(Press-News.org)
“[...] mutations in G-proteins have been associated in the progress of several cancers [...]”
BUFFALO, NY- March 28, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on March 24, 2023, entitled, “Polyisoprenylated cysteinyl amide inhibitors deplete singly polyisoprenylated monomeric G-proteins in lung and breast cancer cell lines.”
Finding effective therapies against cancers driven by mutant and/or overexpressed hyperactive G-proteins remains an area of active research. Polyisoprenylated cysteinyl amide inhibitors (PCAIs) are agents that mimic the essential posttranslational modifications of G-proteins. It is hypothesized that PCAIs work as anticancer agents by disrupting polyisoprenylation-dependent functional interactions of the G-Proteins.
In their new study, researchers Nada Tawfeeq, Jassy Mary S. Lazarte, Yonghao Jin, Matthew D. Gregory, and Nazarius S. Lamango from Florida A&M University College of Pharmacy Pharmaceutical Sciences and Imam Abdulrahman bin Faisal University tested this hypothesis by determining the effect of the PCAIs on the levels of RAS and related monomeric G-proteins.
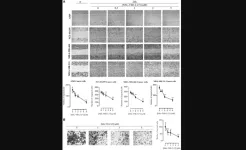
“To investigate the hypothesized anticancer mechanisms of the PCAIs through disruption of G-protein function, we checked the effects of the PCAIs on the G-protein levels in lung cancer (A549 and NCI-H1299) and breast cancer (MDA-MB-231 and MDA-MB-468) cell lines.”
Following 48 hours of exposure, they found significant decreases in the levels of KRAS, RHOA, RAC1, and CDC42 ranging within 20–66% after NSL-YHJ-2-27 (5 μM) treatment in all four cell lines tested, A549, NCI-H1299, MDA-MB-231, and MDA-MB-468. However, no significant difference was observed on the G-protein, RAB5A. Interestingly, 38 and 44% decreases in the levels of the farnesylated and acylated NRAS were observed in the two breast cancer cell lines, MDA-MB-231, and MDA-MB-468, respectively, while HRAS levels showed a 36% decrease only in MDA-MB-468 cells.
Moreover, after PCAIs treatment, migration, and invasion of A549 cells were inhibited by 72 and 70%, respectively while the levels of vinculin and fascin dropped by 33 and 43%, respectively. Their results show that PCAIs deplete the protein levels of some significant G-proteins which are known to be involved in the migration and invasion of cells (i.e., metastasis) such as RAC1, RHOA, and CDC42. These findings implicate the potential role of PCAIs as anticancer agents through their direct interaction with monomeric G-proteins.
“The initial findings presented here indicate how PCAIs can be used as potent agents in developing new anticancer therapeutics, therefore, more extensive studies need to be done to elucidate on its potency. Although we cannot conclusively explain the exact mechanism of action of PCAIs on how they affect the levels of some G-proteins yet, but we can say that these PCAIs have the ability to affect the progression of cancer.”
Read the full research paper: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28390
Correspondence to: Nazarius S. Lamango
Email: nazarius.lamango@famu.edu
Keywords: PCAIs, G-proteins, KRAS, RHOA, RAC1
About Oncotarget: Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
Twitter
Facebook
YouTube
Instagram
LinkedIn
Pinterest
LabTube
Soundcloud
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact: media@impactjournals.com.
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker Str., Suite 1A
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957 (option 2)
###
END
Reston, VA—A newly published literature review sheds light on how nuclear medicine brain imaging can help evaluate the biological changes that cause chemotherapy-related cognitive impairment (CRCI), commonly known as chemo-brain. Armed with this information, patients can understand better the changes in their cognitive status during and after treatment. This summary of findings was published ahead-of-print by The Journal of Nuclear Medicine.
CRCI describes a clinical condition characterized by memory and concentration impairment, difficulties with information processing ...
IIASA researchers collaborated with the FAIRR Initiative – a collaborative investor network – on the development of a new IPCC-aligned climate risk analysis tool for investors. Analyses done using the new tool, show that climate-related cost increases could significantly affect the bottom lines of the largest listed livestock companies unless new strategies are urgently adopted.
The FAIRR Initiative today launched an enhanced iteration of its Coller FAIRR Climate Risk Tool providing investors with company-level data on how climate risks may impact costs and ...
The study surveyed school nurses working across the UK about their current working practices and experiences of working during the pandemic.
Dr Sarah Bekaert RN, Senior Lecturer in Child Health at Oxford Brookes University, said: “This research has highlighted the vital role school nurses play in the identification and prevention of issues that are likely to negatively impact young people as they navigate their teenage years, and then transition into adulthood.
“Our findings call for advocacy by policymakers and professional organisations ...
Understanding What Prevents Shared Decision Making From Wider Implementation With Black Patients
To understand the perspectives of Black patients on shared decision making (SDM) during medical appointments, researchers and clinicians investigated the preferences, needs and challenges around SDM as experienced by Black individuals. The team also offers possible adaptations and modifications for SDM models, practice and research within Black communities. The study team recruited 32 Black patients – 18 men and 17 women – with type ...
The transformative changes brought by deep learning and artificial intelligence are accompanied by immense costs. For example, OpenAI’s ChatGPT algorithm costs at least $100,000 every day to operate. This could be reduced with accelerators, or computer hardware designed to efficiently perform the specific operations of deep learning. However, such a device is only viable if it can be integrated with mainstream silicon-based computing hardware on the material level.
This was preventing the implementation of one highly promising deep learning ...
SAN FRANCISCO – The Public Library of Science (PLOS) is pleased to announce that PLOS Global Public Health and PLOS Digital Health are now fully indexed in PubMed Central (PMC), expanding our reach and furthering our mission of ensuring research content is accessible and discoverable as widely as possible.
Both journals have an explicit mandate to promote equity in research that can tackle the most urgent priorities for the field, such as access to healthcare, or addressing bias in AI and developing machine learning tools for underserved communities. PLOS is proud to feature ...
American Geophysical Union
Press Release 23-12
28 March 2023
For Immediate Release
This press release is available online at: https://news.agu.org/press-release/some-coastal-salt-marshes-are-keeping-up-with-sea-level-rise-for-now
Some coastal salt marshes are keeping up with sea level rise — for now
Salt marshes on the U.S. East Coast have accumulated soil more quickly over the past century, and some appear to be keeping pace with rising waters. But that won’t last forever.
AGU press contact:
Rebecca Dzombak, +1 (202) ...
Free-range organic chicken or factory farming? Scientists at the German Cancer Research Center (DKFZ) have developed a new detection method that can reveal such differences in husbandry. The so-called epigenetic method is based on the analysis of the characteristic patterns of chemical markers on the genome of the animals.
Was the salmon for dinner with friends really caught wild or did it come from aquaculture? What to make of the alleged "biolabel quality“ of the shrimp for the seafood salad? And was the chicken for the Sunday roast really allowed to spend its life in the open air?
Food analysis laboratories can only answer ...
Abscisic acid (ABA) is a plant hormone with essential functions in plant physiology. It is involved in developmental and growth processes and the adaptive stress response. Thus, the plant adaptation to stress situations caused by water deficit can be favored by activating this phytohormone pathway. In this project, the teams led by Pedro Luis Rodríguez at the IBMCP in Valencia and Armando Albert at the IQRF in Madrid developed a genetic-chemical method to activate this route in an inducible way and without penalizing plant growth.
Based ...
Rates of prescriptions for naloxone to people at high risk for opioid overdose, as well as co-prescribing with opioids, has increased in emergency departments throughout the United States over the past decade, providing insight on the positive impact of federal policies and regulations, according to a Rutgers study.
Federal opioid prescribing guidelines in 2016 made it easier for doctors to prescribe naloxone to patients at high risk for opioid overdose. When used properly, naloxone is highly effective at reversing or reducing the life-threatening adverse effects of ...