(Press-News.org) Researchers from the Okinawa Institute of Science and Technology (OIST) have developed a method to measure coral biodiversity through extracting the environmental DNA (or eDNA) from a liter of surface seawater collected from above a reef. The method has been confirmed to work through observations made by scientific divers in the same areas of ocean. The research, conducted in collaboration with the Okinawa Prefecture Environmental Science Center and University of Tokyo, was published in the Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences. This has paved the way for large-scale comprehensive surveys of reef-building coral to take place and removes the reliance of direct observations made through scientific scuba diving or snorkeling.
“Beautiful coral reefs in subtropical and tropical seas account for only 0.2% of the entire ocean,” said co-author Prof. Nori Satoh, Principal Investigator of OIST’s Marine Genomics Unit. “However, they are the most biodiverse areas of the oceans, home to about 30% of all marine life. Reef-building corals play a key role in creating coral reefs, but recent global warming and other factors have caused bleaching, and many coral reefs are in danger of disappearing.”
To conserve and protect the coral reefs, it’s important to first know which coral exists on the reef and how the make-up of a reef is changing over time. Previously, the only way to effectively survey a reef was through divers and snorkelers directly observing the coral and recording the species and the changes over time. This was time consuming, expensive, and labor intensive. But researchers are now utilizing the DNA that living creatures release into the environment, through skin, waste products, and mucus. By extracting this eDNA from the seawater and analyzing it, a clear picture of the organisms that inhabit that part of the ocean can be found, without ever having to enter the water.
Reef-building, or hard, coral are vital parts of coral reefs. It is estimated that there are approximately 1,300 species of reef-building corals in 236 genera worldwide. These corals release mucus into the surrounding seawater, which contains a portion of DNA. In 2021, researchers from OIST and the University of Tokyo succeeded in developing tools that amplify and identify the DNA of 45 genera of reef-building coral.
Now, the researchers have tested whether these tools are effective and accurate by conducting a large-scale survey of the ocean surrounding Okinawa using both the eDNA method and scientific divers. This involved direct visual observation by two divers to identify dominant coral genera and collecting two or three one-liter bottles of surface seawater at each site. Seawater was filtered as soon as possible to fix environmental DNA trapped in the filters and the filters were brought back to the OIST laboratory for analysis. Over a four-month period, from early September to late December 2021, 62 sites from around the main Okinawa Island were surveyed and two to four dominant coral genera at each reef were recorded.
“We found that the eDNA analysis matched that of the direct scientific observations with more than 91% accuracy,” said OIST Research Scientist, Dr. Koki Nishitsuji, first author of the paper. “In fact, 41 out of the 62 sites were identical. The eDNA method indicated the presence of five dominant coral genera at all 62 sites surveyed. What’s more the results of the environmental DNA method suggest the presence of corals never before recorded along the coast of Okinawa.”
The eDNA method requires complex sequencing information, and due to this, only 45 of the estimated 236 genera can currently be detected. With more information, the effectiveness of the eDNA method will increase. And, although further research is needed, the eDNA method may be able to indicate the presence of corals that are difficult to detect by direct observation.
END
Detecting coral biodiversity in seawater samples
Coral eDNA has been accurately detected in seawater samples, and this has huge implications for coral reef conservation, says researchers.
2023-03-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research autopsies reveal how incurable skin cancer resists treatment
2023-03-29
Scientists have found out how some skin cancers stop responding to treatment at the end of life.
An in-depth analysis of 14 patients who died from incurable melanoma has revealed that changes to the order, structure and number of copies of tumour DNA could cause some skin cancers to resist treatment. These changes also explain how melanoma can spread to other parts of the body.
The research, published today (29th March) in the journal Cancer Discovery, was led by scientists and clinicians at the Francis Crick Institute, UCL and The Royal Marsden. It is part of the Cancer ...
COVID vaccine induces robust T cell responses in blood cancer patients
2023-03-29
Researchers found that, despite being heavily immunocompromised, haematology patients generate strong cellular immune responses against SARS-CoV-2 after vaccination, on par with that of healthy individuals.
Published today in Cell Reports Medicine, the research team, led by University of Melbourne Professor Katherine Kedzierska, a Laboratory Head at the Peter Doherty Institute for Infection and Immunity (Doherty Institute), undertook the most comprehensive analysis of adaptive SARS-CoV-2 immunity to ...
Revolutionary battery technology to boost EV range 10-fold or more
2023-03-29
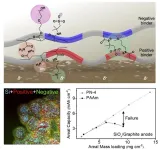
The electric vehicle market has been experiencing explosive growth, with global sales surpassing $1 trillion (approx. KRW 1,283 trillion) in 2022 and domestic sales exceeding 108,000 units. Inevitably, demand is growing for high-capacity batteries that can extend EV driving range. Recently, a joint team of researchers from POSTECH and Sogang University developed a functional polymeric binder for stable, high-capacity anode material that could increase the current EV range at least 10-fold.
A research team led by POSTECH professors Soojin Park (Department of Chemistry) and Youn Soo Kim (Department ...
Cooking up plasmas with microwaves
2023-03-29
Kyoto, Japan -- Lead author Yurii Victorovich Kovtun, despite being forced to evacuate the Kharkiv Institute of Physics and Technology amid the current Russia-Ukraine war, has continued to work with Kyoto University to create stable plasmas using microwaves.
Getting plasma just right is one of the hurdles to harnessing the massive amounts of energy promised by nuclear fusion.
Plasmas -- soups of ions and electrons -- must be held at the right density, temperature, and duration for atomic nuclei to fuse together to achieve the desired release of energy.
One recipe involves the use of large, donut-shaped devices with powerful magnets ...
12th World Conference of Science Journalists opens under open skies
2023-03-29
The opening day of the World Conference of Science Journalists (WCSJ) 2023 in Medellín, Colombia saw hundreds of journalists from 62 countries come together in the stunning setting of the city’s Jardin Botanico.
Over 500 attendees will gather over three days to discuss science journalism, to challenge ideas and to reinforce their professional networks and friendships.
The day began with a keynote on biodiversity delivered by Brigitte Baptiste, a Colombian biologist and expert in biodiversity issues. And it closed with an opening ceremony and vibrant social event for attendees.
Both took place under open skies in the ...
Revealing the nature of fractures caused by hydrogen in high-strength steel
2023-03-29
One of the many ways to reduce the energy required for transportation is to make vehicles lighter. High-strength (HS) steels are perfect candidate materials for this purpose, as their higher weight-to-strength ratio allows for the use of less metal to achieve a similar structural integrity. Many automobile companies believe HS steels will be an essential component of various types of cars in the future. However, for this to become a reality, there is a glaring problem that needs to be solved.
When HS steel is exposed to rainwater (H2O) or hydrogen, a phenomenon known as hydrogen embrittlement occurs. Hydrogen atoms diffuse into the lattice ...
Implementing green corridors throughout Barcelona could reduce annual antidepressant use and visits to mental health specialists by 13%
2023-03-29
A health impact assessment led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the ”la Caixa” Foundation, has concluded that implementing green corridors throughout the city of Barcelona would result in a “considerable reduction” in mental disorder cases in adult residents as well as in direct and indirect costs associated to said cases. The study was published in the journal Environment International.
It is estimated that mental health disorders ...
AI shows the need for healthier diets in long-term care homes
2023-03-29
A detailed analysis of consumed food showed there is a need to improve diets in long-term care (LTC) homes to make them healthier for residents.
The analysis found that eating more whole grains, plant-based proteins, and plain fruits and vegetables would help residents meet government guidelines and reduce their risk of inflammation.
Researchers at the University of Waterloo developed new artificial intelligence (AI) technology to examine data on food and fluids consumed by more than 600 residents over three days at 32 LTC homes.
Results were compared to recommendations in the 2019 Canada’s Food Guide on healthy eating and expert ...
Eye-tracking during building inspections provides insight on how experts think
2023-03-28
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — After a building failure due to natural disasters or poor structural design, safety inspectors must enter a structure to assess the damage before occupants can return. Researchers in the Penn State Department of Architectural Engineering studied how building inspectors make their safety assessments, by analyzing their gaze patterns with eye-tracking software. Eventually, the eye-tracking data could be used to code autonomous robots, like drones, to conduct building assessments in place of humans.
The researchers' results were published in Scientific Reports.
“We ...
New soil sensor may improve efficiency of crop fertilization
2023-03-28
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Measuring temperature and nitrogen levels in soil is important for agriculture systems but detecting them apart from one another is difficult to do. Huanyu “Larry” Cheng, James L. Henderson, Jr. Memorial Associate Professor of Engineering Science and Mechanics at Penn State, led researchers in the development of a multi-parameter sensor that can effectively decouple temperature and nitrogen signals so that each can be measured accurately. The results were recently published by Advanced Materials.
“For efficient fertilization, ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ASU researchers to lead AAAS panel on water insecurity in the United States
ASU professor Anne Stone to present at AAAS Conference in Phoenix on ancient origins of modern disease
Proposals for exploring viruses and skin as the next experimental quantum frontiers share US$30,000 science award
ASU researchers showcase scalable tech solutions for older adults living alone with cognitive decline at AAAS 2026
Scientists identify smooth regional trends in fruit fly survival strategies
Antipathy toward snakes? Your parents likely talked you into that at an early age
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for Feb. 2026
Online exposure to medical misinformation concentrated among older adults
Telehealth improves access to genetic services for adult survivors of childhood cancers
Outdated mortality benchmarks risk missing early signs of famine and delay recognizing mass starvation
Newly discovered bacterium converts carbon dioxide into chemicals using electricity
Flipping and reversing mini-proteins could improve disease treatment
Scientists reveal major hidden source of atmospheric nitrogen pollution in fragile lake basin
Biochar emerges as a powerful tool for soil carbon neutrality and climate mitigation
Tiny cell messengers show big promise for safer protein and gene delivery
AMS releases statement regarding the decision to rescind EPA’s 2009 Endangerment Finding
Parents’ alcohol and drug use influences their children’s consumption, research shows
Modular assembly of chiral nitrogen-bridged rings achieved by palladium-catalyzed diastereoselective and enantioselective cascade cyclization reactions
Promoting civic engagement
AMS Science Preview: Hurricane slowdown, school snow days
Deforestation in the Amazon raises the surface temperature by 3 °C during the dry season
Model more accurately maps the impact of frost on corn crops
How did humans develop sharp vision? Lab-grown retinas show likely answer
Sour grapes? Taste, experience of sour foods depends on individual consumer
At AAAS, professor Krystal Tsosie argues the future of science must be Indigenous-led
From the lab to the living room: Decoding Parkinson’s patients movements in the real world
Research advances in porous materials, as highlighted in the 2025 Nobel Prize in Chemistry
Sally C. Morton, executive vice president of ASU Knowledge Enterprise, presents a bold and practical framework for moving research from discovery to real-world impact
Biochemical parameters in patients with diabetic nephropathy versus individuals with diabetes alone, non-diabetic nephropathy, and healthy controls
Muscular strength and mortality in women ages 63 to 99
[Press-News.org] Detecting coral biodiversity in seawater samplesCoral eDNA has been accurately detected in seawater samples, and this has huge implications for coral reef conservation, says researchers.