(Press-News.org) After a child’s hospital stay, many families covered by private insurance may experience sticker shock – on average spending $1,300 out of pocket – a new study in JAMA Pediatrics suggests.
For one in seven families, the price tag is even higher, exceeding $3,000.
“Bills for a child’s hospitalization can be astonishingly high for some families depending on how their insurance plan is structured,” said lead author Erin Carlton, M.D., a pediatric intensivist at University of Michigan Health C.S. Mott Children's Hospital and researcher at the U-M Medical School, of Michigan Medicine.
“For families without savings, these bills could have negative impacts on their family’s wellbeing.”
Researchers analyzed 183,780 non-birth related hospitalizations among 130,826 privately insured children covered aged 18 and under from 2017-2019.
Out-of-pocket spending was particularly high for hospitalizations that happened early in the year, were covered by insurance plans with high cost-sharing requirements and –interestingly – involved healthy children without chronic conditions.
Why some families may pay more than others
The greatest bulk of out-of-pocket spending for hospitalizations involved co-insurance payments (averaging $861 per hospitalization) while more than a fourth involved deductibles (averaging $389 per hospitalization), researchers found. Just 5% of families’ bills were for copayments.
While 80% of the children in the study had a chronic condition, such as asthma, families whose children didn’t have any such conditions spent the most on hospitalizations, with an average of $1,746 per hospitalization.
One possible explanation, Carlton says, is that families of children with chronic conditions may have been more likely to have already met deductibles before the child was hospitalized.
“For families with healthy children, the hospitalization may be one of the first major medical expenses during the year,” Carlton said. “This could explain why they are subjected to larger deductible and co-insurance payments.”
Children hospitalized in the first quarter of the year were also likely to experience higher costs, which researchers attribute to insurance plans resetting deductibles in January.
Intensive care services and longer hospital stays were associated with higher bills but were generally modest. Meanwhile, out-of-pocket spending was almost twice as high for hospitalizations covered by the least generous plans – those requiring a deductible exceeding $3,000 and co-insurance of 20% or more for hospitalizations – compared to the most generous.
“Our findings suggest that resource intensity, such as intensive care use, isn’t a major driver of hospital bills,” Carlton said.
“Instead, one of the most significant factors driving higher out-of-pocket spending is the degree to which insurance plans expose families to the high cost of hospitalization through deductibles or co-insurance.”
While imposing substantial cost-sharing may help decrease use of medical services that aren’t necessary this approach is inappropriate for potentially life-saving pediatric hospitalizations, according to senior author and Mott pediatrician Kao-Ping Chua, M.D., Ph.D., a member of the Susan B. Meister Child Health Evaluation and Research Center at Michigan Medicine.
“If the goal is to decrease health care spending, there are better way to achieve this than to subject families to huge bills just because their child was unlucky enough to get severely ill,” Chua said.
For example, he says, private insurers may consider denying coverage of unnecessary health care services. Policymakers might also address the drivers behind high prices for inpatient hospital care.
Private insurers may also attempt to spread out deductibles more evenly throughout the year to prevent a significant financial blow from an unexpected hospitalization.
Most of the children in the study were ages four to 16. Two of the top three hospitalization diagnoses were for severe mental health disorders and the other was bronchitis or asthma.
Carlton notes that the study doesn’t account for indirect costs associated with hospitalizations, such as missing work to be at a child’s bedside. The research also doesn’t explore whether hospitalizations led to worsened financial health, such as increased debt.
“A pediatric hospitalization is often unexpected, and many families aren’t prepared for all the financial repercussions once they’re home,” Carlton said. “Our findings show that restructuring how insurance plans cover hospitalizations could help alleviate this financial burden on families.”
Additional authors include Nora Becker, M.D., Ph.D., Michelle Moniz, M.D., M.Sc., John Scott, M.D., M.P.H., Hallie Prescott, M.D., M.Sc., all of U-M.
Study Cited: “Out-of-pocket spending for non-birth-related hospitalizations of privately insured U.S. children, 2017-2019, doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2023.0130.
END
Study: Average privately insured family spends $1,300 for child’s hospitalization
For 1 in 7 pediatric hospitalizations, the out-of-pocket cost exceeds $3,000, new research suggests
2023-03-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Expectations, prior experiences associated with adverse effects of COVID-19 vaccination
2023-03-27
About The Study: In this study of 1,678 participants, expectations of low benefit and high adverse effects, the tendency to catastrophize instead of normalize benign bodily sensations, and prior negative experiences were associated with COVID-19 vaccination adverse effects. Clinician-patient interactions and public vaccine campaigns may both benefit from these insights by optimizing and contextualizing information provided about COVID-19 vaccines.
Authors: Ingmar Schafer, Ph.D., of the University Medical Center Hamburg-Eppendorf ...
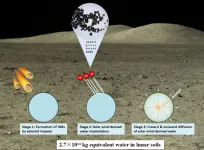
Researchers find new water reservoir on Moon
2023-03-27
Lunar surface water has attracted much attention due to its potential for in-situ resource utilization by future lunar exploration missions and other space missions
Now, a research group led by Prof. HU Sen from the Institute of Geology and Geophysics (IGG) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has found that impact glass beads in Chang'e-5 (CE5) lunar soils contain some water.
Detailed studies show that these glass beads are likely a new water reservoir on the Moon, recording the dynamic ingress and egress of solar wind-derived water and acting ...
Ending THC use may reverse its impacts on male fertility
2023-03-27
A 2022 study from Oregon Health & Science University researchers confirmed that chronic use of cannabis may greatly impact male fertility and reproductive outcomes in nonhuman primates — but it was unclear whether the effects are permanent. Now, the OHSU research team has confirmed that discontinuing use of THC can at least partly reverse these effects, according to a new study published online today in Fertility & Sterility.
This is one of the first studies demonstrating that discontinuation ...
New study: HIV genomes that hide in white blood cells offer new target to eliminate infections
2023-03-27
**EMBARGOED TILL 11 A.M. ET MONDAY, MARCH 27
To develop treatments that may one day entirely rid the body of HIV infection, scientists have long sought to identify all of the places that the virus can hide its genetic code. Now, in a study using blood samples from men and women with HIV on long-term suppressive therapy, a team led by Johns Hopkins Medicine scientists reports new evidence that one such stable reservoir of HIV genomes can be found in circulating white blood cells called monocytes.
Monocytes are short-lived circulating immune cells that are a precursor to macrophages, immune cells able to engulf and destroy viruses, bacteria ...
The search for the missing gravitational signal
2023-03-27
Every year, hundreds of thousands of pairs of black holes merge in a cosmic dance that emits gravitational waves in every direction. Since 2015, the large ground-based LIGO, Virgo and KAGRA interferometers have made it possible to detect these signals, although only about a hundred such events, an infinitesimal fraction of the total, have been observed. Most of the waves remain 'indistinguishable', superimposed and added together, creating a flat, diffuse background signal that scientists call the 'stochastic gravitational wave ...
Study of dietary and nutrition recommendations from worldwide clinical practice guidelines finds close alignment on benefits of plant food groups for treatment and prevention of chronic disease
2023-03-27
The results of a study published in “Advances in Nutrition” that compared dietary and nutrition recommendations from dozens of clinical practice guidelines around the world for treating, managing and preventing major chronic diseases should increase clinician confidence on recommending consumption of fruits, vegetables, legumes and whole grains.
The meta-epidemiological study from the American College of Lifestyle Medicine (ACLM) reviewed 78 clinical practice guidelines published between 2010 and 2021 in North America, Europe and Asia and found close alignment in their recommendations for encouraging daily intake of plant food sources, while ...
Don Quixote gives his name to a new plant species only known from La Mancha, Spain
2023-03-27
The knowledge of biodiversity in allegedly well-known places is not as complete as one would expect and its detailed study by researchers continues to offer surprises, is what we find out in a new study of the flora of south-central Spain.
Now, Spanish botanists from Pablo de Olavide University (Seville, Spain) have described a new plant species of the papyrus family (Cyperaceae) restricted to the La Mancha region in south-central Spain. This region is in fact well-known for classic literary fans, who might recognise the name ...
SwRI-developed instrument delivered for lunar lander mission
2023-03-27
SAN ANTONIO — March 27, 2023 —Southwest Research Institute recently delivered the Lunar Magnetotelluric Sounder (LMS) to Firefly Aerospace in Cedar Park, Texas, for integration into the Blue Ghost 1 lunar lander scheduled to arrive at the Moon in 2024. The sounder will determine the electrical conductivity of the interior of the Moon by measuring low-frequency electric and magnetic fields.
“For more than 50 years, scientists have used magnetotelluric techniques, which use natural characteristics of the Earth’s electromagnetic fields to determine the electrical resistivity of the subsurface for research and resource exploration,” said SwRI’s Bob Grimm, ...
Socially vulnerable carry disproportionate COVID burden due to lower likelihood of vaccination not vaccine effectiveness
2023-03-27
INDIANAPOLIS – The burden of the pandemic has disproportionately affected socially vulnerable populations. One of the first studies to look at the intersection of social vulnerability with COVID-19 vaccine utilization and effectiveness has found that while vaccination rates have varied substantially between socially vulnerable and communities that are not socially vulnerable, there has been no difference in vaccine effectiveness between those who are socially vulnerable and those who are not.
“We found that protection against emergency room and urgent care center visits, hospitalization and death conveyed by a COVID-19 mRNA vaccination ...
Positive experiences in close relationships are associated with better physical health, new research suggests
2023-03-27
Social relationships influence physical health, but questions remain about the nature of this connection. New research in Social Psychological and Personality Science suggests that the way you feel about your close relationships may be affecting the way your body functions.
Previous smaller-scale studies have examined the connection between relationship conflict or satisfaction with stress levels and blood pressure. The new research examines the effects of positive and negative relationship experiences on the body, as well as how these experiences and health outcomes change ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Study: Reported crop yield gains from breeding may be overstated
Stem cells from human baby teeth show promise for treating cerebral palsy
Chimps’ love for crystals could help us understand our own ancestors’ fascination with these stones
Vaginal estrogen therapy not linked to cancer recurrence in survivors of endometrial cancer
How estrogen helps protect women from high blood pressure
Breaking the efficiency barrier: Researchers propose multi-stage solar system to harness the full spectrum
A new name, a new beginning: Building a green energy future together
From algorithms to atoms: How artificial intelligence is accelerating the discovery of next-generation energy materials
Loneliness linked to fear of embarrassment: teen research
New MOH–NUS Fellowship launched to strengthen everyday ethics in Singapore’s healthcare sector
Sungkyunkwan University researchers develop next-generation transparent electrode without rare metal indium
What's going on inside quantum computers?: New method simplifies process tomography
This ancient plant-eater had a twisted jaw and sideways-facing teeth
Jackdaw chicks listen to adults to learn about predators
Toxic algal bloom has taken a heavy toll on mental health
Beyond silicon: SKKU team presents Indium Selenide roadmap for ultra-low-power AI and quantum computing
Sugar comforts newborn babies during painful procedures
Pollen exposure linked to poorer exam results taken at the end of secondary school
7 hours 18 mins may be optimal sleep length for avoiding type 2 diabetes precursor
Around 6 deaths a year linked to clubbing in the UK
Children’s development set back years by Covid lockdowns, study reveals
Four decades of data give unique insight into the Sun’s inner life
Urban trees can absorb more CO₂ than cars emit during summer
Fund for Science and Technology awards $15 million to Scripps Oceanography
New NIH grant advances Lupus protein research
New farm-scale biochar system could cut agricultural emissions by 75 percent while removing carbon from the atmosphere
From herbal waste to high performance clean water material: Turning traditional medicine residues into powerful biochar
New sulfur-iron biochar shows powerful ability to lock up arsenic and cadmium in contaminated soils
AI-driven chart review accurately identifies potential rare disease trial participants in new study
Paleontologist Stephen Chester and colleagues reveal new clues about early primate evolution
[Press-News.org] Study: Average privately insured family spends $1,300 for child’s hospitalizationFor 1 in 7 pediatric hospitalizations, the out-of-pocket cost exceeds $3,000, new research suggests