(Press-News.org) The electric vehicle market has been experiencing explosive growth, with global sales surpassing $1 trillion (approx. KRW 1,283 trillion) in 2022 and domestic sales exceeding 108,000 units. Inevitably, demand is growing for high-capacity batteries that can extend EV driving range. Recently, a joint team of researchers from POSTECH and Sogang University developed a functional polymeric binder for stable, high-capacity anode material that could increase the current EV range at least 10-fold.
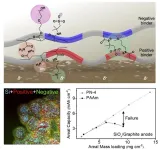
A research team led by POSTECH professors Soojin Park (Department of Chemistry) and Youn Soo Kim (Department of Materials Science and Engineering) and Professor Jaegeon Ryu (Department of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering) of Sogang University developed charged polymeric binder for a high-capacity anode material that is both stable and reliable, offering a capacity that is 10 times or higher than that of conventional graphite anodes. This breakthrough was achieved by replacing graphite with Si anode combined with layering-charged polymers while maintaining stability and reliability. The research results were published as the Front Cover Article in Advanced Functional Materials.
High-capacity anode materials such as silicon are essential for creating high-energy density lithium-ion batteries; they can offer at least 10 times the capacity of graphite or other anode materials now available. The challenge here is that the volume expansion of high-capacity anode materials during the reaction with lithium poses a threat to battery performance and stability. To mitigate this issue, researchers have been investigating polymer binders that can effectively control the volumetric expansion.
However, research to date has focused solely on chemical crosslinking and hydrogen bonding. Chemical crosslinking involves covalent bonding between binder molecules, making them solid but has a fatal flaw: once broken, the bonds cannot be restored. On the other hand, hydrogen bonding is a reversible secondary bonding between molecules based on electronegativity differences, but its strength (10-65 kJ/mol) is relatively weak.
The new polymer developed by the research team not only utilizes hydrogen bonding but also takes advantage of Coulombic forces (attraction between positive and negative charges). These forces have a strength of 250 kJ/mol, much higher than that for hydrogen bonding, yet they are reversible, making it easy to control volumetric expansion. The surface of high-capacity anode materials is mostly negatively charged, and the layering-charged polymers are arrayed alternately with positive and negative charges to effectively bind with the anode. Furthermore, the team introduced polyethylene glycol to regulate the physical properties and facilitate Li-ion diffusion, resulting in the thick high-capacity electrode and maximum energy density found in Li-ion batteries.
Professor Soojin Park explained, “The research holds the potential to significantly increase the energy density of lithium-ion batteries through the incorporation of high-capacity anode materials, thereby extending the driving range of electric vehicles. Silicon-based anode materials could potentially increase driving range at least tenfold."
This study was conducted with the support from the Ministry of Science and ICT, the Nano-Material Technology Development Program, and the National Research Laboratory for Future Technology of Korea.
END
Revolutionary battery technology to boost EV range 10-fold or more
2023-03-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cooking up plasmas with microwaves
2023-03-29
Kyoto, Japan -- Lead author Yurii Victorovich Kovtun, despite being forced to evacuate the Kharkiv Institute of Physics and Technology amid the current Russia-Ukraine war, has continued to work with Kyoto University to create stable plasmas using microwaves.
Getting plasma just right is one of the hurdles to harnessing the massive amounts of energy promised by nuclear fusion.
Plasmas -- soups of ions and electrons -- must be held at the right density, temperature, and duration for atomic nuclei to fuse together to achieve the desired release of energy.
One recipe involves the use of large, donut-shaped devices with powerful magnets ...
12th World Conference of Science Journalists opens under open skies
2023-03-29
The opening day of the World Conference of Science Journalists (WCSJ) 2023 in Medellín, Colombia saw hundreds of journalists from 62 countries come together in the stunning setting of the city’s Jardin Botanico.
Over 500 attendees will gather over three days to discuss science journalism, to challenge ideas and to reinforce their professional networks and friendships.
The day began with a keynote on biodiversity delivered by Brigitte Baptiste, a Colombian biologist and expert in biodiversity issues. And it closed with an opening ceremony and vibrant social event for attendees.
Both took place under open skies in the ...
Revealing the nature of fractures caused by hydrogen in high-strength steel
2023-03-29
One of the many ways to reduce the energy required for transportation is to make vehicles lighter. High-strength (HS) steels are perfect candidate materials for this purpose, as their higher weight-to-strength ratio allows for the use of less metal to achieve a similar structural integrity. Many automobile companies believe HS steels will be an essential component of various types of cars in the future. However, for this to become a reality, there is a glaring problem that needs to be solved.
When HS steel is exposed to rainwater (H2O) or hydrogen, a phenomenon known as hydrogen embrittlement occurs. Hydrogen atoms diffuse into the lattice ...
Implementing green corridors throughout Barcelona could reduce annual antidepressant use and visits to mental health specialists by 13%
2023-03-29
A health impact assessment led by the Barcelona Institute for Global Health (ISGlobal), a centre supported by the ”la Caixa” Foundation, has concluded that implementing green corridors throughout the city of Barcelona would result in a “considerable reduction” in mental disorder cases in adult residents as well as in direct and indirect costs associated to said cases. The study was published in the journal Environment International.
It is estimated that mental health disorders ...
AI shows the need for healthier diets in long-term care homes
2023-03-29
A detailed analysis of consumed food showed there is a need to improve diets in long-term care (LTC) homes to make them healthier for residents.
The analysis found that eating more whole grains, plant-based proteins, and plain fruits and vegetables would help residents meet government guidelines and reduce their risk of inflammation.
Researchers at the University of Waterloo developed new artificial intelligence (AI) technology to examine data on food and fluids consumed by more than 600 residents over three days at 32 LTC homes.
Results were compared to recommendations in the 2019 Canada’s Food Guide on healthy eating and expert ...
Eye-tracking during building inspections provides insight on how experts think
2023-03-28
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — After a building failure due to natural disasters or poor structural design, safety inspectors must enter a structure to assess the damage before occupants can return. Researchers in the Penn State Department of Architectural Engineering studied how building inspectors make their safety assessments, by analyzing their gaze patterns with eye-tracking software. Eventually, the eye-tracking data could be used to code autonomous robots, like drones, to conduct building assessments in place of humans.
The researchers' results were published in Scientific Reports.
“We ...
New soil sensor may improve efficiency of crop fertilization
2023-03-28
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Measuring temperature and nitrogen levels in soil is important for agriculture systems but detecting them apart from one another is difficult to do. Huanyu “Larry” Cheng, James L. Henderson, Jr. Memorial Associate Professor of Engineering Science and Mechanics at Penn State, led researchers in the development of a multi-parameter sensor that can effectively decouple temperature and nitrogen signals so that each can be measured accurately. The results were recently published by Advanced Materials.
“For efficient fertilization, ...
Story tip: A wise tool for modifying microbes
2023-03-28
A DNA editing tool adapted by Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists makes engineering microbes for everything from bioenergy production to plastics recycling easier and faster.
The Serine recombinase-Assisted Genome Engineering, or SAGE system, lets scientists quickly insert and test new DNA designs in a variety of microorganisms. Engineered microbes hold promise for making biofuels, recycling mixed plastics, aiding soil carbon storage and treating health disorders.
“SAGE works in virtually all microorganisms, revolutionizing what we’re able to do with microbes,” ...
Individualized brain fingerprints can help to uncover early signs of Alzheimer’s disease
2023-03-28
Neuroscientists from the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) report in Brain Connectivity that they have detected subtle differences in the way the brain functions in older adults with preclinical Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
Adults with preclinical AD have the earliest signs of disease, such as buildup of amyloid-beta proteins in their brains. However, they have no noticeable symptoms of cognitive decline.
The research team, led by Andreana Benitez, Ph.D., and Stephanie Fountain-Zaragoza, Ph.D., used a novel brain imaging analysis technique to construct individualized maps of brain function. They then looked to see if there were ...
Tax on sugary drinks helps health during pregnancy
2023-03-28
Taxes on sugary drinks reduce the risk of gestational diabetes and unhealthy weight gain in pregnant women, reports a new UC San Francisco study of more than 5 million women.
Published by the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, this is the first study to examine how sugar-sweetened beverage (SSB) taxes affect the health of mothers and children immediately before and after birth. Researchers compared mothers who were living in cities that had SSB taxes in effect while they were pregnant to mothers in cities with no SSB taxes. In addition to significantly lowering the risk of diabetes and unhealthy weight gain ...