(Press-News.org) PRESS RELEASE FROM THE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE
EMBARGOED UNTIL 00.05 LONDON TIME (GMT) ON 23 March 2023
Paper available at: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/18wVryz17-8PmtYDudp5NPXE75onO12FF?usp=sharing
At least 80% of the world’s most important sites for biodiversity on land currently contain human developments, study finds
At least 80% of sites identified as being internationally important for biodiversity on land currently contain infrastructure − of which more than 75% contain roads.
In the future, more sites that are important for biodiversity could contain powerplants, mines and oil and gas infrastructure
A study has found that infrastructure worldwide is widespread in sites that have been identified as internationally important for biodiversity, and its prevalence is likely to increase.
This is the first ever assessment of the presence of infrastructure in Key Biodiversity Areas (KBAs): a global network of thousands of sites recognised internationally as being the world’s most critical areas for wildlife.
Infrastructure is one of the greatest drivers of threats to biodiversity according to the International Union for Conservation of Nature. It can cause natural habitat destruction and fragmentation, pollution, increased disturbance or hunting by humans, the spread of invasive species, direct mortality, and can have wider impacts beyond the development site.
Now, researchers from BirdLife International, WWF and the RSPB, in association with the University of Cambridge, have conducted an assessment of infrastructure in KBAs, finding that it is widespread and likely to increase. The results are published today in Biological Conservation.
“It’s concerning that human developments exist in the vast majority of sites that have been identified as being critical for nature,” said Ash Simkins, a Zoology PhD student at the University of Cambridge who led the study.
KBAs are sites that contribute significantly to the global persistence of biodiversity. For example, they may contain species that are under a high risk of extinction or are home to species or ecosystems that are found in only a small area worldwide.
Researchers assessed 15,150 KBAs on land and found that 80% contained infrastructure. Multiple combinations of infrastructure types occurred in KBAs with the most common being roads (75%), power lines (37%) and urban areas (37%).
They found that potential future planned infrastructure developments could lead to an additional 2,201 KBAs containing mines (from 754 to 2,955; 292% increase), an additional 1,508 KBAs containing oil and gas infrastructure (from 2,081 to 3,589; 72% increase) and an additional 1,372 KBAs containing power plants (from 233 to 1,605; 589% increase).
Maps of KBAs were intersected with spatial datasets of different types of infrastructure that researchers categorised as transport, dams and reservoirs, extractives (relating to natural resources), energy (power lines and power plants) and urban areas.
Energy and extractives were the only categories for which some global data on potential future planned developments was available.
“We recognise that infrastructure is essential to human development but it’s about building smartly. This means ideally avoiding or otherwise minimising infrastructure in the most important locations for biodiversity. If the infrastructure must be there, then it should be designed to cause as little damage as possible, and the impacts more than compensated for elsewhere,” said Simkins.
Researchers found that countries in South America, (for example 82% of KBAs in Brazil), Sub-Saharan, Central and Southern Africa, and parts of South-east Asia are amongst the areas with the highest proportion of extractive claims, concessions or planned development in their KBA networks. All of the KBAs identified to date in Bangladesh, Kuwait, the Republic of the Congo and Serbia have potential extractive claims, concessions or planned development.
“It’s also concerning to see that in the future, extensive mining and oil and gas related infrastructure is planned to be built in many of the world’s most important sites for biodiversity,” said Simkins.
Some of the technology to tackle the climate crisis, like solar panels and wind turbines, is also dependent on mining for precious metals. “We need smart solutions to the climate crisis whilst avoiding or minimising negative impacts on biodiversity,” said Simkins.
“At the UN biodiversity COP15 meetings in Montreal last year, governments committed to halting human-induced extinctions,” said co-author Dr Stuart Butchart, Chief Scientist at BirdLife International and Honorary Research Fellow at Cambridge’s Department of Zoology. “Widespread destruction or degradation of the natural habitats within KBAs could lead to wholesale extinctions, so existing infrastructure in KBAs must be managed to minimise impacts, and further development in these sites has to be avoided as far as possible.”
“Infrastructure underpins our societies, delivering the water we drink, the roads we travel on, and the electricity that powers livelihoods,” said Wendy Elliott, Deputy Leader for Wildlife at WWF. “This study illustrates the crucial importance of ensuring smart infrastructure development that provides social and economic value for all, whilst ensuring positive outcomes for nature. Making this happen will be the challenge of our time, but with the right planning, design and commitment it is well within the realms of possibility.”
Researchers say that infrastructure within a KBA varies in the degree to which it may drive a loss of biodiversity. More research is required to find out the extent to which infrastructure in a particular KBA affects wildlife within the site and what measures are needed to mitigate this.
Reference:
A.T Simkins et al, A global assessment of the prevalence of current and potential future infrastructure in Key Biodiversity Areas, Biological Conservation, DOI: 10.1016/j.biocon.2023.109953
Contact details:
Charis Goodyear, Communications Coordinator, University of Cambridge Office of External Affairs and Communications Charis.Goodyear@admin.cam.ac.uk
Ash Simkins, University of Cambridge ats43@cam.ac.uk
About the University of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge is one of the world’s leading universities, with a rich history of radical thinking dating back to 1209. Its mission is to contribute to society through the pursuit of education, learning and research at the highest international levels of excellence.
Cambridge was second in the influential 2023 QS World University Rankings, the highest rated institution in the UK.
The University comprises 31 autonomous Colleges and over 100 departments, faculties and institutions. Its 20,000 students include around 9,000 international students from 147 countries. In 2022, 72.5% of its new undergraduate students were from state schools and more than 25% from economically disadvantaged backgrounds.
Cambridge research spans almost every discipline, from science, technology, engineering and medicine through to the arts, humanities and social sciences, with multi-disciplinary teams working to address major global challenges. In the Times Higher Education’s rankings based on the UK Research Excellence Framework, the University was rated as the highest scoring institution covering all the major disciplines.
The University sits at the heart of the ‘Cambridge cluster’, in which more than 5,200 knowledge-intensive firms employ more than 71,000 people and generate £19 billion in turnover. Cambridge has the highest number of patent applications per 100,000 residents in the UK.
www.cam.ac.uk
About BirdLife International
BirdLife International is the world’s largest nature conservation Partnership: a global family of over 115 national NGOs covering all continents, landscapes and seascapes. BirdLife is driven by its belief that local people, working for nature in their own places but connected nationally and internationally through the global Partnership, are the key to sustaining all life on this planet. This unique local-to-global approach delivers high impact and long-term conservation for the benefit of nature and people.
About WWF
WWF is an independent conservation organization active in nearly 100 countries, working to sustain the natural world for the benefit of people and wildlife.
WWF’s mission is to stop the degradation of the earth’s natural environment and to build a future in which humans live in harmony with nature by:
conserving the world’s biological diversity
ensuring that the use of renewable natural resources is sustainable
promoting the reduction of pollution and wasteful consumption.
www.panda.org
About RSPB
The RSPB is the UK’s largest nature conservation charity, protecting habitats, saving species, and helping to end the nature and climate emergency. For over a century we’ve acted for nature through practical conservation and powerful partnerships, campaigning and influence, and inspiring and empowering millions of people, including almost 1.2 million members. Our network of over 200 nature reserves sits at the heart of our world-leading science and conservation delivery.
Nature is in crisis, but together we can save it.
www.rspb.org.uk
END
At least 80% of the world’s most important sites for biodiversity on land currently contain human developments, study finds
A study has found that infrastructure worldwide is widespread in sites that have been identified as internationally important for biodiversity, and its prevalence is likely to increase
2023-03-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Enzyme-regulating macrophages found in both humans and mice open the door to translating findings in mice into human therapies.
2023-03-23
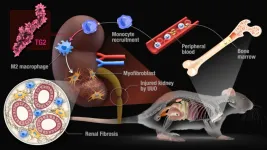
Researchers at Nagoya University in Japan have identified two enzymes that are involved in macrophage polarization, one of the key factors affecting fibrosis. The group’s findings, reported in Cell Death & Disease, suggest a potential treatment for human patients.
Kidney fibrosis is a dangerous inflammatory disease that causes the organs to stiffen and lose normal function. The disease is linked to a process called macrophage polarization. Polarization is the process by which macrophages, the white blood cells that help the body fight infection and repair tissue, are changed into two types as a response to changes in the microenvironment of the cell: the M1 type, which ...
Can artificial intelligence predict spatiotemporal distribution of dengue fever outbreaks with remote sensing data? New study finds answers
2023-03-23
Outbreaks of zoonotic diseases, which are those transmitted from animals to humans, are globally on the rise owing to climate change. In particular, the spread of diseases transmitted by mosquitoes is very sensitive to climate change, and Chinese Taiwan has seen a worrisome increase in the number of cases of dengue fever in recent years.
Like for most known diseases, the popular saying “an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure” also rings true for dengue fever. Since there is still no safe and effective vaccine for all on a global scale, dengue fever prevention efforts rely on limiting places where mosquitoes can lay their eggs and giving people an early warning when ...
New in-home AI tool monitors the health of elderly residents
2023-03-23
Engineers are harnessing artificial intelligence (AI) and wireless technology to unobtrusively monitor elderly people in their living spaces and provide early detection of emerging health problems.
The new system, built by researchers at the University of Waterloo, follows an individual’s activities accurately and continuously as it gathers vital information without the need for a wearable device and alerts medical experts to the need to step in and provide help.
“After more than five years of working on this technology, we’ve demonstrated that very low-power, millimetre-wave radio systems enabled by machine learning ...
New insights into the origins of spinal muscular atrophy
2023-03-22
NEW YORK, NY--Columbia researchers have discovered how a genetic defect leads to spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), a critical piece of information about the disease that neurologists have been seeking for decades.
The discovery suggests a new way to treat SMA—a devastating childhood motor neuron disease that affects 1 in 6,000 children. In the most severe cases, and when left untreated, children born with SMA die within the first two years of life.
The researchers also used their finding to develop an experimental therapy that improved survival in mice with severe SMA by ...
Oncotarget | Attenuation of cancer proliferation by suppression of glypican-1
2023-03-22
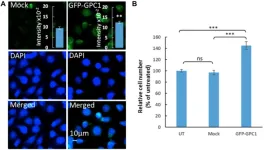
“This study was designed to increase the knowledge on the potential of GPCs and in particular GPC1 as a biomarker in cancer diagnosis and prognosis.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 22, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on March 21, 2023, entitled, “Attenuation of cancer proliferation by suppression of glypican-1 and its pleiotropic effects in neoplastic behavior.”
Glypicans (GPC1-6) are associated with tumorigenic processes and their involvement in neoplastic behavior has been ...
Geothermal energy has potential to be cost-competitive with other renewables and fossil fuels
2023-03-22
CAMBRIDGE, Mass.—Clean geothermal energy—the heat beneath our feet—has the potential to be cost competitive with other renewables and even fossil fuels if we can drill deep enough to access the mother lode of the resource. That’s according to one speaker at a geothermal conference last month held by the Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE). Other speakers addressed growing interest in the field by the oil and gas sector, key challenges it faces, and solutions to help solve those challenges.
Geothermal 2023: Realising the Ambition was organized by the Aberdeen, ...
Towards reducing biodiversity loss in fragmented habitats
2023-03-22
When natural habitats are cleared to make way for cities, roads and agriculture, this often leaves behind “islands” of fragmented habitat that can place species at risk of extinction. Species are at risk when they find it hard to move among habitat patches to find resources and reproduce.
By combining lab experiments and mathematical modelling, researchers at McGill University and the Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology have found a way to predict the movement of species that could guide conservation efforts to reconnect fragmented habitats.
The ...
How the brain's 'internal compass' works
2023-03-22
Scientists have gained new insights into the part of the brain that gives us a sense of direction, by tracking neural activity with the latest advances in brain imaging techniques. The findings shed light on how the brain orients itself in changing environments – and even the processes that can go wrong with degenerative diseases like dementia, that leave people feeling lost and confused.
“Neuroscience research has witnessed a technology revolution in the last decade allowing us to ...
Patricia M. LoRusso, DO, Ph.D. (hc), elected as American Association for Cancer Research President-Elect for 2023-2024
2023-03-22
PHILADELPHIA – The members of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) have elected Patricia M. LoRusso, DO, PhD (hc), as the AACR President-Elect for 2023-2024. LoRusso will become President-Elect on Monday, April 17, during the AACR’s Annual Business Meeting of Members at the AACR Annual Meeting 2023 in Orlando, Florida. She will assume the Presidency in April 2024 at the AACR Annual Meeting in San Diego, California.
LoRusso is a professor of medicine (medical oncology); chief of experimental therapeutics; associate cancer center director for experimental therapeutics; and leader of the Phase I disease aligned research ...
Is bone health linked to brain health?
2023-03-22
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, MARCH 22, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – People who have low bone density may have an increased risk of developing dementia compared to people who have higher bone density, according to a study published in the March 22, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study does not prove that low bone density causes dementia. It only shows an association.
“Low bone density and dementia are two conditions that commonly affect older people simultaneously, especially as bone loss often increases due to physical inactivity and poor ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
When safety starts with a text message
CSIC develops an antibody that protects immune system cells in vitro from a dangerous hospital-acquired bacterium
New study challenges assumptions behind Africa’s Green Revolution efforts and calls for farmer-centered development models
Immune cells link lactation to long-lasting health
Evolution: Ancient mosquitoes developed a taste for early hominins
Pickleball players’ reported use of protective eyewear
Changes in organ donation after circulatory death in the US
Fertility preservation in people with cancer
A universal 'instruction manual' helps immune cells protect our organs
Fifteen-year results from SWOG S0016 trial suggest follicular lymphoma is curable
The breasts of a breastfeeding mother may protect a newborn from the cold – researchers offer a new perspective on breast evolution
More organ donations now come from people who die after their heart stops beating
How stepping into nature affects the brain
Study: Cancer’s clues in the bloodstream reveal the role androgen receptor alterations play in metastatic prostate cancer
FAU Harbor Branch awarded $900,000 for Gulf of America sea-level research
Terminal ileum intubation and biopsy in routine colonoscopy practice
Researchers find important clue to healthy heartbeats
Characteristic genomic and clinicopathologic landscape of DNA polymerase epsilon mutant colorectal adenocarcinomas
Start school later, sleep longer, learn better
Many nations underestimate greenhouse emissions from wastewater systems, but the lapse is fixable
The Lancet: New weight loss pill leads to greater blood sugar control and weight loss for people with diabetes than current oral GLP-1, phase 3 trial finds
Pediatric investigation study highlights two-way association between teen fitness and confidence
Researchers develop cognitive tool kit enabling early Alzheimer's detection in Mandarin Chinese
New book captures hidden toll of immigration enforcement on families
New record: Laser cuts bone deeper than before
Heart attack deaths rose between 2011 and 2022 among adults younger than age 55
Will melting glaciers slow climate change? A prevailing theory is on shaky ground
New treatment may dramatically improve survival for those with deadly brain cancer
Here we grow: chondrocytes’ behavior reveals novel targets for bone growth disorders
Leaping puddles create new rules for water physics
[Press-News.org] At least 80% of the world’s most important sites for biodiversity on land currently contain human developments, study findsA study has found that infrastructure worldwide is widespread in sites that have been identified as internationally important for biodiversity, and its prevalence is likely to increase