(Press-News.org) The research published in the Journal of Infection investigated the use of metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) in diagnosing bloodstream infections (BSIs) for immunocompromised hematology patients. Hematology patients are highly susceptible to BSIs, which can have severe consequences such as septic shock, multiple-organ failure, disseminated intravascular coagulation, and even death. An accurate and quick microbiological diagnosis of BSI is therefore essential for the control of the infection.
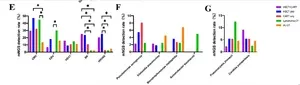
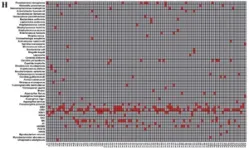
In the study, conducted between January 2019 and December 2020 at Tongji Hospital with the participation of BGI Genomics researcher Wenqian Zhang, peripheral blood samples were collected from 256 immunocompromised hematology patients suspected of BSI, and both mNGS and conventional microbiological tests (CMTs) were performed. BSI diagnosis was confirmed in 189 out of 256 patients (73.8%). The detection rate of mNGS was significantly higher than that of CMTs, with mNGS identifying 187 infection cases and CMTs identifying 81. Results indicate mNGS outperformed CMT in detecting bloodstream infections.
Bacteria were detected in 17 patients (6.6%), fungi in 15 patients (5.9%), rare pathogens in 4 patients (1.6%), and multiple species in 55 patients (21.5%).
Based on mNGS results, viral infection was the most frequent BSI, identified in 96 out of 256 patients (37.5%). The five most common causative viruses were CMV (31.3%), EBV (14.8%), HSV1 (11.7%), BK virus (11.7%) and HHV6B (9.4%).
The results also showed that it was more likely for patients who had undergone hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT), than those who had not, to be infected by BK virus and HHV6B.
Overall, the study highlights the potential of mNGS as a powerful tool for the rapid and accurate diagnosis of BSIs in immunocompromised hematology patients, allowing for timely and effective treatment.
About BGI Genomics
BGI Genomics, headquartered in Shenzhen China, is the world's leading integrated solutions provider of precision medicine. Our services cover over 100 countries and regions, involving more than 2,300 medical institutions. In July 2017, as a subsidiary of BGI Group, BGI Genomics (300676.SZ) was officially listed on the Shenzhen Stock Exchange.
END
mNGS outperforms microbiological tests to diagnose bloodstream infections – BGI Insight
Next-generation sequencing (mNGS) leverages genetic testing advantage to save more lives; twice as effective at identifying infection cases
2023-03-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Beyond ‘good vs. bad’ – A new, more comprehensive approach to evaluate carbohydrate quality and improve health equity
2023-03-23
March 23, 2023 – Despite the broad diversity of the U.S. population, dietary recommendations often overlook the positive contributions of cultural foods to build healthy dietary patterns. This is especially true when it comes to carbohydrate food guidance, where prevailing approaches have historically focused on only three components— carbohydrates, sugar, and dietary fiber—ignoring other important nutrient and cultural considerations. However, a new paper published in Nutrients highlights a more holistic approach, called the Carbohydrate Food Quality ...
Robotic system offers hidden window into collective bee behavior
2023-03-23
Honeybees are famously finicky when it comes to being studied. Research instruments and conditions and even unfamiliar smells can disrupt a colony’s behavior. Now, a joint research team from the Mobile Robotic Systems Group in EPFL’s School of Engineering and School of Computer and Communication Sciences and the Hiveopolis project at Austria’s University of Graz have developed a robotic system that can be unobtrusively built into the frame of a standard honeybee hive.
Composed of an array of thermal sensors and actuators, the system measures and modulates honeybee behavior through ...
Octapharma USA grant supports PANS/PANDAS education event at NHIA Conference March 27 in Washington, D.C.
2023-03-23
PARAMUS, N.J. (March 23, 2023) – Octapharma USA has provided a grant for an educational program on pediatric acute-onset neuropsychiatric syndrome (PANS) and PANDAS, a subset of PANS associated with strep, to be held during the National Home Infusion Association (NHIA) Annual Conference scheduled for March 25 – 27 in Washington, D.C.
Octapharma is enrolling more patients and sites for its phase 3 multicenter superiority study comparing the effectiveness of panzyga® (immune globulin intravenous, human - ifas) 10% liquid preparation versus placebo ...
Scientists warn of rise in potentially fatal bacterial infection due to global warming
2023-03-23
Continued warming of the climate would see a rise in the number and spread of potentially fatal infections caused by bacteria found along parts of the coast of the United States.
Vibrio vulnificus bacteria grow in warm shallow coastal waters and can infect a cut or insect bite during contact with seawater. A new study led by the UK’s University of East Anglia (UEA) shows that the number of V. vulnificus infections along the East Coast of the US, a global hotspot for such infections, has gone ...
UTSA researchers exploit vulnerabilities of smart device microphones and voice assistants
2023-03-23
(SAN ANTONIO) MARCH 23, 2023 - Guenevere Chen, an associate professor in the UTSA Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering, recently published a paper on USENIX Security 2023 that demonstrates a novel inaudible voice trojan attack to exploit vulnerabilities of smart device microphones and voice assistants — like Siri, Google Assistant, Alexa or Amazon’s Echo and Microsoft Cortana — and provide defense mechanisms for users.
The researchers developed Near-Ultrasound Inaudible Trojan, or NUIT (French for “nighttime”) to study how hackers exploit speakers and ...
Without this, plants cannot respond to temperature
2023-03-23
UC Riverside scientists have significantly advanced the race to control plant responses to temperature on a rapidly warming planet. Key to this breakthrough is miRNA, a molecule nearly 200,000 times smaller than the width of a human hair.
With moderate increases in temperature, plants grow taller to avoid hotter ground and get fresher air. A landmark study published in the journal Nature Communications demonstrates that microRNA or miRNA is required for this growth. The study also identifies which miRNA molecules — out of more than 100 possibilities — are the essential ones.
“We found that without miRNA plants will not grow, even ...
Use of melatonin linked to decreased self-harm in young people
2023-03-23
Medical sleep treatment may reduce self-harm in young people with anxiety and depression, an observational study from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden suggests. The risk of self-harm increased in the months preceding melatonin prescription and decreased thereafter, especially in girls. The study is published in The Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry.
Melatonin is a hormone that controls the sleep-wake cycle and is the most commonly prescribed drug for sleep disturbances in children and adolescents in Sweden. Melatonin use has dramatically increased in recent years, and it is available over the counter in Sweden since 2020.
“Given the established link between sleep ...
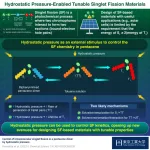
Pressure-based control enables tunable singlet fission materials for efficient photoconversion
2023-03-23
Applying hydrostatic pressure as an external stimulus, Tokyo Tech and Keio University researchers demonstrate a new way to regulate singlet fission (SF), a process in which two electrons are generated from a single photon, in chromophores, opening doors to the design of SF-based materials with enhanced (photo)energy conversion. Their method overrides the strict requirements that limit the molecular design of such materials by realizing an alternative control strategy.
Singlet fission (SF) is a process in which ...
New wood-based technology removes 80% of dye pollutants in wastewater
2023-03-23
Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, have developed a new method that can easily purify contaminated water using a cellulose-based material. This discovery could have implications for countries with poor water treatment technologies and combat the widespread problem of toxic dye discharge from the textile industry.
Clean water is a prerequisite for our health and living environment, but far from a given for everyone. According to the World Health Organization, WHO, there are currently over two billion people living with limited or no access to clean water.
This global challenge ...
Optical switching at record speeds opens door for ultrafast, light-based electronics and computers
2023-03-23
Imagine a home computer operating 1 million times faster than the most expensive hardware on the market. Now, imagine that level of computing power as the industry standard. University of Arizona researchers hope to pave the way for that reality using light-based optical computing, a marked improvement from the semiconductor-based transistors that currently run the world.
"Semiconductor-based transistors are in all of the electronics that we use today," said Mohammed Hassan, assistant professor of physics and optical sciences. "They're part of every industry – from kids' toys to ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
[Press-News.org] mNGS outperforms microbiological tests to diagnose bloodstream infections – BGI InsightNext-generation sequencing (mNGS) leverages genetic testing advantage to save more lives; twice as effective at identifying infection cases