(Press-News.org) INDIANAPOLIS, March 29, 2023 — Imagine getting the benefits of gastric bypass surgery without going under the knife — a new class of compounds could do just that. In lab animals, these potential treatments reduce weight dramatically and lower blood glucose. The injectable compounds also avoid the side effects of nausea and vomiting that are common with current weight-loss and diabetes drugs. Now, scientists report that the new treatment not only reduces eating but also boosts calorie burn.
The researchers will present their results today at the spring meeting of the American Chemical Society (ACS). ACS Spring 2023 is a hybrid meeting being held virtually and in-person March 26–30, and features more than 10,000 presentations on a wide range of science topics.
“Obesity and diabetes were the pandemic before the COVID-19 pandemic,” says Robert Doyle, Ph.D., one of the two principal investigators on the project, along with Christian Roth, M.D. “They are a massive problem, and they are projected to only get worse.”
Gastric bypass and related procedures, known collectively as bariatric surgery, offer one solution, often resulting in lasting weight loss and even remission of diabetes. But these operations carry risk, aren’t suitable for everyone and aren’t accessible for many of the hundreds of millions of people worldwide who are obese or diabetic. As an alternative, Doyle says, they could tackle their metabolic problems with a drug that replicates the long-term benefits of surgery.
Those benefits are linked to a post-bypass-surgery change in the gut’s secretion levels of certain hormones — including glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) and peptide YY (PYY) — that signal fullness, curb appetite and normalize blood sugar. Current drugs that aim to replicate this effect primarily activate cellular receptors for GLP-1 in the pancreas and brain. That approach has shown great success in reducing weight and treating type 2 diabetes, drawing a lot of social media postings from celebrities in recent months. But many people can’t tolerate the drugs’ side effects, says Doyle. “Within a year, 80 to 90% of people who start on these drugs are no longer taking them.” Doyle is at Syracuse University and SUNY Upstate Medical University, and Roth is at Seattle Children’s Research Institute.
To address that drawback, various researchers have designed other treatments that interact with more than one type of gut hormone receptor. For example, Doyle’s group created a peptide that activates two receptors for PYY, as well as the receptor for GLP-1. Dubbed GEP44, this compound caused obese rats to eat up to 80% less than they would typically eat. By the end of one 16-day study, they lost an average of 12% of their weight. That was more than three times the amount lost by rats treated with liraglutide, an injected drug that activates only the GLP-1 receptor and that is approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for treating obesity. In contrast to liraglutide, tests with GEP44 in rats and shrews (a mammal that, unlike rats, is capable of vomiting) revealed no sign of nausea or vomiting, possibly because activating multiple receptors may cancel out the intracellular signaling pathway that drives those symptoms, Doyle says.
In its latest results, his team is now reporting that the weight loss caused by GEP44 can be traced not only to decreased eating, but also to higher energy expenditure, which can take the form of increased movement, heart rate or body temperature.
GEP44 has a half-life in the body of only about an hour, but Doyle’s group has just designed a peptide with a much longer half-life. That means it could be injected only once or twice a week instead of multiple times a day. The researchers are now reporting that rats treated with this next-generation compound keep their new, slimmer physique even after treatment ends, which often isn’t the case with currently approved drugs, Doyle says.
But weight loss isn’t the only benefit of the peptide treatments. They also reduce blood sugar by pulling glucose into muscle tissue, where it can be used as fuel, and by converting certain cells in the pancreas into insulin-producing cells, helping replace those that are damaged by diabetes. And there’s yet another benefit: Doyle and Heath Schmidt, Ph.D., of the University of Pennsylvania, recently reported that GEP44 reduces the craving for opioids such as fentanyl in rats. If that also works in humans, Doyle says, it could help addicts quit the illicit drugs or fend off a relapse.
The researchers have filed for patents on their compounds, and they plan to test their peptides in primates. They will also study how the treatments change gene expression and rewire the brain, and what that could mean for these compounds, as well as other types of medication.
“For a long time, we didn't think you could separate weight reduction from nausea and vomiting, because they’re linked to the exact same part of the brain,” Doyle says. But the researchers have now uncoupled those two pathways — and that has implications for chemotherapy, which causes similar side effects. “What if we could maintain the benefit of chemotherapy drugs but tell the part of the brain that causes vomiting and nausea to knock it off? Then we could dose patients at a higher level, so they would have a better prognosis, and they would also have a better quality of life while undergoing chemotherapy,” he says.
The researchers acknowledge funding from the Congressionally Directed Medical Research Programs of the U.S. Department of Defense, which is interested in the topic because many veterans have weight-related type 2 diabetes, Doyle notes.
A recorded media briefing on this topic will be posted Wednesday, March 29, by 10 a.m. Eastern time at www.acs.org/acsspring2023briefings. Reporters can request access to media briefings during the embargo period by contacting newsroom@acs.org.
For health and safety information for ACS Spring 2023, please visit the FAQ webpage.
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, eBooks and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
To automatically receive news releases from the American Chemical Society, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Note to journalists: Please report that this research was presented at a meeting of the American Chemical Society.
Follow us: Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
Title
Peptide triagonists of the GLP-1-, neuropeptide Y1- and neuropeptide Y2- receptors for glycemic control and weight loss
Abstract
Mechanisms of long-term sustained weight loss and glycemic normalization after obesity surgery have been tied to changes in gut hormone levels, including glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) and neuropeptide YY (PYY). We demonstrate that unimolecular peptide biased agonists (GEP44 and GEP12) of the GLP-1-, neuropeptide Y1- and Y2-receptors (GLP-1R; Y1-R, Y2-R) result in Y1-R antagonist controlled, GLP-1R dependent, stimulation of insulin secretion rate in rat and human islets; along with insulin-independent Y1-R mediated glucose uptake in muscle tissue ex vivo; and profound reductions in food intake and body weight relative to liraglutide in a chronic study in obese rats. Our findings support the role of Y1-R signaling in glucoregulation and highlights the therapeutic potential of targeting GLP-1R and both Y1-/Y2-Rs, simultaneously, as a route to ‘bypass’ obesity surgery, while achieving the long-term benefits of such, addressing a need for millions of patients, especially when surgery is not an option.
END
Obesity treatment could offer dramatic weight loss without surgery or nausea
2023-03-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
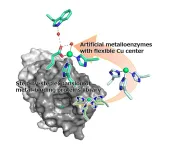
Success in simple creation of artificial metalloenzymes with high stereoselectivity
2023-03-29
Enzymes work in the cells of all living organisms, allowing specific and complex reactions to be carried out quite easily. However, few natural enzymes are effective for industrial applications, which could benefit greatly from discoveries that make targeted enzyme creation a reality.
Artificial metalloenzymes can be created simply by binding metal ions or metallic compounds to proteins, so that they exhibit enzymatic activity. Currently, metalloenzymes are being studied to discover new functions or improve their reactivity ...
Lizards at US Army installation are stress eating during flyovers
2023-03-29
Lizards may be small, with only a single hearing bonelet compared to our three, and without earflaps, but their hearing is typically good. Most lizards can hear frequencies between 100 and 5,000 Hz (although they are most sensitive between 400 and 1,500 Hz), compared to between 20 and 20,000 Hz in humans. So how do lizards react to noise pollution?
Here, scientists studied the impact of noise from low-flying military aircraft on the behavior and well-being of an uncommon lizard, the Colorado checkered whiptail (Aspidoscelis neotesselatus). This ...
How whale shark rhodopsin evolved to see, in the deep blue sea!
2023-03-29
A research group including Professors Mitsumasa Koyanagi and Akihisa Terakita of the Osaka Metropolitan University Graduate School of Science has investigated both the genetic information and structure of the photoreceptor rhodopsin, responsible for detecting dim light, of whale sharks to investigate how they can see in the dim light at extreme depths. The research group compared the whale sharks to zebra sharks, which are considered their closest relative, and brown-banded bamboo sharks, which are in the same group: the order orectolobiformes—commonly known as carpet sharks.
“This research used genetic ...
Strengthening general practice will save lives, researcher argues
2023-03-29
In his new book Primary Health Care and Population Mortality, released next week, Professor Richard Baker draws on international evidence to show how primary health care is key to the effect of health systems on population mortality and inequality in mortality. His conclusion is that it is time to think about primary health care in a new way.
He explains: “It is as if policymakers think primary health care is little more than a triage mechanism for the health system, that its purpose is to manage access to other ...
Light-bending gravity reveals one of the biggest black holes ever found
2023-03-29
A team of astronomers has discovered one of the biggest black holes ever found, taking advantage of a phenomenon called gravitational lensing.
The team, led by Durham University, UK, used gravitational lensing - where a foreground galaxy bends the light from a more distant object and magnifies it – and supercomputer simulations on the DiRAC HPC facility, which enabled the team to closely examine how light is bent by a black hole inside a galaxy hundreds of millions of light years from Earth.
They found an ultramassive black hole, an object over 30 billion times the ...
Detecting coral biodiversity in seawater samples
2023-03-29
Researchers from the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) have developed a method to measure coral biodiversity through extracting the environmental DNA (or eDNA) from a liter of surface seawater collected from above a reef. The method has been confirmed to work through observations made by scientific divers in the same areas of ocean. The research, conducted in collaboration with the Okinawa Prefecture Environmental Science Center and University of Tokyo, was published in the Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. This has paved the way for large-scale comprehensive surveys of reef-building coral to take place and removes the reliance of ...
Research autopsies reveal how incurable skin cancer resists treatment
2023-03-29
Scientists have found out how some skin cancers stop responding to treatment at the end of life.
An in-depth analysis of 14 patients who died from incurable melanoma has revealed that changes to the order, structure and number of copies of tumour DNA could cause some skin cancers to resist treatment. These changes also explain how melanoma can spread to other parts of the body.
The research, published today (29th March) in the journal Cancer Discovery, was led by scientists and clinicians at the Francis Crick Institute, UCL and The Royal Marsden. It is part of the Cancer ...
COVID vaccine induces robust T cell responses in blood cancer patients
2023-03-29
Researchers found that, despite being heavily immunocompromised, haematology patients generate strong cellular immune responses against SARS-CoV-2 after vaccination, on par with that of healthy individuals.
Published today in Cell Reports Medicine, the research team, led by University of Melbourne Professor Katherine Kedzierska, a Laboratory Head at the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity (Doherty Institute), undertook the most comprehensive analysis of adaptive SARS-CoV-2 immunity to ...
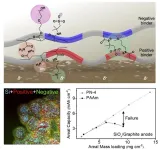
Revolutionary battery technology to boost EV range 10-fold or more
2023-03-29
The electric vehicle market has been experiencing explosive growth, with global sales surpassing $1 trillion (approx. KRW 1,283 trillion) in 2022 and domestic sales exceeding 108,000 units. Inevitably, demand is growing for high-capacity batteries that can extend EV driving range. Recently, a joint team of researchers from POSTECH and Sogang University developed a functional polymeric binder for stable, high-capacity anode material that could increase the current EV range at least 10-fold.
A research team led by POSTECH professors Soojin Park (Department of Chemistry) and Youn Soo Kim (Department ...
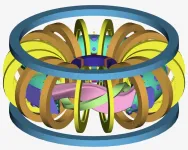
Cooking up plasmas with microwaves
2023-03-29
Kyoto, Japan -- Lead author Yurii Victorovich Kovtun, despite being forced to evacuate the Kharkiv Institute of Physics and Technology amid the current Russia-Ukraine war, has continued to work with Kyoto University to create stable plasmas using microwaves.
Getting plasma just right is one of the hurdles to harnessing the massive amounts of energy promised by nuclear fusion.
Plasmas -- soups of ions and electrons -- must be held at the right density, temperature, and duration for atomic nuclei to fuse together to achieve the desired release of energy.
One recipe involves the use of large, donut-shaped devices with powerful magnets ...