(Press-News.org) NEW YORK, NY--Columbia researchers have discovered how a genetic defect leads to spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), a critical piece of information about the disease that neurologists have been seeking for decades.
The discovery suggests a new way to treat SMA—a devastating childhood motor neuron disease that affects 1 in 6,000 children. In the most severe cases, and when left untreated, children born with SMA die within the first two years of life.
The researchers also used their finding to develop an experimental therapy that improved survival in mice with severe SMA by 30-fold, one of the greatest increases seen with any treatment in mouse models of SMA.
Why the finding matters
Almost all cases of SMA are caused by a mutation in a single gene—SMN1 (survival motor neuron 1)—that reduces the amount of SMN protein inside motor neurons. SMN protein deficiency harms the neurons, and eventually the neurons can no longer control the body's muscles.
SMA has no cure but is commonly treated with therapies that increase SMN production, including a gene therapy that inserts a new SMN gene into the motor neurons.
“For many patients, the therapies are fairly effective if given early in the course of the disease,” says Umrao Monani, PhD, an SMA researcher at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons who led the research team.
“But the treatments don’t work for everyone, they can have significant side effects, and since these therapies are only a few years old, we don’t know how long they will last. There’s clearly a need for new approaches.”
What the study found
In the search for a different kind of treatment, Monani’s team looked at mice with SMA and tried to uncover how SMN deficiency harms neurons—something that’s remained hidden from investigators for decades—so they could find a way to prevent the harm.
The researchers found that SMN deficiency usually harms neurons by impairing a different protein, Hspa8, that helps assemble a critical communication link between motor neurons and muscle cells.
With Hspa8 out of action, the communication links are never built and messages cannot be sent from the neuron to the muscle. Muscles cannot contract without receiving these messages and they eventually waste away.
But some mice with SMA, the team noticed, were stronger and less affected by the disease. These mice, the researchers learned, harbored a specific variant of the Hspa8 gene that was not impaired by SMN deficiency.
A potential new treatment pathway for SMA?
A treatment that mimics the protective effect of the Hspa8 variant could have a potent effect in people, Monani says, if the researchers’ mouse experiments are any indication.
Using an approach that converted Hspa8 into its variant form, the researchers found significant recovery of neuromuscular function and survival in mice with severe SMA. The treated mice survived roughly 300 days, compared to just 10 days for untreated mice.
“We’ve never seen such a big increase in survival in these mice before, even when treated with nusinersen, a current SMA treatment,” Monani says.
Further study is needed to determine how best to translate the findings into a new SMA treatment. "The simplest way would be to encapsulate the HSPA8 variant in a virus and deliver the gene therapy to patients, as we did with the mice,” says Monani. “Another possibility is to use viruses or small molecules to convert normal Hspa8 into the variant.”
The researchers are currently working to develop therapies that are suitable for testing in patients.
More information
The study was published in Neuron on March 1 and is titled “A spinal muscular atrophy modifier implicates the SMN protein in SNARE complex assembly at neuromuscular synapses(link is external and opens in a new window).”
The other contributors (all from Columbia unless noted): Jeong-Ki Kim, Narendra N. Jha, Tomoyuki Awano, Charlotte Caine, Kishore Gollapalli, Emily Welby (Medical College of Wisconsin), Seung-Soo Kim, Andrea Fuentes-Moliz (University of Seville School of Medicine, Spain), Xueyong Wang (Wright State University), Zhihua Feng (University of Southern California), Fusako Sera, Taishi Takeda, Shunichi Homma, Chien-Ping Ko (University of Southern California), Lucia Tabares (University of Seville School of Medicine), Allison D. Ebert (Medical College of Wisconsin), and Mark M. Rich (Wright State University).
###
Columbia University Irving Medical Center (CUIMC) is a clinical, research, and educational campus located in New York City. Founded in 1928, CUIMC was one of the first academic medical centers established in the United States of America. CUIMC is home to four professional colleges and schools that provide global leadership in scientific research, health and medical education, and patient care including the Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons, the Mailman School of Public Health, the College of Dental Medicine, the School of Nursing. For more information, please visit cuimc.columbia.edu.
END
New insights into the origins of spinal muscular atrophy
2023-03-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Oncotarget | Attenuation of cancer proliferation by suppression of glypican-1
2023-03-22
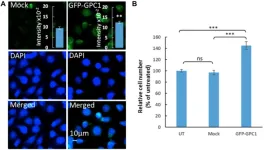
“This study was designed to increase the knowledge on the potential of GPCs and in particular GPC1 as a biomarker in cancer diagnosis and prognosis.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 22, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on March 21, 2023, entitled, “Attenuation of cancer proliferation by suppression of glypican-1 and its pleiotropic effects in neoplastic behavior.”
Glypicans (GPC1-6) are associated with tumorigenic processes and their involvement in neoplastic behavior has been ...
Geothermal energy has potential to be cost-competitive with other renewables and fossil fuels
2023-03-22
CAMBRIDGE, Mass.—Clean geothermal energy—the heat beneath our feet—has the potential to be cost competitive with other renewables and even fossil fuels if we can drill deep enough to access the mother lode of the resource. That’s according to one speaker at a geothermal conference last month held by the Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE). Other speakers addressed growing interest in the field by the oil and gas sector, key challenges it faces, and solutions to help solve those challenges.
Geothermal 2023: Realising the Ambition was organized by the Aberdeen, ...
Towards reducing biodiversity loss in fragmented habitats
2023-03-22
When natural habitats are cleared to make way for cities, roads and agriculture, this often leaves behind “islands” of fragmented habitat that can place species at risk of extinction. Species are at risk when they find it hard to move among habitat patches to find resources and reproduce.
By combining lab experiments and mathematical modelling, researchers at McGill University and the Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology have found a way to predict the movement of species that could guide conservation efforts to reconnect fragmented habitats.
The ...
How the brain's 'internal compass' works
2023-03-22
Scientists have gained new insights into the part of the brain that gives us a sense of direction, by tracking neural activity with the latest advances in brain imaging techniques. The findings shed light on how the brain orients itself in changing environments – and even the processes that can go wrong with degenerative diseases like dementia, that leave people feeling lost and confused.
“Neuroscience research has witnessed a technology revolution in the last decade allowing us to ...
Patricia M. LoRusso, DO, Ph.D. (hc), elected as American Association for Cancer Research President-Elect for 2023-2024
2023-03-22
PHILADELPHIA – The members of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) have elected Patricia M. LoRusso, DO, PhD (hc), as the AACR President-Elect for 2023-2024. LoRusso will become President-Elect on Monday, April 17, during the AACR’s Annual Business Meeting of Members at the AACR Annual Meeting 2023 in Orlando, Florida. She will assume the Presidency in April 2024 at the AACR Annual Meeting in San Diego, California.
LoRusso is a professor of medicine (medical oncology); chief of experimental therapeutics; associate cancer center director for experimental therapeutics; and leader of the Phase I disease aligned research ...
Is bone health linked to brain health?
2023-03-22
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, MARCH 22, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – People who have low bone density may have an increased risk of developing dementia compared to people who have higher bone density, according to a study published in the March 22, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study does not prove that low bone density causes dementia. It only shows an association.
“Low bone density and dementia are two conditions that commonly affect older people simultaneously, especially as bone loss often increases due to physical inactivity and poor ...
In epilepsy, higher risk of early death varies based on severity, other factors
2023-03-22
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, MARCH 22, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – A new study has found that people with epilepsy have an increased risk of early death and the increased risk varies depending on where they live, the number of medications they take and what other diseases they may have. The study is published in the March 22, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
“Our research found an increased risk even among those who do not have ...
Air flow research could reduce disease, contamination spread
2023-03-22
Air flow in a room can impact the transmission of viruses like COVID-19.
A Texas A&M AgriLife Research scientist is studying how heating, ventilation and air conditioning, HVAC, system configurations and building designs could mitigate the spread of microorganisms, including viruses, that are detrimental to human health.
Maria King, Ph.D., director of the Center for Agricultural Air Quality Engineering and Science in the Department of Biological and Agricultural Engineering, recently received a $400,000, two-year National ...
Memory B cell marker predicts long-lived antibody response to flu vaccine
2023-03-22
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – Memory B cells play a critical role to provide long-term immunity after a vaccination or infection. In a study published in the journal Immunity, researchers describe a distinct and novel subset of memory B cells that predict long-lived antibody responses to influenza vaccination in humans.
These effector memory B cells appear to be poised for a rapid serum antibody response upon secondary challenge one year later, Anoma Nellore, M.D., Fran Lund, Ph.D., and colleagues at the University of Alabama at Birmingham and Emory University report. Evidence from transcriptional and epigenetic profiling shows that the cells in this subset differ from ...
Copper artifacts unearth new cultural connections in southern Africa
2023-03-22
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Chemical and isotopic analysis of copper artifacts from southern Africa reveals new cultural connections among people living in the region between the 5th and 20th centuries according to a University of Missouri researcher and colleagues.
People in the area between northern South Africa and the Copperbelt region in central Africa were more connected to one another than scholars previously thought, said Jay Stephens, a post-doctoral fellow in the MU Research Reactor (MURR) Archaeometry Lab.
“Over the past 20 to 30 years, most archaeologists ...