(Press-News.org) Medical sleep treatment may reduce self-harm in young people with anxiety and depression, an observational study from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden suggests. The risk of self-harm increased in the months preceding melatonin prescription and decreased thereafter, especially in girls. The study is published in The Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry.
Melatonin is a hormone that controls the sleep-wake cycle and is the most commonly prescribed drug for sleep disturbances in children and adolescents in Sweden. Melatonin use has dramatically increased in recent years, and it is available over the counter in Sweden since 2020.
“Given the established link between sleep problems, depression, and self-harm, we wanted to explore whether medical sleep treatment is associated with a lower rate of intentional self-harm in young people,” says Dr Sarah Bergen, docent at the Department of Medical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Karolinska Institutet, who led the study.
Psychiatric disorders were common
The study identified over 25,500 children and teenagers between the ages of 6 and 18 who were prescribed melatonin in Sweden. Over 87 percent had at least one psychiatric disorder, mainly attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD), anxiety disorders, depression, or autism spectrum disorder. Self-harm was about five times more common in girls than in boys.
The researchers estimated the risks of self-harm in the same individual while on or off medication by comparing the risk in the last unmedicated month with the twelve months after melatonin treatment was initiated. By doing so, they were able to take into account background factors that may affect associations, such as genetics, sleep disorder severity, or psychiatric disorders.
The risk of self-harm increased shortly before melatonin was prescribed and decreased by about half in the months following the initiation of treatment. Risk reduction was particularly evident among adolescent girls with depression and/or anxiety disorders.
Youth mental health crisis
“There is currently a youth mental health crisis, and the risk of self-harm and suicide is high,” says Sarah Bergen. “Our findings support the hypothesis that sleep interventions may reduce self-harm in this population, especially in girls.”
As it was an observational study, it cannot establish a causal relationship between melatonin and reduced self-harm rates. To check whether the use of other medications might have affected the findings, analyses were also carried out which excluded antidepressant users. The results were similar.
“This suggests that melatonin might be responsible for the reduced self-harm rates, but we cannot rule out that the use of other psychiatric medications or psychotherapy may have influenced the findings,” says Dr Marica Leone, first author of the study and former PhD student in Sarah Bergen’s research group.
The research was mainly financed by the European Union’s Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme. Co-authors Marica Leone and Amy Leval are employees of Johnson & Johnson. Co-author Henrik Larsson has received grants from Shire Pharmaceuticals, personal and speaker fees from Medice, Shire/Takeda Pharmaceuticals and Evolan Pharma AB, and sponsorship for a conference on ADHD from Shire/Takeda Pharmaceuticals and Evolan Pharma AB, all outside the submitted work.
Publication: ”Melatonin use and the risk of self-harm and unintentional injuries in youths with and without psychiatric disorders”. Marica Leone, Ralf Kuja-Halkola, Tyra Lagerberg, Johan Bjureberg, Agnieszka Butwicka, Zheng Chang, Henrik Larsson, Brian M. D’Onofrio, Amy Leval, Sarah E. Bergen. The Journal of Child Psychology and Psychiatry, online 23 March 2023, doi: 10.1111/jcpp.13785.
END
Use of melatonin linked to decreased self-harm in young people
2023-03-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Pressure-based control enables tunable singlet fission materials for efficient photoconversion
2023-03-23
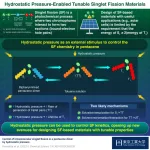
Applying hydrostatic pressure as an external stimulus, Tokyo Tech and Keio University researchers demonstrate a new way to regulate singlet fission (SF), a process in which two electrons are generated from a single photon, in chromophores, opening doors to the design of SF-based materials with enhanced (photo)energy conversion. Their method overrides the strict requirements that limit the molecular design of such materials by realizing an alternative control strategy.
Singlet fission (SF) is a process in which ...
New wood-based technology removes 80% of dye pollutants in wastewater
2023-03-23
Researchers at Chalmers University of Technology, Sweden, have developed a new method that can easily purify contaminated water using a cellulose-based material. This discovery could have implications for countries with poor water treatment technologies and combat the widespread problem of toxic dye discharge from the textile industry.
Clean water is a prerequisite for our health and living environment, but far from a given for everyone. According to the World Health Organization, WHO, there are currently over two billion people living with limited or no access to clean water.
This global challenge ...
Optical switching at record speeds opens door for ultrafast, light-based electronics and computers
2023-03-23
Imagine a home computer operating 1 million times faster than the most expensive hardware on the market. Now, imagine that level of computing power as the industry standard. University of Arizona researchers hope to pave the way for that reality using light-based optical computing, a marked improvement from the semiconductor-based transistors that currently run the world.
"Semiconductor-based transistors are in all of the electronics that we use today," said Mohammed Hassan, assistant professor of physics and optical sciences. "They're part of every industry – from kids' toys to ...
Depressed, and aging fast
2023-03-23
Older adults with depression are actually aging faster than their peers, UConn Center on Aging researchers report.
“These patients show evidence of accelerated biological aging, and poor physical and brain health,” which are the main drivers of this association, says Breno Diniz, a UConn School of Medicine geriatric psychiatrist and author of the study, which appears in Nature Mental Health on March 22.
Diniz and colleagues from several other institutions looked at 426 people with late-in-life ...
Study finds “considerable uncertainty” around effectiveness and safety of analgesics for low back pain
2023-03-23
Despite nearly 60 years of research, there is still a lack of high certainty evidence on the effectiveness and safety of commonly used painkillers (analgesics) for short bouts of low back pain, finds an analysis of the evidence published by The BMJ.
The researchers say that until higher quality trials comparing analgesics with each other are published, “clinicians and patients are advised to take a cautious approach to manage acute non-specific low back pain with analgesic medicines.”
Analgesics such as paracetamol, ibuprofen, and codeine ...
Ending GP performance pay in Scotland linked to decline in quality of some care
2023-03-23
Ending performance related payments for NHS GPs in Scotland was associated with a decline in the quality of some aspects of care compared with England where financial incentives have continued, finds a study published by The BMJ today.
The researchers say further research is needed to better understand the full impact of withdrawal and the accompanying refocusing of quality improvement resources.
The NHS Quality and Outcomes Framework (QOF) pay-for-performance scheme began in 2004. It was designed to remunerate general practices for providing good quality care across a range of key areas such as cancer, diabetes, heart disease, mental health, and obesity.
In 2016, Scotland abolished ...
CHOP researchers develop first-of-its-kind prediction model for newborn seizures
2023-03-23
Philadelphia, March 22, 2023 – Researchers from the Neuroscience Center at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have developed a prediction model that determines which newborn babies are likely to experience seizures in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU). This model could be incorporated into routine care to help the clinical team decide which babies will need electroencephalograms (EEGs) and which babies can be safely managed in the Neonatal Care Unit without monitoring through EEGs. This would allow families and providers to care for babies ...
A higher dose of magnesium each day keeps dementia at bay
2023-03-23
More magnesium in our daily diet leads to better brain health as we age, according to scientists from the Neuroimaging and Brain Lab at The Australian National University (ANU).
The researchers say increased intake of magnesium-rich foods such as spinach and nuts could also help reduce the risk of dementia, which is the second leading cause of death in Australia and the seventh biggest killer globally.
The study of more than 6,000 cognitively healthy participants in the United Kingdom aged 40 to 73 found ...
2022 heatwave struck off surgery in fifth of UK hospitals
2023-03-23
The 2022 summer heatwave resulted in a fifth of UK hospitals being forced to cancel operations during the three days when temperatures soared, a new study reveals.
Had the high temperatures continued, a further third of hospitals would have had to cancel surgery, as NHS buildings are not set up to withstand dangerously high temperatures.
The team surveyed surgeons, anaesthetists, and critical care doctors working during the heatwave of 16 – 19 July 2022.
They received 271 responses from 140 UK hospitals with one in five ...
British Ecological Society calls for greater funding for ecological research and sets out research agenda for next 25 years
2023-03-23
Two landmark reports published today (23 March) by the British Ecological Society reveal that ecological sciences are losing out on funding compared to other sciences. The reports also set out a research agenda for ecology over the next 25 years.
With the twin crises of climate change and biodiversity loss, an ecological understanding of the world has never been more pivotal to the future of humanity and all life on Earth.
To further this ecological understanding and highlight the importance of ecology to our future, the British ...