate these mechanisms in B. thetaiotaomicron, one of the most abundant bacterial species in the human gut of healthy individuals and a species currently being tested in clinical trials as a potential therapeutic for gastrointestinal disorders. The authors focused on the highly conserved transcription termination factor Rho, which is essential in regulating gene transcription in bacteria. However, unlike other bacteria, B. thetaiotaomicron’s Rho protein harbors a large intrinsically disordered domain (IDR). Krypotou et al. now show that the unique IDR of this Rho protein enables liquid-liquid phase separation of the transcription termination factor and is critical for B. thetaiotaomicron gene regulation in the gut. Through in vitro and in vivo experiments in a mouse model, the authors found that B. thetaiotaomicron responded to the mammalian gut environment by sequestering Rho molecules within a membraneless compartment via phase separation. This IDR-dependent molecular condensation increased Rho termination activity, resulting in the modified transcription of hundreds of genes, including several required for gut fitness and colonization.
END
Common gut bacterium exploits Rho factor phase separation to colonize the mammalian gut
2023-03-16
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Lessons from China’s coal strategy can inform environmental cooperation
2023-03-16
In 2021, China unilaterally announced that it would stop building new coal-fueled power plants overseas, which was lauded as an important climate milestone. However, this decision stands in contrast to the nation’s continued support for the domestic use of coal plants. In a Policy Forum, Christoph Nedopil discusses this dichotomy and provides new insights into how these decisions were made. According to Nedopil, the findings could inform efforts to improve environmental cooperation with China. China has become the world’s greatest source of greenhouse gas emissions, and its international influence through trade, ...
Nano cut-and-sew: New method for chemically tailoring layered nanomaterials could open pathways to designing 2D materials on demand
2023-03-16
A new process that lets scientists chemically cut apart and stitch together nanoscopic layers of two-dimensional materials — like a tailor altering a suit — could be just the tool for designing the technology of a sustainable energy future. Researchers from Drexel University, China and Sweden, have developed a method for structurally splitting, editing and reconstituting layered materials, called MAX phases and MXenes, with the potential of producing new materials with very unusual compositions and exceptional properties.
A “chemical scissor” is a chemical designed to react with a specific compound to break ...
Fomepizole helps overcome antibiotic-resistant pneumonia in mice
2023-03-16
Pneumococcal disease leads to over three million hospitalizations and hundreds of thousands of deaths annually. A study publishing March 16th in the open access journal PLOS Biology by Carlos J. Orihuela at the University of Alabama at Birmingham, Alabama, United States, and colleagues suggests that the FDA-approved drug Fomepizole may reduce disease severity in the lungs of mice with some forms of bacterial pneumonia and enhance the efficacy of the antibiotic erythromycin as well.
Streptococcus pneumoniae is the leading cause of community-acquired ...
Losing key type of pancreatic cell may contribute to diabetes
2023-03-16
Losing Key Type of Pancreatic Cell May Contribute to Diabetes
Multiple types of beta cells produce insulin in the pancreas, helping to balance blood sugar levels. Losing a particularly productive type of beta cell may contribute to the development of diabetes, according to a new study by Weill Cornell Medicine investigators.
In the study, published March 16 in Nature Cell Biology, Dr. James Lo, associate professor of medicine at Weill Cornell Medicine, and colleagues measured gene expression in individual beta cells collected from mice to determine how many different types of beta cells exist in the pancreas. The team discovered four distinct beta cell types, including one that stood out. ...
Spin-off: 12 million euros for a novel gene editing platform
2023-03-16
The TU Dresden Spin-off Seamless Therapeutics Launches with $12.5M Seed Financing to Advance Transformative Gene Editing Platform Based on Programmable Precision Designer Recombinases in Dresden
Seed round co-led by Wellington Partners and Forbion, with additional non-dilutive financial support from the BMBF (GO-Bio funding) enables maturation of the proprietary platform and pipeline towards first clinical evaluation
Seamless Therapeutics, a Dresden based start-up of the Technische Universität Dresden, today announced a $12.5 million (€11.8M) seed financing round which will accelerate further development ...
Paxlovid associated with lower risk of hospital admission
2023-03-16
PASADENA, Calif. — A Kaiser Permanente study confirms the benefit of nirmatrelvir-ritonavir, also known as Paxlovid, as an early-stage treatment to prevent hospitalization for people with mild to moderate COVID-19, regardless of prior immunity or age. The study was published March 15, 2023, in Lancet ID.
“Among Kaiser Permanente members in Southern California who tested positive for coronavirus infection, receiving Paxlovid within 5 days of the start of COVID-19 symptoms was associated with substantial reductions in the risk of hospital admission or death,” said Sara Tartof, PhD, the senior author of the study and an epidemiologist with the Kaiser ...
Children at risk of multiple sclerosis often go undetected in early stages
2023-03-16
Criteria used by neurologists to assess for multiple sclerosis (MS) in adults may fail to identify the illness in children with imaging suspicious for the disease, an oversight that could delay treatment of the disease at its earliest stages, according to a Rutgers study.
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the primary tool used for diagnosis of MS, and doctors have applied various standards over the years to classify those most likely to develop the disease. The most recent standard, known as the McDonald criteria, was last updated in 2017.
In some cases, imaging suspicious for MS is found incidentally ...
Breakthrough in the understanding of quantum turbulence
2023-03-16
Researchers have shown how energy disappears in quantum turbulence, paving the way for a better understanding of turbulence in scales ranging from the microscopic to the planetary.
Dr Samuli Autti from Lancaster University is one of the authors of a new study of quantum wave turbulence together with researchers at Aalto University.
The team’s findings, published in Nature Physics, demonstrate a new understanding of how wave-like motion transfers energy from macroscopic to microscopic length scales, and their results confirm ...
Selwyn Rogers named associate editor of prestigious New England Journal of Medicine
2023-03-16
Renowned University of Chicago Medicine trauma surgeon Selwyn O. Rogers Jr., MD, MPH, has been named an associate editor of the New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM), effective March 16.
The founding director of the UChicago Medicine Trauma Center, Rogers is a Professor of Surgery at UChicago and Chief of Trauma and Acute Care Surgery at its 1,296-bed academic health system based on Chicago’s South Side.
A leading public health expert whose research focuses on the healthcare needs of underserved populations — particularly those impacted by intentional violence — he is the first surgeon in more than a decade to serve as an associate editor at NEJM, ...
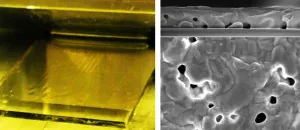
Perovskite solar cells from the slot die coater - a step towards industrial production
2023-03-16
Metal halide perovskites are considered to be a particularly low-cost and promising class of materials for next-generation solar modules. Perovskite solar cells can be produced with coating processes using liquid inks made from precursor materials and various solvents. After coating, the solvents evaporate and the perovskites crystallise to form a more or less homogeneous layer.
Options for upscaling
Prof. Dr. Eva Unger's team at Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin has extensive expertise in solution-based processing methods and is investigating options for upscaling. "Perovskite photovoltaics is the best solution-processable PV technology available," says Eva Unger, ...