(Press-News.org)
Have you ever marveled at the vast diversity of life on our planet, from tiny creatures living only a few hours to majestic beings that can survive for centuries? These differences in lifespan, size, and reproductive age are known as life-history strategies, and they have evolved over time as organisms adapt to their environments.
Evolutionary biologists have long been interested in understanding the factors that contribute to the evolution and maintenance of multiple alternative life-history strategies (ALHS) within species that lead to adaptation and novel traits. A new study published in Science Advances has not only revealed that an ALHS in Colias butterflies has an ancient origin, but also determined the mechanisms contributing to its persistence over millions of generations.
Colias butterflies are a charismatic group of butterflies, found on almost all continents and are characterized by their brightly colored orange or yellow wings in both males and females. However, in about one third of the 90 Colias species, a portion of females instead have white colored wings, called an Alba morph. This change in color appears to be a tradeoff in how females invest energy reserves gathered when in the caterpillar stage.
During the transition into a butterfly, females either spend these reserves to make orange wings and become very attractive to males, or they make no color (Alba) and use these resources to have more offspring. Thus, Alba is not just a simple color variant, but a visual representation of an ALHS unique to female Colias butterflies.
Led by researchers from Stockholm University, the international team used diverse genomic analyses to identify the genetic basis of the female-limited Alba ALHS, and then to place this discovery within an evolutionary framework. They found that Alba evolved once near the last common ancestor in the genus, more than 1.2 million generations ago.
Their results further suggest that the Alba and orange alleles has been maintained among species within the genus via gene flow among hybridizing species (introgression) and by balancing selection within species. The genetic basis of Alba appeared to be a regulatory region in the DNA, a hypothesis the researchers tested using CRISPR/Cas9 mutagenesis, which confirmed the Alba allele as a modular enhancer for the induction of the Alba ALHS.
These findings are significant, as they provide a better understanding of how life-history traits evolve, suggesting that some strategies used by different species might in fact have a shared genetic basis.
“By investigating the origins and evolutionary dynamics acting upon an ALHS, we hope to advance the understanding of how novel traits and life histories evolve, eventually helping us understand the conditions that have generated the diversity in life-history variation we observe today”, said Kalle Tunström, PhD student at the Department of Zoology, Stockholm University, and lead author of the study.
More information
The article “Evidence for a single, ancient origin of a genus-wide alternative life history strategy” is published in the scientific journal Science Advances.
https://www.science.org/doi/10.1126/sciadv.abq3713
DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abq3713
Contact
Kalle Tunström, PhD student at the Department of Zoology, Stockholm University
E-post: kalle.tunstrom@zoologi.su.se
Research funding
The Swedish Research Council, Academy of Finland, The U.S. National Science Foundation
END
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
March 22, 2023
THE PROTEIN SOCIETY ANNOUNCES ITS 2023 AWARD RECIPIENTS
LOS ANGELES, CA – The Protein Society, the premier international society dedicated to supporting protein research, announces the winners of the 2023 Protein Society Awards, which will be conferred at the 37th Anniversary Symposium, July 13 – 16, 2023, in Boston, Massachusetts. Plenary talks from select award recipients will take place throughout the 3.5-day event. The scientific accomplishments of the awardees, highlighted here as described by their nominators, demonstrate their lasting impact on protein science.
The Carl Brändén Award, sponsored by Rigaku ...
If you live near a busy road you might feel like the constant sound of roaring engines, honking horns and wailing sirens makes your blood pressure rise. Now a new study published today in JACC: Advances confirms it can do exactly that.
Previous studies have shown a connection between noisy road traffic and increased risk of hypertension. However, strong evidence was lacking, and it was unclear whether noise or air pollution played a bigger role. The new research shows that it is exposure to road traffic noise itself that can elevate hypertension risk.
“We were a ...
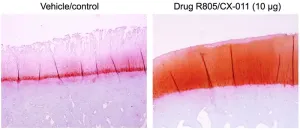
A team of researchers at the Keck School of Medicine of USC have found a drug with the potential for curbing painful hyperinflammation from osteoarthritis, according to results of an animal study.
The findings, published March 22nd in Science Translational Medicine, indicate that a drug compound, R805/CX-011, may modulate an important cell receptor in the body’s immune system, GP130, that signals when antibodies should attack a virus or infection. The animal model studies showed that the drug compound can disrupt the receptor’s over-activation of inflammation, and still manage pain ...
The first year of the COVID pandemic saw significant increases in drug overdose deaths across the USA, with rates higher than recent trends could have predicted. Research published in the open access journal PLOS Global Public Health, reports trends in drug overdose deaths between 2013-20 across four major drug categories by gender, race and geography. It finds high levels of heterogeneity in overdose patterns across different demographic groups and that the gap in overdose fatalities between black and white individuals continues to widen. Drug prevention and mitigation campaigns should therefore be tailored to specific at-risk groups.
Drug overdose deaths have been ...
Mutations in genes that form the desmosome are the most common cause of the cardiac disease arrhythmogenic cardiomyopathy (ACM), which affects one in 2000 to 5000 people worldwide. Researchers from the group of Eva van Rooij now discovered how a mutation in the desmosomal gene plakophilin-2 leads to ACM. They found that the structural and functional changes in ACM hearts caused by a plakophilin-2 mutation are the result of increased desmosomal protein degradation. The results of this study, published in Science Translational Medicine ...
Average crop yields in Africa are consistently far below expected, and one significant reason is the prevalence of counterfeit seeds whose germination rates are far lower than those of the genuine ones. The World Bank estimates that as much as half of all seeds sold in some African countries are fake, which could help to account for crop production that is far below potential.
There have been many attempts to prevent this counterfeiting through tracking labels, but none have proved effective; among other issues, such labels have been vulnerable to hacking because of the deterministic ...
Clearing a path for non-invasive muscle therapy for the elderly
Controlling inflammation enables injured aged muscle recovery via non-invasive mechanical loading, offering promise for the future of mechanotherapies for elderly patients.
By Benjamin Boettner
(BOSTON) — Mechanotherapy, the concept of using mechanical forces to stimulate tissue healing, has been used for decades as a form of physical therapy to help heal injured muscles. However, the biological basis and optimal settings for mechanotherapies are still poorly understood, ...
Stuttgart, Linz, Boulder – Artificial muscles are a progressing technology that could one day enable robots to function like living organisms. Such muscles open up new possibilities for how robots can shape the world around us; from assistive wearable devices that can redefine our physical abilities at old age, to rescue robots that can navigate rubble in search of the missing. But just because artificial muscles can have a strong societal impact during use, doesn’t mean they have to leave a strong ...
Below is a brief roundup of news and story ideas from the experts at UCLA Health. For more information on these stories or for help on other stories, please contact us at uclahealthnews@mednet.ucla.edu.
Journal scan
Mixed ancestry study provides clues to genetic traits A new multi-institutional study led by scientists at the Bioinformatics Interdepartmental Program at UCLA has found that individuals of mixed ancestry, such as African Americans, inherit a mosaic of ancestry segments from ...
Nitroxoline is the name of the new drug candidate that could potentially be used to treat mpox. It was identified by scientists at Goethe University and the University of Kent as part of a multi-site study. The results of their research will now allow clinical trials to begin soon.
The current mpox outbreak is the first of this size to occur outside of Africa and also the first mpox outbreak caused by human-to-human transmission. People with immunodeficiencies are particularly at risk from the disease. Although antiviral agents have already been shown to inhibit the replication ...