(Press-News.org) Nitroxoline is the name of the new drug candidate that could potentially be used to treat mpox. It was identified by scientists at Goethe University and the University of Kent as part of a multi-site study. The results of their research will now allow clinical trials to begin soon.
The current mpox outbreak is the first of this size to occur outside of Africa and also the first mpox outbreak caused by human-to-human transmission. People with immunodeficiencies are particularly at risk from the disease. Although antiviral agents have already been shown to inhibit the replication of the mpox virus in experimental models, the efficacy of these substances has not yet been confirmed in humans and some may have significant side effects. In addition, there are insufficient stocks to treat all mpox patients. Moreover, resistance formation against tecovirimat, the most promising mpox drug candidate to date, has already been reported.
In the present study, the international team led by Professor Jindrich Cinatl (of Goethe University Frankfurt and the Dr. Petra Joh-Research Institute) and Professor Martin Michaelis (School of Biosciences, University of Kent) has identified nitroxoline, a well-tolerated antibiotic, as a potential treatment alternative for the mpox virus based on experiments using cell culture and skin explant models.
Nitroxoline is also effective against a tecovirimat-resistant strain of the mpox virus, as well as other bacterial and viral pathogens that are frequently co-transmitted with mpox viruses, meaning it simultaneously suppresses multiple pathogens that are often involved in severe courses of mpox. Since nitroxoline is a well-tolerated antibiotic that has long been used to treat humans, it can be tested directly against mpox in clinical trials.
"The emergence of resistant virus strains is a cause of great concern,” says Professor Jindrich Cinatl of Goethe University and the Dr. Petra Joh-Research Institute. "It is very reassuring that nitroxoline is effective against a tecovirimat-resistant virus."
Professor Martin Michaelis of the University of Kent adds: "The more different drugs become available to treat viral diseases, the better. We hope that nitroxoline will turn out to be an effective treatment for mpox patients."
Further information
Prof. Jindrich Cinatl
Working Group Head
Institute for Medical Virology
Goethe University
Tel.: +49 (0)69 6301-6409
E-Mail Cinatl@em.uni-frankfurt.de
https://www.kgu.de/einrichtungen/institute/zentrum-der-hygiene/medizinische-virologie/forschung/research-group-cinatl/
END
Known active ingredient as new drug candidate against “monkeypox”
2023-03-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Why subvariants of the SARS-CoV-2 virus accelerated the pandemic
2023-03-22
The COVID-19 pandemic has killed nearly 7 million people worldwide (1.1 million in the United States) and severely harmed many millions more, though vaccines and antiviral treatments measurably reduced the potential loss of life and health.
A Commonwealth Fund report, for example, estimated COVID-19 vaccines alone prevented more than 18 million additional hospitalizations and 3.2 million additional deaths in the U.S.
The pandemic has never been simple or easy. For example, the emergence of viral variants, in particular recent versions of the Omicron, fueled new surges of infection and disease throughout 2022 and into 2023.
“There were real concerns ...
Semiconductor lattice marries electrons and magnetic moments
2023-03-22
ITHACA, N.Y. -- A model system created by stacking a pair of monolayer semiconductors is giving physicists a simpler way to study confounding quantum behavior, from heavy fermions to exotic quantum phase transitions.
The group’s paper, “Gate-Tunable Heavy Fermions in a Moiré Kondo Lattice,” published March 15 in Nature. The lead author is postdoctoral fellow Wenjin Zhao in the Kavli Institute at Cornell.
The project was led by Kin Fai Mak, professor of physics in the College of Arts and Sciences, and Jie Shan, professor of applied and engineering physics in Cornell Engineering ...
Nominations sought for 2024 Watanabe Prize in Translational Research
2023-03-22
Indiana University School of Medicine is accepting nominations until May 1 for the 2024 August M. Watanabe Prize in Translational Research.
The Watanabe Prize is one of the nation’s largest and most prestigious research awards recognizing senior investigators focused on shepherding scientific discoveries into new therapies for patients. Nominees should be members of the scientific or medical communities who have demonstrated outstanding accomplishments in translational research.
The winner will receive $100,000 and will spend Sept. 18-20, 2024, in Indianapolis as a vising dignitary, sharing insights and knowledge with audiences at IU School of Medicine and its partner institutions. ...
Dr. Ekta Khurana receives grant to study prostate cancer evolution
2023-03-22
Dr. Ekta Khurana, an associate professor of physiology and biophysics at Weill Cornell Medicine, has received a 3-year, $1.2 million grant from the United States Department of Defense to investigate how prostate cancer cells evolve to become resistant to hormone-blocking therapy. This work will contribute to further understanding prostate cancer and the development of effective targeted therapies for the disease.
Prostate cancer growth is dependent on androgens – male hormones such as testosterone – binding ...
New UBC water treatment zaps ‘forever chemicals’ for good
2023-03-22
Engineers at the University of British Columbia have developed a new water treatment that removes “forever chemicals” from drinking water safely, efficiently – and for good.
“Think Brita filter, but a thousand times better,” says UBC chemical and biological engineering professor Dr. Madjid Mohseni, who developed the technology.
Forever chemicals, formally known as PFAS (per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances) are a large group of substances that make certain products non-stick or stain-resistant. There are more than ...
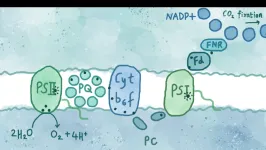
Photosynthesis ‘hack’ could lead to new ways of generating renewable energy
2023-03-22
Researchers have ‘hacked’ the earliest stages of photosynthesis, the natural machine that powers the vast majority of life on Earth, and discovered new ways to extract energy from the process, a finding that could lead to new ways of generating clean fuel and renewable energy.
An international team of physicists, chemists and biologists, led by the University of Cambridge, was able to study photosynthesis – the process by which plants, algae and some bacteria convert sunlight into energy – ...
Simulated terrible drivers cut the time and cost of AV testing by a factor of one thousand
2023-03-22
Photos // Video
The push toward truly autonomous vehicles has been hindered by the cost and time associated with safety testing, but a new system developed at the University of Michigan shows that artificial intelligence can reduce the testing miles required by 99.99%.
It could kick off a paradigm shift that enables manufacturers to more quickly verify whether their autonomous vehicle technology can save lives and reduce crashes. In a simulated environment, vehicles trained by artificial intelligence perform perilous maneuvers, forcing the AV to make decisions that confront drivers only rarely on ...
Multiple substance use disorders may share inherited genetic signature
2023-03-22
A new study suggests that a common genetic signature may increase a person’s risk of developing substance use disorders, regardless of whether the addiction is to alcohol, tobacco, cannabis or opioids. The research, led by Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis, eventually could lead to universal therapies to treat multiple substance use disorders and potentially help people diagnosed with more than one.
Published March 22 in the journal Nature Mental Health, the study’s findings are drawn from an analysis of genomic data from more than 1.1 million people of mostly European ancestry and a smaller ...
How vision begins
2023-03-22
Researchers at the Paul Scherrer Institute PSI have deciphered the molecular processes that first occur in the eye when light hits the retina. The processes – which take only a fraction of a trillionth of a second – are essential for human sight. The study has now been published in the scientific journal Nature.
It only involves a microscopic change of a protein in our retina, and this change occurs within an incredibly small time frame: it is the very first step in our light perception and ability to see. It is also the ...
New NIH study reveals shared genetic markers underlying substance use disorders
2023-03-22
By combing through genomic data of over 1 million people, scientists have identified genes commonly inherited across addiction disorders, regardless of the substance being used. This dataset – one of the largest of its kind – may help reveal new treatment targets across multiple substance use disorders, including for people diagnosed with more than one. The findings also reinforce the role of the dopamine system in addiction, by showing that the combination of genes underlying addiction disorders was also associated with regulation of dopamine signaling.
Published ...