Oncotarget | Attenuation of cancer proliferation by suppression of glypican-1
2023-03-22
(Press-News.org)
“This study was designed to increase the knowledge on the potential of GPCs and in particular GPC1 as a biomarker in cancer diagnosis and prognosis.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 22, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on March 21, 2023, entitled, “Attenuation of cancer proliferation by suppression of glypican-1 and its pleiotropic effects in neoplastic behavior.”
Glypicans (GPC1-6) are associated with tumorigenic processes and their involvement in neoplastic behavior has been discussed in different cancer types. In this recent cancer-wide GPC expression study, researchers Fang Cheng, Victor Chérouvrier Hansson, Grigorios Georgolopoulos, and Katrin Mani from Lund University and Genevia Technologies used clinical cancer patient data in The Cancer Genome Atlas to reveal net upregulation of GPC1 and GPC2 in primary solid tumors. On the other hand, GPC3, GPC5 and GPC6 displayed lowered expression patterns compared to normal tissues.
“[...] we identify and propose a mechanism where GPC1 interacts with extracellular matrix mediating signal transduction by mitogenic molecules involving TGF-β and p38 MAPK.”
Focusing on GPC1, the researchers conducted survival analyses of the clinical cancer patient data that revealed a statistically significant correlation between high expression of GPC1 and poor prognosis in 10 particular cancer types: bladder urothelial carcinoma, brain lower grade glioma, liver hepatocellular carcinoma, colon adenocarcinoma, kidney renal clear cell carcinoma, lung adenocarcinoma, mesothelioma, ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma, uterine corpus endometrial carcinoma, and uveal melanoma.
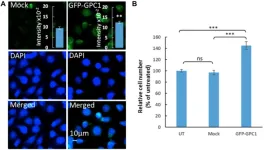
In vitro studies targeting GPC1 expression by CRISPR/Cas9 or siRNA or treatment with an anti-GPC1 antibody resulted in attenuation of proliferation of cancer cells from bladder carcinoma, glioma and hepatocellular carcinoma patients (T24, U87 and HepG2 cells). Further, GPC1 overexpression exhibited a significant and negative correlation between GPC1 expression and proliferation of T24 cells. Their attempt to reveal the mechanism through which downregulation of GPC1 leads to attenuation of tumor growth using systematic Ingenuity Pathway Analysis indicated that suppression of GPC1 results in ECM-mediated inhibition of specific pro-cancer signaling pathways involving TGF-β and p38 MAPK. The team also identified differential expression and pleiotropic effects of GPCs in specific cancer types. This emphasizes their potential as novel diagnostic tools and prognostic factors, and open doors for future GPC targeted therapy.
“It is plausible to measure circulating GPCs in serum, plasma or urine using a variety of methods including ELISA, urine cell sediments or exosome isolation [13, 24]. Further, detection and quantification of GPC1 by histopathological and immunohistochemical methods in tumor biopsies could be a new way to predict the biological outcome. The results of this investigation would also emphasize the potential of GPCs as novel tumor antigens, and open for GPC targeted immunotherapy. GPC targeted immunotherapy would be of high value, especially as we move into an era of precision and personalized cancer therapy.”
Read the full research paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28388
Correspondence to: Katrin Mani
Email: katrin.mani@med.lu.se
Keywords: Glypican-1, TCGA, bladder carcinoma, hepatocellular carcinoma, glioma
About Oncotarget: Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
Twitter
Facebook
YouTube
Instagram
LinkedIn
Pinterest
LabTube
Soundcloud
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact: media@impactjournals.com.
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Str., Suite 1A
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957 (option 2)
###
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-03-22
CAMBRIDGE, Mass.—Clean geothermal energy—the heat beneath our feet—has the potential to be cost competitive with other renewables and even fossil fuels if we can drill deep enough to access the mother lode of the resource. That’s according to one speaker at a geothermal conference last month held by the Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE). Other speakers addressed growing interest in the field by the oil and gas sector, key challenges it faces, and solutions to help solve those challenges.
Geothermal 2023: Realising the Ambition was organized by the Aberdeen, ...
2023-03-22
When natural habitats are cleared to make way for cities, roads and agriculture, this often leaves behind “islands” of fragmented habitat that can place species at risk of extinction. Species are at risk when they find it hard to move among habitat patches to find resources and reproduce.
By combining lab experiments and mathematical modelling, researchers at McGill University and the Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology have found a way to predict the movement of species that could guide conservation efforts to reconnect fragmented habitats.
The ...
2023-03-22
Scientists have gained new insights into the part of the brain that gives us a sense of direction, by tracking neural activity with the latest advances in brain imaging techniques. The findings shed light on how the brain orients itself in changing environments – and even the processes that can go wrong with degenerative diseases like dementia, that leave people feeling lost and confused.
“Neuroscience research has witnessed a technology revolution in the last decade allowing us to ...
2023-03-22
PHILADELPHIA – The members of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) have elected Patricia M. LoRusso, DO, PhD (hc), as the AACR President-Elect for 2023-2024. LoRusso will become President-Elect on Monday, April 17, during the AACR’s Annual Business Meeting of Members at the AACR Annual Meeting 2023 in Orlando, Florida. She will assume the Presidency in April 2024 at the AACR Annual Meeting in San Diego, California.
LoRusso is a professor of medicine (medical oncology); chief of experimental therapeutics; associate cancer center director for experimental therapeutics; and leader of the Phase I disease aligned research ...
2023-03-22
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, MARCH 22, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – People who have low bone density may have an increased risk of developing dementia compared to people who have higher bone density, according to a study published in the March 22, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology. The study does not prove that low bone density causes dementia. It only shows an association.
“Low bone density and dementia are two conditions that commonly affect older people simultaneously, especially as bone loss often increases due to physical inactivity and poor ...
2023-03-22
EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL 4 P.M. ET, WEDNESDAY, MARCH 22, 2023
MINNEAPOLIS – A new study has found that people with epilepsy have an increased risk of early death and the increased risk varies depending on where they live, the number of medications they take and what other diseases they may have. The study is published in the March 22, 2023, online issue of Neurology®, the medical journal of the American Academy of Neurology.
“Our research found an increased risk even among those who do not have ...
2023-03-22
Air flow in a room can impact the transmission of viruses like COVID-19.
A Texas A&M AgriLife Research scientist is studying how heating, ventilation and air conditioning, HVAC, system configurations and building designs could mitigate the spread of microorganisms, including viruses, that are detrimental to human health.
Maria King, Ph.D., director of the Center for Agricultural Air Quality Engineering and Science in the Department of Biological and Agricultural Engineering, recently received a $400,000, two-year National ...
2023-03-22
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – Memory B cells play a critical role to provide long-term immunity after a vaccination or infection. In a study published in the journal Immunity, researchers describe a distinct and novel subset of memory B cells that predict long-lived antibody responses to influenza vaccination in humans.
These effector memory B cells appear to be poised for a rapid serum antibody response upon secondary challenge one year later, Anoma Nellore, M.D., Fran Lund, Ph.D., and colleagues at the University of Alabama at Birmingham and Emory University report. Evidence from transcriptional and epigenetic profiling shows that the cells in this subset differ from ...
2023-03-22
COLUMBIA, Mo. – Chemical and isotopic analysis of copper artifacts from southern Africa reveals new cultural connections among people living in the region between the 5th and 20th centuries according to a University of Missouri researcher and colleagues.
People in the area between northern South Africa and the Copperbelt region in central Africa were more connected to one another than scholars previously thought, said Jay Stephens, a post-doctoral fellow in the MU Research Reactor (MURR) Archaeometry Lab.
“Over the past 20 to 30 years, most archaeologists ...
2023-03-22
Have you ever marveled at the vast diversity of life on our planet, from tiny creatures living only a few hours to majestic beings that can survive for centuries? These differences in lifespan, size, and reproductive age are known as life-history strategies, and they have evolved over time as organisms adapt to their environments.
Evolutionary biologists have long been interested in understanding the factors that contribute to the evolution and maintenance of multiple alternative life-history strategies (ALHS) within species that lead to adaptation and novel traits. A new study published in Science Advances has not only revealed that an ALHS in Colias ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Oncotarget | Attenuation of cancer proliferation by suppression of glypican-1






