(Press-News.org) Older adults with depression are actually aging faster than their peers, UConn Center on Aging researchers report.
“These patients show evidence of accelerated biological aging, and poor physical and brain health,” which are the main drivers of this association, says Breno Diniz, a UConn School of Medicine geriatric psychiatrist and author of the study, which appears in Nature Mental Health on March 22.
Diniz and colleagues from several other institutions looked at 426 people with late-in-life depression. They measured the levels of proteins associated with aging in each person’s blood. When a cell gets old, it begins to function differently, less efficiently, than a “young” cell. It often produces proteins that promote inflammation or other unhealthy conditions, and those proteins can be measured in the blood. Diniz and the other researchers compared the levels of these proteins with measures of the participants’ physical health, medical problems, brain function, and the severity of their depression.
To their surprise, the severity of a person’s depression seemed unrelated to their level of accelerated aging. However, they did find that accelerated aging was associated with worse cardiovascular health overall. People with higher levels of aging-associated proteins were more likely to have high blood pressure, high cholesterol, and multiple medical problems. The accelerated aging was also associated with worse performance on tests of brain health such as working memory and other cognitive skills.
“Those two findings open up opportunities for preventive strategies to reduce the disability associated with major depression in older adults, and to prevent their acceleration of biological aging,” Diniz says.
The researchers are now looking at whether therapies to reduce the number of aged, “senescent” cells in a person’s body can improve late in life depression. They are also looking at specific sources and patterns of proteins associated with aging, to see if this might lead to personalized treatments in the future.
END
Depressed, and aging fast
Older adults with late-in-life-depression age biologically older than their chronological peers.
2023-03-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study finds “considerable uncertainty” around effectiveness and safety of analgesics for low back pain
2023-03-23
Despite nearly 60 years of research, there is still a lack of high certainty evidence on the effectiveness and safety of commonly used painkillers (analgesics) for short bouts of low back pain, finds an analysis of the evidence published by The BMJ.
The researchers say that until higher quality trials comparing analgesics with each other are published, “clinicians and patients are advised to take a cautious approach to manage acute non-specific low back pain with analgesic medicines.”
Analgesics such as paracetamol, ibuprofen, and codeine ...
Ending GP performance pay in Scotland linked to decline in quality of some care
2023-03-23
Ending performance related payments for NHS GPs in Scotland was associated with a decline in the quality of some aspects of care compared with England where financial incentives have continued, finds a study published by The BMJ today.
The researchers say further research is needed to better understand the full impact of withdrawal and the accompanying refocusing of quality improvement resources.
The NHS Quality and Outcomes Framework (QOF) pay-for-performance scheme began in 2004. It was designed to remunerate general practices for providing good quality care across a range of key areas such as cancer, diabetes, heart disease, mental health, and obesity.
In 2016, Scotland abolished ...
CHOP researchers develop first-of-its-kind prediction model for newborn seizures
2023-03-23
Philadelphia, March 22, 2023 – Researchers from the Neuroscience Center at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) have developed a prediction model that determines which newborn babies are likely to experience seizures in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU). This model could be incorporated into routine care to help the clinical team decide which babies will need electroencephalograms (EEGs) and which babies can be safely managed in the Neonatal Care Unit without monitoring through EEGs. This would allow families and providers to care for babies ...
A higher dose of magnesium each day keeps dementia at bay
2023-03-23
More magnesium in our daily diet leads to better brain health as we age, according to scientists from the Neuroimaging and Brain Lab at The Australian National University (ANU).
The researchers say increased intake of magnesium-rich foods such as spinach and nuts could also help reduce the risk of dementia, which is the second leading cause of death in Australia and the seventh biggest killer globally.
The study of more than 6,000 cognitively healthy participants in the United Kingdom aged 40 to 73 found ...
2022 heatwave struck off surgery in fifth of UK hospitals
2023-03-23
The 2022 summer heatwave resulted in a fifth of UK hospitals being forced to cancel operations during the three days when temperatures soared, a new study reveals.
Had the high temperatures continued, a further third of hospitals would have had to cancel surgery, as NHS buildings are not set up to withstand dangerously high temperatures.
The team surveyed surgeons, anaesthetists, and critical care doctors working during the heatwave of 16 – 19 July 2022.
They received 271 responses from 140 UK hospitals with one in five ...
British Ecological Society calls for greater funding for ecological research and sets out research agenda for next 25 years
2023-03-23
Two landmark reports published today (23 March) by the British Ecological Society reveal that ecological sciences are losing out on funding compared to other sciences. The reports also set out a research agenda for ecology over the next 25 years.
With the twin crises of climate change and biodiversity loss, an ecological understanding of the world has never been more pivotal to the future of humanity and all life on Earth.
To further this ecological understanding and highlight the importance of ecology to our future, the British ...
At least 80% of the world’s most important sites for biodiversity on land currently contain human developments, study finds
2023-03-23
PRESS RELEASE FROM THE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE
EMBARGOED UNTIL 00.05 LONDON TIME (GMT) ON 23 March 2023
Paper available at: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/18wVryz17-8PmtYDudp5NPXE75onO12FF?usp=sharing
At least 80% of the world’s most important sites for biodiversity on land currently contain human developments, study finds
At least 80% of sites identified as being internationally important for biodiversity on land currently contain infrastructure − of which more than 75% contain roads.
In the future, more sites that are important for biodiversity could contain powerplants, mines ...
Enzyme-regulating macrophages found in both humans and mice open the door to translating findings in mice into human therapies.
2023-03-23
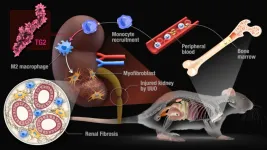
Researchers at Nagoya University in Japan have identified two enzymes that are involved in macrophage polarization, one of the key factors affecting fibrosis. The group’s findings, reported in Cell Death & Disease, suggest a potential treatment for human patients.
Kidney fibrosis is a dangerous inflammatory disease that causes the organs to stiffen and lose normal function. The disease is linked to a process called macrophage polarization. Polarization is the process by which macrophages, the white blood cells that help the body fight infection and repair tissue, are changed into two types as a response to changes in the microenvironment of the cell: the M1 type, which ...
Can artificial intelligence predict spatiotemporal distribution of dengue fever outbreaks with remote sensing data? New study finds answers
2023-03-23
Outbreaks of zoonotic diseases, which are those transmitted from animals to humans, are globally on the rise owing to climate change. In particular, the spread of diseases transmitted by mosquitoes is very sensitive to climate change, and Chinese Taiwan has seen a worrisome increase in the number of cases of dengue fever in recent years.
Like for most known diseases, the popular saying “an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure” also rings true for dengue fever. Since there is still no safe and effective vaccine for all on a global scale, dengue fever prevention efforts rely on limiting places where mosquitoes can lay their eggs and giving people an early warning when ...
New in-home AI tool monitors the health of elderly residents
2023-03-23
Engineers are harnessing artificial intelligence (AI) and wireless technology to unobtrusively monitor elderly people in their living spaces and provide early detection of emerging health problems.
The new system, built by researchers at the University of Waterloo, follows an individual’s activities accurately and continuously as it gathers vital information without the need for a wearable device and alerts medical experts to the need to step in and provide help.
“After more than five years of working on this technology, we’ve demonstrated that very low-power, millimetre-wave radio systems enabled by machine learning ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
[Press-News.org] Depressed, and aging fastOlder adults with late-in-life-depression age biologically older than their chronological peers.