(Press-News.org) In humanity’s ongoing quest for the elixir of life, the science keeps pointing to stem cells. Research increasingly shows that maintaining stem cell fitness promotes a long healthspan, and new findings show keeping stem cells clean and tidy is an integral step.
In a study published March 21, 2023 in Cell Stem Cell, researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine found that blood stem cells use an unexpected method to get rid of their misfolded proteins, and that this pathway’s activity degrades with age. The authors say boosting this specialized garbage disposal system could help protect against age-related diseases.
The study focused on hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs), the cells in our bone marrow that produce new blood and immune cells throughout our lives. When their function is weakened or lost, this can lead to blood and immune disorders, such as anemia, blood clotting and cancer.
“Stem cells are in it for the long haul,” said senior study author Robert Signer, PhD, associate professor at UC San Diego School of Medicine. “Their need for longevity requires them to be wired differently than all the short-lived cells in the body.”
A key to keeping stem cells happy is maintaining protein homeostasis. Previous work showed that stem cells, including HSCs, synthesize proteins much slower than other cell types, prioritizing quality over quantity. This helps them make fewer mistakes in the process, as misfolded proteins can become toxic to cells if allowed to build up.
Still, some mistakes or protein damage are inevitable, so the researchers set out to understand how stem cells ensure these proteins are properly discarded.
In most cells, damaged or misfolded proteins get individually tagged for disposal. A mobile protein destroyer called the proteasome then finds the labeled proteins and breaks them down into their original amino acid components. But in the new study, the researchers found proteasome activity was especially low in HSCs. This left the team puzzled: if getting rid of damaged proteins is so important to stem cells, why is the proteasome less active?
Through a series of subsequent experiments, the team discovered that HSCs use a different system entirely. Here, damaged and misfolded proteins are collected and trafficked into clusters called aggresomes. Once corralled into a single location, they can be collectively destroyed by the lysosome (a cell organelle containing digestive enzymes) in a process called aggrephagy.
“What's very unusual here is this pathway was thought to only be triggered as an extreme stress response, but it’s actually the normal physiological pathway that’s used by stem cells,” said Signer. “This emphasizes how critical it is for stem cells to prevent stress so they can preserve their health and longevity."
So why this different system? A main advantage of the proteasome method is that it breaks proteins down immediately, producing amino acids that the cell can reuse to build new proteins. But stem cells are less interested in building new proteins. Thus the authors suggest that by storing a collection of damaged proteins in one place, stem cells may be creating their own cache of resources that can be used at a later time when they are actually needed, such as after an injury or when it is time to regenerate.
“The body really can’t risk losing its stem cells, so having this stockpile of raw materials makes them more protected against rainy days,” said Signer. “Stem cells are marathon runners, but they also need to be world-class sprinters when the circumstances call for it.”
When the researchers genetically disabled the aggrephagy pathway, the stem cells started to accumulate aggregated protein, which impaired their fitness, longevity and regenerative activity.
The team then discovered that while almost all young stem cells had aggresomes, at a certain point in aging, they were almost completely gone. The authors suggest that stem cells’ inability to efficiently destroy misfolded proteins during aging is likely a key contributing factor to their declining function and the resulting age-related disorders.
“Our hope is that if we can improve stem cells’ ability to maintain the aggrephagy pathway, we will preserve better stem cell fitness during aging and mitigate blood and immune disorders,” said Signer.
The authors suspect that other types of stem cells and long-lived cells like neurons have a similar requirement for strict regulation of protein homeostasis, suggesting therapeutics to boost this pathway may be beneficial across multiple organs and pathologies.
Co-authors of this study include: Bernadette A. Chua, Connor J. Lennan, Mary Jean Sunshine, Daniela Dreifke and Eric J. Bennett at UC San Diego and Ashu Chawla at La Jolla Institute for Immunology.
Full link to study: https://www.cell.com/cell-stem-cell/fulltext/S1934-5909(23)00071-1
# # #
END
To ward off aging, stem cells must take out the trash
UC San Diego scientists find stem cells’ unique way of discarding misfolded proteins could be the key to maintaining long-term health and preventing disease
2023-03-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
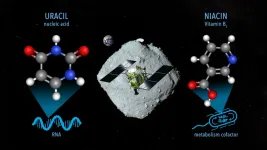
Uracil found in Ryugu samples
2023-03-21
Samples from the asteroid Ryugu collected by the Hayabusa2 mission contain nitrogenous organic compounds, including the nucleobase uracil, which is a part of RNA.
Researchers have analyzed samples of asteroid Ryugu collected by the Japanese Space Agency’s Hayabusa2 spacecraft and found uracil—one of the informational units that make up RNA, the molecules that contain the instructions for how to build and operate living organisms. Nicotinic acid, also known as Vitamin B3 or niacin, which is an important cofactor for metabolism in living organisms, was also detected in the same samples.
This discovery by an international team, led by Associate Professor ...
Honey, the 3D print--I mean, dessert--is ready!
2023-03-21
New York, NY—March 21, 2023—Cooking devices that incorporate three-dimensional (3D) printers, lasers, or other software-driven processes may soon replace conventional cooking appliances such as ovens, stovetops, and microwaves. But will people want to use a 3D printer--even one as beautifully designed as a high-end coffee maker--on their kitchen counters to calibrate the exact micro- and macro-nutrients they need to stay healthy? Will 3D food printing improve the ways we nourish ourselves? What sorts of ...
Albert Einstein College of Medicine and Montefiore Health System awarded $30 million from NIH to support its Institute for Clinical and Translational Research
2023-03-21
March 21, 2023—BRONX, NY—Albert Einstein College of Medicine and Montefiore Health System have received a seven-year, $30 million grant from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) to continue support for the Harold and Muriel Block Institute for Clinical and Translational Research at Einstein and Montefiore (ICTR). The latest Clinical and Translational Science Award (CTSA) will ensure the ICTR will further its vision to improve health in the Bronx, Westchester, and lower Hudson Valley by accelerating the translation of scientific discoveries into effective and equitable prevention and treatment approaches.
“Since establishing ...
Diet and exercise programs alone won’t tackle childhood obesity
2023-03-21
Focusing on immediate fixes such as diet and exercise programs alone won’t curb the tide of childhood obesity, according to a new study that for the first time maps the complex pathways that lead to obesity in childhood.
Coordinated by the University of Sydney’s Charles Perkins Centre the study finds children whose parents did not complete high school and who live with social disadvantage, were more likely to be affected by overweight or obesity in mid-adolescence. High school completion is a strong indicator of socio-economic status.
These factors were ‘on ramps’ which flow down to influence the body ...
New Yale study evaluates PAXLOVID’s use in Long COVID recovery
2023-03-21
New Haven, Conn. — Yale School of Medicine announces the initiation of a novel, randomized trial that will test whether receiving PAXLOVIDTM (nirmatrelvir tablets; ritonavir tablets) for 15 days can improve the health of highly symptomatic adults with Long COVID.
The trial, led by Yale School of Medicine Professors Harlan Krumholz and Akiko Iwasaki, has a decentralized design, meaning that participants do not have to travel to study sites. It also uses a novel, participant-centric, digital approach to data collection.
Long COVID, also known as post-acute sequelae SARS-CoV-2 ...
ESMT Berlin: New book on how industrial companies can survive deglobalization
2023-03-21
Deglobalization and the unpredictability of global business have led technology-based industries to review their overall strategies. Current geopolitical changes – the war in Ukraine, effects of the pandemic, and greenhouse gas emission targets – revived discussions about the value of globalization. However, international trade of goods and services has been slowing down significantly since 2011, with increasing nationalism being a factor. Additionally, lower salary differentials between developed and emerging economies have reduced overseas product shipments – which are increasingly criticized regarding environmental impact. So, how ...
Scientists find a common thread linking subatomic color glass condensate and massive black holes
2023-03-21
The Science
Physicists have discovered a remarkable correspondence between dense states of gluons—the gluelike carriers of the strong nuclear force within atomic nuclei—and enormous black holes in the cosmos. The dense walls of gluons, known as a color glass condensate (CGC), are generated in collisions of atomic nuclei. This CGC measures a mere 10-19 kilometers across—less than a billionth of a kilometer. Black holes, in contrast, span billions of kilometers across. The new work shows that both systems are made of densely packed, self-interacting force carrier particles. In CGC, those particles are ...
Vocal tract size, shape dictate speech sounds
2023-03-21
WASHINGTON, March 21, 2023 – Only humans have the ability to use speech. Remarkably, this communication is understandable across accent, social background, and anatomy despite a wide variety of ways to produce the necessary sounds.
In JASA, published on behalf of the Acoustical Society of America by AIP Publishing, researchers from University Hospital and Medical Faculty of the RWTH Aachen University explored how anatomical variations in a speaker’s vocal tract affect speech production.
The vocal tract looks like an air duct, starting at the vocal cords and moving vertically through the larynx before bending at the back of the mouth and running ...
Healthy men who have vaginal sex have a distinct urethral microbiome
2023-03-21
Contrary to common beliefs, your urine is not germ free. In fact, a new study shows that the urethra of healthy men is teeming with microbial life and that a specific activity—vaginal sex—can shape its composition. The research, published March 24 in the journal Cell Reports Medicine, provides a healthy baseline for clinicians and scientists to contrast between healthy and diseased states of the urethra, an entrance to the urinary and reproductive systems.
“We know where bugs in the gut come from; they primarily come from our surroundings ...
A recipe for 3D-printing food
2023-03-21
WASHINGTON, March 21, 2023 – 3D-printing food could address global challenges in food supply and nutrition. But there are hurdles involved in adapting additive manufacturing to produce edible materials.
In Physics of Fluids, from AIP Publishing, University of Ottawa researchers Ezgi Pulatsu and Chibuike Udenigwe identify a range of factors that affect the print quality and shape complexity of food created with additive manufacturing. Accounting for these features can increase food quality, improve control, and speed up printing.
Additive manufacturing of food involves designing (3D shapes and their geometric codes), ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
GLP-1 drugs associated with reduced need for emergency care for migraine
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
[Press-News.org] To ward off aging, stem cells must take out the trashUC San Diego scientists find stem cells’ unique way of discarding misfolded proteins could be the key to maintaining long-term health and preventing disease