(Press-News.org) World-first ‘phase change inks’ that could transform how we heat and cool buildings, homes and cars – to achieve sophisticated ‘passive climate’ control – have been developed, with enormous potential to help reduce energy use and global greenhouse gas emissions.
New research published in The Royal Society of Chemistry’s Journal of Materials Chemistry A led by Dr Mohammad Taha, documents proof-of-concept ‘phase change inks’ that use nanotechnology to control temperature in everyday environments. They achieve this by adjusting the amount of radiation that can pass through them, based on the surrounding environment.
Dr Taha said these inks could be used to develop coatings to achieve passive heating and cooling, reducing our need to rely on energy creation to regulate temperatures.
“Humans use a lot of energy to create and maintain comfortable environments – heating and cooling our buildings, homes, cars and even our bodies,” Dr Taha said.
“We can no longer only focus on energy generation from renewable resources to reduce our environmental impact. We also need to consider reducing our energy consumption as part of our proposed energy solutions, as the impacts of climate change become a reality.
“By engineering our inks to respond to their surroundings, we not only reduce the energy expenditure, but we also remove the need for auxiliary control systems to control temperatures, which is an additional energy waste.”
Passive climate control would enable comfortable living conditions without expending energy unnecessarily. For example, to provide comfortable heating in winter, the inks applied on a building façade could automatically transform to allow greater sun radiation to pass through during the day, and greater insulation to keep warmth in at night. In summer, they could transform to form a barrier to block heat radiation from the sun and the surrounding environment.
The versatile ‘phase change inks’ are a proof-of-concept that can be laminated, sprayed or added to paints and building materials. They could also be incorporated into clothing, regulating body temperature in extreme environments, or in the creation of large-scale, flexible and wearable electronic devices like bendable circuits, cameras and detectors, and gas and temperature sensors.
Dr Taha said: “Our research removes the previous restrictions on applying these inks on a large scale cheaply. It means existing structures and building materials can be retrofitted. With manufacturing interest, the inks could reach market in five to 10 years.
“Through collaboration with industry, we can scale up and integrate them into existing and new technologies as part of a holistic approach to tackling the world’s climate change energy challenges.
“The potential of this material is huge as it can be used for so many different purposes – like preventing heat build-up in laptop electronics or on car windshields. But the beauty of this material is that we can adjust its heat absorption properties to suit our needs.
“Already, a different type of phase change material is used to manufacture smart glass, but our new material means we can engineer smarter bricks and paint. This new nanotechnology can help retrofit existing buildings to make them more efficient. It’s better for the environment and sustainable for the future.”
The breakthrough was achieved by discovering how to modify one of the main components of ‘phase change materials’ – vanadium oxide (VO2). Phase change materials use triggers, like heat or electricity, to create enough energy for the material to transform itself under stress. However, phase change materials previously needed to be heated to very high temperatures for their ‘phase changing’ properties to be activated.
“We used our understanding of how these materials are put together to test how we could trigger the insulator to metal (IMT) reaction, where the material basically acts as a switch to block heat beyond a particular temperature – near-room temperature (30-40oC),” Dr Taha said.
Dr Taha said the next step will involve taking the research, patented by the University of Melbourne, to production.
END
'Nano inks' could passively control temperature in buildings, cars
World-first ‘phase change inks’ that could transform how we heat and cool buildings, homes and cars – to achieve sophisticated ‘passive climate’ control – have been developed, with potential to help reduce energy use and global greenhouse gas emissions
2023-03-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Project helps thousands of people in England and France into employment and entrepreneurship
2023-03-27
New research led by the University of East Anglia (UEA) shows that large infrastructure projects which are the focus of the UK government’s levelling up agenda and include support for business start-ups, must also offer sustainable, local investment in deprived communities.
Through place-based micro-enterprise training and employment support over a longer time frame, lasting local impact can be demonstrated, according to the study’s policy recommendations.
Supporting people to return to their communities, increasing social cohesion within them, boosting digital literacy and enabling net zero jobs are also likely to play a role.
These goals can be easily ...
Embryos’ development is delayed in pregnancies that end in miscarriage
2023-03-27
Embryos in pregnancies that end in miscarriage take longer to develop in the womb than those in pregnancies that result in live births, according to new research published today (Monday) in Human Reproduction [1], one of the world’s leading reproductive medicine journals.
For the first time, researchers in The Netherlands have been able to look at the way embryos develop while pregnancies are ongoing. They used state-of-the-art imaging technology, including 3D ultrasound with high resolution transvaginal probes and ...
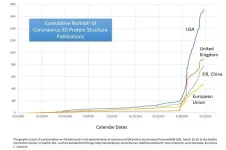
Global analysis of coronavirus protein research reveals how countries respond to disease
2023-03-27
In a new study, researchers examined how a country’s number of published 3D protein structures for coronaviruses, including the one responsible for COVID-19, correlated with its economic output and population. The findings reveal important insights into how different countries' research establishments respond to disease outbreaks and could be useful for planning responses to future pandemics.
The study showed that countries with larger economies generated more 3D structure determinations for the protein components ...
Shh! Intensive care incubators resonate sounds and risk damage to premature babies’ hearing, scientists say
2023-03-27
For vulnerable premature babies, an incubator in the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) is a lifesaver, but the consequences can last a lifetime. Many studies have shown that the NICU is a noisy environment and that babies who spend time there have higher rates of hearing impairment, which can lead to delays in language acquisition. Scientists from Vienna, Hamburg, Munich, and Osnabruck set out to investigate the role of the incubator, an underestimated element in the soundscape that surrounds babies during their time in the NICU.
“The ...
Securing new metal 3D printing technology that drives the renaissance of the manufacturing industry!
2023-03-27
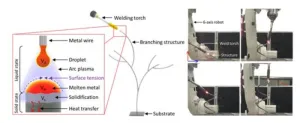
□ A research team led by Dr. Sang-woo Song, Dr. Chan-kyu Kim, Dr. Kang-myung Seo at the Department of Joining Technology of the Korea Institute of Materials Science(KIMS), a government-funded research institute under the Ministry of Science and ICT, has developed a foundational technology for controlling the volume of molten metal in the process of 3D printing metal using welding techniques. They achieved this through collaborative research with a research team led by Professor Young-tae Cho and Professor ...
Advanced technologies for longer-lasting electric vehicles
2023-03-27
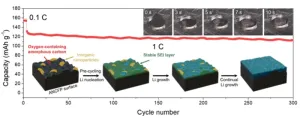
Owing to the worldwide trend of utilizing electric vehicles, there has been a rise in demand for next-generation secondary batteries with higher capacity and faster charging than the lithium-ion batteries currently in use. Lithium metal batteries have been recognized as promising rechargeable batteries because lithium metal anode exhibits theoretical capacity 10 times higher than commercial graphite anode. During charging-discharging processes, however, lithium dendrites grow on the anode, leading to poor battery performance and short-circuit.
Dr. Sungho Lee, Head of the ...
The genetics of temperature adaptation: how does life thrive in extreme conditions?
2023-03-27
The history of the Earth has been one of physical extremes—extreme atmospheric conditions, extreme chemical environments, and extreme temperatures. There was a time when the Earth was so hot all the water was vapor, and the first rain only fell once the planet cooled enough. Soon after, life emerged and through it all, life has found a way. Today life is found almost everywhere on Earth we have looked; it is difficult to find places where life does not exist. The remarkable ability of life to adapt to variable conditions is one of its defining characteristics. Of its many adaptations, the ability of life to adapt to varying temperatures ...
Opening up a different conversation about violence
2023-03-27
20 years on from the invasion of Iraq, nearly 25 years since the Good Friday Agreement in Northern Ireland, and in the midst of war in Ukraine and contested questions about migration and the legacies of war, a brand new Centre for the Study of Violence will launch this week at the University of Bath.
Led by academics across the University’s Faculty of Humanities & Social Sciences, including political theorists, development and humanitarian scholars, plus crime, defence and security experts, the new Centre will be the first of its kind in the UK. It aims to help society rethink how violence operates and to find ways to imagine a more peaceful world.
The Centre ...
Students who played sports before the pandemic did better during lockdowns
2023-03-27
A history of participating in campus recreational sports can offset stress and contribute to academic competence even during high-stress periods such as a pandemic lockdown, shows a new study.
Researchers at the University of Waterloo found that participation in activities such as fitness classes and intramural and drop-in sports before the pandemic was linked to lower levels of stress and higher levels of perceived competence to handle challenges and master school workload during the lockdown.
The study used factor and regression analyses based on self-reported ...
What do the elements sound like? (video)
2023-03-26
INDIANAPOLIS, March 26, 2023 — In chemistry, we have He, Fe and Ca — but what about do, re and mi? Hauntingly beautiful melodies aren’t the first things that come to mind when looking at the periodic table of the elements. However, using a technique called data sonification, a recent college graduate has converted the visible light given off by the elements into audio, creating unique, complex sounds for each one. Today, the researcher reports the first step toward an interactive, musical periodic table.
The researcher will present his results at the spring meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Spring 2023 is a hybrid meeting ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
[Press-News.org] 'Nano inks' could passively control temperature in buildings, carsWorld-first ‘phase change inks’ that could transform how we heat and cool buildings, homes and cars – to achieve sophisticated ‘passive climate’ control – have been developed, with potential to help reduce energy use and global greenhouse gas emissions