(Press-News.org) A research group from Nagoya University in central Japan has discovered three new species of bioluminescent polycirrus worms from different parts of Japan. Usually found in shallow water, polycirrus are small worms, known for their bioluminescence. The researchers named one of their discoveries after a ghostly yokai, a creature in Japanese foklore; another after a lantern yokai; and the other after an influential Japanese marine biologist. They published their findings in the journal Royal Society Open Science.
Scientists have studied only a small fraction of the more than 7,000 species of luminescent organisms in the world. Research remains limited to certain species because of the existence of specimens that are difficult to classify into species. Without correct identification of the species, comparisons of different results are of limited use.
Naoto Jimi (he/him) and Special Assistant Professor Manabu Bessho-Uehara (he/him) at Nagoya University’s Graduate School of Science, led a research group with members from AIST, Olympus Corporation, and Japan Underwater Films Corporation, that organized Polycirrus according to their diversity. They discovered the three new species, all of which emit blue-violet light.
Jimi said that when they discovered these new species, they were amazed and felt a sense of duty to document and classify them. “Our previous research on the luminescence of the genus Polycirrus had established it as a valuable subject for bioluminescence studies,” he added. “However, we later discovered what we thought was a single species of Polycirrus was actually three different species.”
As the researchers found the worms in Japan, they gave them Japanese names. They named two of the three species Polycirrus onibi and Polycirrus aoandon as a reference to their bluish-violet luminescence. In Japanese folklore, onibi (demon fire) describes a will-o'-the-wisp type of yokai, shaped like a small, floating ball of light, that is believed to lead travellers in mountains and forests astray. Meanwhile, aoandon (blue lantern) is a ghost-like yokai that appears as a woman wearing a white kimono with horns and sharp teeth. It haunts lanterns found in Japanese homes by turning their light an unnatural blue color. The other worm was named Polycirrus ikeguchii in honor of Shinichiro Ikeguchi, the former director of the Notojima Aquarium.
“We used the names of Japanese yokai, such as onibi and aoandon, for the new species because the hazy violet-blue bioluminescence emitted by the Polycirrus species is strikingly similar to the descriptions of these creatures found in folklore,” said Jimi. “Polycirrus ikeguchii, on the other hand, was described from specimens collected in the Notojima region in Japan. As Shinichi Ikeguchi was the former director of Notojima Aquarium and helped to find the worm, it seemed appropriate to name it after him.”
The researchers hope to use their findings to deepen their understanding of the molecular nature of bioluminescence, which could lead to the development of new technologies. “The discovery that all three new species are luminescent has allowed us to link taxonomic and ecological findings and establish research that others can readily apply to the study of luminescent organisms,” said Jimi. “Understanding these luminescence mechanisms contributes to medical and life science research. Bioluminescence is a treasure trove of interesting and unusual chemistry. We intend to use our findings to deepen our understanding of the molecular nature of this phenomenon and apply this knowledge to the development of new life sciences technologies.”
END
Three newly discovered sea worms that glow in the dark named after creatures from Japanese folklore and marine biologist
2023-03-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The element of surprise: How unexpected syntax makes marketing communications more effective
2023-03-29
Researchers from Frankfurt School of Finance and Management published a new Journal of Marketing article that examines the role of syntactic surprise in formulating effective written messages.
The study, forthcoming in the Journal of Marketing, is titled “Creating Effective Marketing Messages Through Moderately Surprising Syntax” and is authored by A. Selin Atalay, Siham El Kihal, and Florian Ellsaesser.
Consider a manager advertising for a job, deciding whether to go with “Apply today to join a great ...
Hemex Health awarded $3M NIH grant to bring Gazelle Hb Variant Test for sickle cell disease to US market
2023-03-29
Portland, Ore. – March 27, 2023 – Hemex Health, a medical diagnostic device company focused on expanding healthcare access to underrepresented patient populations, announced it has been awarded a 3-year, $3 million grant from the National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute (NHLBI). NHLBI, part of the National Institutes of Health, awarded a SBIR Phase IIB Bridge Award to Hemex to advance the commercialization of the company’s Gazelle® Hb Variant Test for the United States market.
Hemex intends to use the grant to complete activities required for FDA 510(k) clearance.
The Hb Variant Test, one of the tests supported ...
New virtual entrepreneurial training launches to support innovators addressing health equity
2023-03-29
DALLAS, March 29, 2023 — New training tools from the American Heart Association will help health equity innovators address issues like structural racism and other social factors that impact health in urban and rural communities. A recent study found that Black and LatinX founders represented just 2.6% of total funding raised by venture capital in 2020.[1] In its commitment to ensuring equitable health for all, the Association supports innovators and other social enterprises, start-ups, non-profits, and digital and health tech companies that are addressing health equity challenges in their local communities with mentoring, funding opportunities and – now – ongoing ...
Institute for Protein Innovation welcomes top researchers at first symposium
2023-03-29
BOSTON, March 29, 2023 — The Institute for Protein Innovation (IPI) will host IPI Surfacing, a symposium on cell surface receptor biology, on Thursday, June 15, 2023. The free, day-long event convenes biomedical scientists at the Joseph B. Martin Conference Center at Harvard Medical School. Registration opens today.
As its inaugural symposium, IPI Surfacing reflects the Institute’s mission to advance protein science to accelerate research and improve human health. In addition to providing ...
Researchers hope to uncover hidden mechanisms of why ultra-processed foods are so rewarding – and so overconsumed
2023-03-29
Scientists at the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC are looking to uncover the “why” of the American diet. Why are people drawn to ultra-processed foods, which have been linked to obesity, Type 2 diabetes, different types of cancer, and increased risk of heart disease and death?
It’s a critical question because ultra-processed foods make up about 58 percent of calories consumed in the United States. These foods have been through multiple manufacturing processes and contain many added ingredients. Examples include sweetened cereals, hot dogs, chips, and soft drinks.
“We ...
Fermented coffee’s fruity aromas demystified
2023-03-29
INDIANAPOLIS, March 29, 2023 — Specialty coffees are gaining traction in coffeehouses around the world — and now a fermented version could bring a fruity taste to your morning cup of joe. This new kind of beverage has a raspberry-like taste and aroma, but what causes these sensations has been a mystery. Today, scientists report six compounds that contribute to the fermented coffee experience. The work could help increase production of the drink and make it more readily available for everyone to enjoy.
The researchers ...
Obesity treatment could offer dramatic weight loss without surgery or nausea
2023-03-29
INDIANAPOLIS, March 29, 2023 — Imagine getting the benefits of gastric bypass surgery without going under the knife — a new class of compounds could do just that. In lab animals, these potential treatments reduce weight dramatically and lower blood glucose. The injectable compounds also avoid the side effects of nausea and vomiting that are common with current weight-loss and diabetes drugs. Now, scientists report that the new treatment not only reduces eating but also boosts calorie burn.
The researchers will present their results today at the spring meeting of the American Chemical Society ...
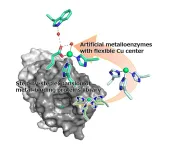
Success in simple creation of artificial metalloenzymes with high stereoselectivity
2023-03-29
Enzymes work in the cells of all living organisms, allowing specific and complex reactions to be carried out quite easily. However, few natural enzymes are effective for industrial applications, which could benefit greatly from discoveries that make targeted enzyme creation a reality.
Artificial metalloenzymes can be created simply by binding metal ions or metallic compounds to proteins, so that they exhibit enzymatic activity. Currently, metalloenzymes are being studied to discover new functions or improve their reactivity ...
Lizards at US Army installation are stress eating during flyovers
2023-03-29
Lizards may be small, with only a single hearing bonelet compared to our three, and without earflaps, but their hearing is typically good. Most lizards can hear frequencies between 100 and 5,000 Hz (although they are most sensitive between 400 and 1,500 Hz), compared to between 20 and 20,000 Hz in humans. So how do lizards react to noise pollution?
Here, scientists studied the impact of noise from low-flying military aircraft on the behavior and well-being of an uncommon lizard, the Colorado checkered whiptail (Aspidoscelis neotesselatus). This ...
How whale shark rhodopsin evolved to see, in the deep blue sea!
2023-03-29
A research group including Professors Mitsumasa Koyanagi and Akihisa Terakita of the Osaka Metropolitan University Graduate School of Science has investigated both the genetic information and structure of the photoreceptor rhodopsin, responsible for detecting dim light, of whale sharks to investigate how they can see in the dim light at extreme depths. The research group compared the whale sharks to zebra sharks, which are considered their closest relative, and brown-banded bamboo sharks, which are in the same group: the order orectolobiformes—commonly known as carpet sharks.
“This research used genetic ...