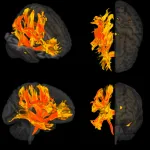
(Press-News.org) For the first time, researchers have identified specific regions of the brain that are damaged by high blood pressure and may contribute to a decline in mental processes and the development of dementia.
High blood pressure is known to be involved in causing dementia and damage to brain function. The study, which is published in the European Heart Journal [1] today (Tuesday), shows how this happens. It gathered information from a combination of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of brains, genetic analyses and observational data from thousands of patients to look at the effect of high blood pressure on cognitive function. The researchers then checked their findings in a separate, large group of patients in Italy.
Tomasz Guzik, Professor of Cardiovascular Medicine, at the University of Edinburgh (UK) and Jagiellonian University Medical College, Krakow (Poland), who led the research, said: “By using this combination of imaging, genetic and observational approaches, we have identified specific parts of the brain that are affected by increases in blood pressure, including areas called the putamen and specific white matter regions. We thought these areas might be where high blood pressure affects cognitive function, such as memory loss, thinking skills and dementia. When we checked our findings by studying a group of patients in Italy who had high blood pressure, we found that the parts of the brain we had identified were indeed affected.
“We hope that our findings may help us to develop new ways to treat cognitive impairment in people with high blood pressure. Studying the genes and proteins in these brain structures could help us understand how high blood pressure affects the brain and causes cognitive problems. Moreover, by looking at these specific regions of the brain, we may be able to predict who will develop memory loss and dementia faster in the context of high blood pressure. This could help with precision medicine, so that we can target more intensive therapies to prevent the development of cognitive impairment in patients most at risk.”
High blood pressure is common and occurs in 30% of people worldwide, with an additional 30% showing the initial stages of the disease. Studies have shown that it affects how well the brain works and that it can cause long-term changes. However, until now it was not known exactly how high blood pressure damages the brain and which specific regions are affected.
In research co-funded by the European Research Council, the British Heart Foundation and the Italian Ministry of Health, Prof. Guzik and an international team of researchers used brain MRI imaging data from over 30,000 participants in the UK Biobank study, genetic information from genome-wide association studies (GWAS) from UK Biobank and two other international groups (COGENT and the International Consortium for Blood Pressure), and a technique called Mendelian randomisation, to see if high blood pressure was actually the cause of changes to specific parts of the brain rather than just being associated with these changes.
“Mendelian randomisation is a way of using genetic information to understand how one thing affects another,” said Prof. Guzik. “In particular, it tests if something is potentially causing a certain effect, or if the effect is just a coincidence. It works by using a person's genetic information to see if there is a relationship between genes predisposing to higher blood pressure and outcomes. If there is a relationship, then it is more likely that the high blood pressure is causing the outcome. This is because genes are randomly passed down from parents, so they are not influenced by other factors that could confuse the results. In our study, if a gene that causes high blood pressure is also linked to certain brain structures and their function, then it suggests that high blood pressure might really be causing brain dysfunction at that location, leading to problems with memory, thinking and dementia.”
The researchers found changes to nine parts of the brain were related to higher blood pressure and worse cognitive function. These included the putamen, which is a round structure in the base of the front of the brain, responsible for regulating movement and influencing various types of learning. Other areas affected were the anterior thalamic radiation, anterior corona radiata and anterior limb of the internal capsule, which are regions of white matter that connect and enable signalling between different parts of the brain. The anterior thalamic radiation is involved in executive functions, such as the planning of simple and complex daily tasks, while the other two regions are involved in decision-making and the management of emotions.
The changes to these areas included decreases in brain volume and the amount of surface area on the brain cortex, changes to connections between different parts of the brain, and changes in measures of brain activity.
First author of the study, Associate Professor Mateusz Siedlinski, also a researcher at the Jagiellonian University Medical College, said: “Our study has, for the first time, identified specific places in the brain that are potentially causally associated with high blood pressure and cognitive impairment. This was uniquely possible thanks to the availability of data from UK Biobank, including MRI brain images, and thanks to previous research identifying genetic variants that affect the structure and function of over 3000 areas of the brain.”
Co-author of the study, Professor Joanna Wardlaw, Head of Neuroimaging Sciences at the University of Edinburgh, said: “It has been known for a long time that high blood pressure is a risk factor for cognitive decline, but how high blood pressure damages the brain was not clear. This study shows that specific brain regions are at particularly high risk of blood pressure damage, which may help to identify people at risk of cognitive decline in the earliest stages, and potentially to target therapies more effectively in future.”
Limitations of the study include that participants in the UK Biobank study are mainly white and middle-aged, so it might not be possible to extrapolate the findings to older people.
An accompanying editorial [2] is written by Dr Ernesto Schiffrin, from Sir Mortimer B. Davis-Jewish General Hospital and McGill University, Montreal, (Canada), and Dr James Engert, from the McGill University Health Centre Research Institute, Montreal. They make the point that “Further mechanistic studies of the effects of BP [blood pressure] on cognitive function are required to determine precise causal pathways and relevant brain regions”.
They highlight one of the study’s findings about systolic and diastolic blood pressure (SBP and DBP). “Perhaps one of the more interesting results in this study is the possible distinct causal effects of SBP vs. DBP. The authors observed some overlapping results for SBP and DBP on cognitive function when analysed in isolation. However, when each parameter is analysed after adjusting for the other, or in multivariable models, intriguing findings begin to emerge. DBP alone does not predict a decline in cognitive function, but in fact, is protective when adjusted for SBP. This result was true both observationally and when using Mendelian randomisation.” They go on to discuss the possible reasons for this.
(ends)
[1] “Genetic analyses identify brain structures related to cognitive impairment associated with elevated blood pressure”, by Mateusz Siedlinski et al. European Heart Journal. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehad101
[2] “Hypertension, brain imaging phenotypes and cognitive impairment: lessons from Mendelian randomisation”, by Ernesto L. Schiffrin and James C. Engert. European Heart Journal. doi:10.1093/eurheartj/ehad187
END
World first: Researchers identify specific regions of the brain that are damaged by high blood pressure and are involved in a decline in mental processes and dementia
2023-03-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Phthalate alternative may harm brain development and health
2023-03-28
Growing concerns over the potential health effects of exposure to phthalates, a component of many plastics and also known as a plasticizer, have led to a search for safer alternatives. In a new study conducted in cell cultures, researchers found that the chemical acetyl tributyl citrate (ATBC) might not be the best replacement because it appears to interfere with the growth and maintenance of neurons.
“In the past, industries have promptly shifted away from the usage of toxic chemicals only to produce an equally toxic chemical, so this is something we are actively trying to avoid repeating,” said Kyle Sease, a graduate student at Central Washington ...
Researchers identify markers of PTSD in the blood
2023-03-28
A new study found that people who are currently suffering or face a high risk of post-traumatic stress disorder show particular patterns in four biomarkers measurable with a simple blood test. The findings suggest these biomarkers could be used to predict a person’s likelihood of developing PTSD, diagnose the disorder or monitor the response to treatment.
PTSD can occur after experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event. It is currently diagnosed based on symptoms such as flashbacks, difficulty sleeping or concentrating, ...
Labeling macrophages associated with cancer progression using a selective dye
2023-03-28
M1 and M2 are activated macrophages that protect our immune system and maintain homeostasis. Interestingly, they are characterized by distinct and opposing phenotypes. M1 macrophages are known for their bactericidal and tumoricidal properties by secreting pro-inflammatory cytokines, while M2 macrophages facilitate immunosuppressive responses and help cancer progression. As such, reprogramming macrophages from M2 to M1 phenotype has been regarded as a significant interest in the view of potential cancer ...
How repeated questions could put you at risk of cyber crime
2023-03-28
People reveal more personal information when you ask them the same questions a second time – according to new research from the University of East Anglia.
A new study published today reveals how simple repetition can make people over-disclose, and potentially put themselves at risk of identity theft and cyber crime.
The research team say that understanding why people disclose personal data could help inform measures to address the problem.
From subscribing to online newspapers to completing customer surveys, our personal data is being mined continuously; the world’s most valuable resource is no longer oil, but data.
But for consumers who provide their personal ...
Graphenest and Hubron to explore development and commercialization of graphene
2023-03-28
In February of this year, Graphene Flagship associated member Graphenest and manufacturing company Hubron International entered a new strategic partnership. Their shared aim is to explore the development and commercialization of graphene-based polymer masterbatch and compounds with unprecedented electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding performance for electronic enclosures manufacturing.
This new product line will start with a graphene-based thermoplastic suitable to be implemented as a remarkable EMI shielding solution in medium-high and high frequencies (for 5G and beyond).
The agreement brings together Graphenest’s knowledge around graphene ...
ENZAMET shows promise as prostate cancer treatment
2023-03-28
A new drug combination for men with advanced prostate cancer has shown sustained increase in survival rates.
The results from the clinical trial of ENZAMET, co-chaired by Professor Christopher Sweeney, Director of the South Australian immunoGENomics Cancer Institute (SAiGENCI) that operates within the University of Adelaide, have been published today in The Lancet Oncology.
For people with metastatic hormone-sensitive prostate cancer, the addition of an androgen receptor blocker with enzalutamide ...
Cancer that spreads to the lung maneuvers to avoid being attacked by “killer” T cells
2023-03-28
AUGUSTA, Ga. (March 28, 2023) – Cancer that has spread to areas like the lungs can apply the brakes to a natural pathway that should recruit killer T cells directly to where it has metastasized, scientists report.
That newly found strategy used by tumors that have spread — and are consequently more deadly — may help explain why sometimes promising immunotherapies designed to help the immune system kill cancer don’t, says Kebin Liu, PhD, cancer immunologist in the Department of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology at the Medical College of Georgia.
It also may mean an additional therapeutic maneuver is needed to stop some tumors, which ...
Hispanic, Black, and low-income adults are less likely to replace smoking with vaping
2023-03-27
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
March 27, 2023
Contact:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
##
Growing evidence suggests that e-cigarettes may serve as a less harmful alternative to smoking traditional cigarettes, but socioeconomic and racial inequities in cigarette and e-cigarette use are preventing certain populations from reaping these potential health benefits, according to a new study led by Boston University School of Public Health (BUSPH) and the Keck School of Medicine of the University of Southern California (Keck School of Medicine of USC).
Published in the American Journal of Preventive ...
Rare beetle, rediscovered after 55 years, named in honor of Jerry Brown
2023-03-27
Berkeley — When University of California, Berkeley, entomologist Kipling Will first heard that former Gov. Jerry Brown was hosting field scientists on his Colusa County ranch, he jumped at the chance to hunt for beetles on the property.
“I reached out and said, ‘Hey, I want to sample your beetles,’” Will said. “And [Brown] was quite game to let me come up there.”
Will, a professor of environmental science, policy and management, has travelled to all corners of California ...
JNM explores potential applications for ChatGPT in nuclear medicine and molecular imaging
2023-03-27
Reston, VA—A new article in The Journal of Nuclear Medicine explores the potential for using ChatGPT, an artificial intelligence chatbot, in the field of nuclear medicine and molecular imaging. In the article, Irène Buvat, PhD, and Wolfgang Weber, MD, PhD, report on discussions they held with ChatGPT regarding several nuclear medicine and molecular imaging topics and provide their commentary on the pros and cons of using the chatbot.
Developed by OpenAI, ChatGPT is a natural language processing chatbot that can intelligently respond to questions. ...