(Press-News.org) The 2022 summer heatwave resulted in a fifth of UK hospitals being forced to cancel operations during the three days when temperatures soared, a new study reveals.
Had the high temperatures continued, a further third of hospitals would have had to cancel surgery, as NHS buildings are not set up to withstand dangerously high temperatures.
The team surveyed surgeons, anaesthetists, and critical care doctors working during the heatwave of 16 – 19 July 2022.
They received 271 responses from 140 UK hospitals with one in five respondents (18.5%) reporting the heatwave resulted in elective surgery being cancelled. A further third (35.1%) anticipated that cancellations would have been likely had the heatwave continued.
Factors contributing to heatwave-related cancellations included staff shortages (35.8% of respondents), unsafe theatre environments (30.3%), and bed shortages (22.1%).
Surgical services were poorly prepared for heatwaves with ambient temperature uncontrollable in 41.0% of operating theatres. Most hospitals which responded (85%) lacked ‘summer pressure’ plans to maintain elective surgical safety and capacity. Over a third of respondents (35.4%) reported making adaptations to maintain the routine surgical activity during the heatwave.
Co-author Mr James Glasbey, NIHR Doctoral Research Fellow in Global Surgery at the University of Birmingham, commented: “Even short heatwaves may result in widespread disruption to surgical services in the UK. The likelihood of extreme weather events is growing - we could find ourselves in both a 'winter' and 'summer' stress situation within the next few years.
“As hospitals tackle post-COVID surgery backlogs, they must consider how to safeguard against further climate change-related disruption to the delivery of surgical services. This should be included in the preparation of ‘summer pressure’ plans to improve the resilience of elective surgery services.”
Supported by a National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Global Health Research Unit Grant, the GreenSurg Collaborative, led by researchers at the University of Birmingham, published their findings in a letter to British Journal of Surgery.
The researchers discovered that hospitals adopted several strategies during the heatwave to cushion the impact of rising temperatures on surgical patients. These included delayed discharge of high-risk patients, changes to surgical teams, selecting lower risk patients to have surgery, and restricting surgical activity to day-cases.
Some hospitals also introduced longer staff breaks, gave extra fluids to patients admitted, and started surgeries earlier in the morning when temperatures were lower.
ENDS
For more information, please contact Tony Moran, University of Birmingham on +44 (0)782 783 2312 or t.moran@bham.ac.uk Out-of-hours please call +44 (0) 121 414 2772.
Note for Editors
The University of Birmingham is ranked amongst the world’s top 100 institutions, its work brings people from across the world to Birmingham, including researchers and teachers and more than 8,000 international students from over 150 countries.
The letter was written by Maria Picciochi, James C Glasbey, Elizabeth Li, Sivesh K Kamarajah, Dmitri Nepogodiev, Joana FF Simoes, and Aneel Bhangu as part of the GreenSurg Collaborative and published in British Journal of Surgery.
About The National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR)
The mission of the National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) is to
improve the health and wealth of the nation through research. It d this by:
Funding high quality, timely research that benefits the NHS, public
health and social care;
Investing in world-class expertise, facilities and a skilled delivery workforce to translate discoveries into improved treatments and services;
Partnering with patients, service users, carers and communities, improving the relevance, quality and impact of our research;
Attracting, training and supporting the best researchers to tackle complex health and social care challenges;
Collaborating with other public funders, charities and industry to help shape a cohesive and globally competitive research system;
Funding applied global health research and training to meet the needs of the poorest people in low- and middle-income countries.
NIHR is funded by the Department of Health and Social Care. Its work in low- and middle-income countries (LMICs) is principally funded through UK Aid from the UK government. END
2022 heatwave struck off surgery in fifth of UK hospitals
2023-03-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
British Ecological Society calls for greater funding for ecological research and sets out research agenda for next 25 years
2023-03-23
Two landmark reports published today (23 March) by the British Ecological Society reveal that ecological sciences are losing out on funding compared to other sciences. The reports also set out a research agenda for ecology over the next 25 years.
With the twin crises of climate change and biodiversity loss, an ecological understanding of the world has never been more pivotal to the future of humanity and all life on Earth.
To further this ecological understanding and highlight the importance of ecology to our future, the British ...
At least 80% of the world’s most important sites for biodiversity on land currently contain human developments, study finds
2023-03-23
PRESS RELEASE FROM THE UNIVERSITY OF CAMBRIDGE
EMBARGOED UNTIL 00.05 LONDON TIME (GMT) ON 23 March 2023
Paper available at: https://drive.google.com/drive/folders/18wVryz17-8PmtYDudp5NPXE75onO12FF?usp=sharing
At least 80% of the world’s most important sites for biodiversity on land currently contain human developments, study finds
At least 80% of sites identified as being internationally important for biodiversity on land currently contain infrastructure − of which more than 75% contain roads.
In the future, more sites that are important for biodiversity could contain powerplants, mines ...
Enzyme-regulating macrophages found in both humans and mice open the door to translating findings in mice into human therapies.
2023-03-23
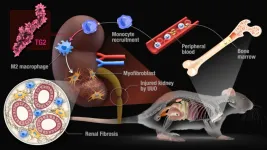
Researchers at Nagoya University in Japan have identified two enzymes that are involved in macrophage polarization, one of the key factors affecting fibrosis. The group’s findings, reported in Cell Death & Disease, suggest a potential treatment for human patients.
Kidney fibrosis is a dangerous inflammatory disease that causes the organs to stiffen and lose normal function. The disease is linked to a process called macrophage polarization. Polarization is the process by which macrophages, the white blood cells that help the body fight infection and repair tissue, are changed into two types as a response to changes in the microenvironment of the cell: the M1 type, which ...
Can artificial intelligence predict spatiotemporal distribution of dengue fever outbreaks with remote sensing data? New study finds answers
2023-03-23
Outbreaks of zoonotic diseases, which are those transmitted from animals to humans, are globally on the rise owing to climate change. In particular, the spread of diseases transmitted by mosquitoes is very sensitive to climate change, and Chinese Taiwan has seen a worrisome increase in the number of cases of dengue fever in recent years.
Like for most known diseases, the popular saying “an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure” also rings true for dengue fever. Since there is still no safe and effective vaccine for all on a global scale, dengue fever prevention efforts rely on limiting places where mosquitoes can lay their eggs and giving people an early warning when ...
New in-home AI tool monitors the health of elderly residents
2023-03-23
Engineers are harnessing artificial intelligence (AI) and wireless technology to unobtrusively monitor elderly people in their living spaces and provide early detection of emerging health problems.
The new system, built by researchers at the University of Waterloo, follows an individual’s activities accurately and continuously as it gathers vital information without the need for a wearable device and alerts medical experts to the need to step in and provide help.
“After more than five years of working on this technology, we’ve demonstrated that very low-power, millimetre-wave radio systems enabled by machine learning ...
New insights into the origins of spinal muscular atrophy
2023-03-22
NEW YORK, NY--Columbia researchers have discovered how a genetic defect leads to spinal muscular atrophy (SMA), a critical piece of information about the disease that neurologists have been seeking for decades.
The discovery suggests a new way to treat SMA—a devastating childhood motor neuron disease that affects 1 in 6,000 children. In the most severe cases, and when left untreated, children born with SMA die within the first two years of life.
The researchers also used their finding to develop an experimental therapy that improved survival in mice with severe SMA by ...
Oncotarget | Attenuation of cancer proliferation by suppression of glypican-1
2023-03-22
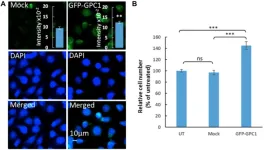
“This study was designed to increase the knowledge on the potential of GPCs and in particular GPC1 as a biomarker in cancer diagnosis and prognosis.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 22, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on March 21, 2023, entitled, “Attenuation of cancer proliferation by suppression of glypican-1 and its pleiotropic effects in neoplastic behavior.”
Glypicans (GPC1-6) are associated with tumorigenic processes and their involvement in neoplastic behavior has been ...
Geothermal energy has potential to be cost-competitive with other renewables and fossil fuels
2023-03-22
CAMBRIDGE, Mass.—Clean geothermal energy—the heat beneath our feet—has the potential to be cost competitive with other renewables and even fossil fuels if we can drill deep enough to access the mother lode of the resource. That’s according to one speaker at a geothermal conference last month held by the Society of Petroleum Engineers (SPE). Other speakers addressed growing interest in the field by the oil and gas sector, key challenges it faces, and solutions to help solve those challenges.
Geothermal 2023: Realising the Ambition was organized by the Aberdeen, ...
Towards reducing biodiversity loss in fragmented habitats
2023-03-22
When natural habitats are cleared to make way for cities, roads and agriculture, this often leaves behind “islands” of fragmented habitat that can place species at risk of extinction. Species are at risk when they find it hard to move among habitat patches to find resources and reproduce.
By combining lab experiments and mathematical modelling, researchers at McGill University and the Swiss Federal Institute of Aquatic Science and Technology have found a way to predict the movement of species that could guide conservation efforts to reconnect fragmented habitats.
The ...
How the brain's 'internal compass' works
2023-03-22
Scientists have gained new insights into the part of the brain that gives us a sense of direction, by tracking neural activity with the latest advances in brain imaging techniques. The findings shed light on how the brain orients itself in changing environments – and even the processes that can go wrong with degenerative diseases like dementia, that leave people feeling lost and confused.
“Neuroscience research has witnessed a technology revolution in the last decade allowing us to ...