(Press-News.org) A DNA editing tool adapted by Oak Ridge National Laboratory scientists makes engineering microbes for everything from bioenergy production to plastics recycling easier and faster.
The Serine recombinase-Assisted Genome Engineering, or SAGE system, lets scientists quickly insert and test new DNA designs in a variety of microorganisms. Engineered microbes hold promise for making biofuels, recycling mixed plastics, aiding soil carbon storage and treating health disorders.
“SAGE works in virtually all microorganisms, revolutionizing what we’re able to do with microbes,” said ORNL’s Adam Guss. Microbes were modified in a few days with SAGE, compared with a tailoring process that can take weeks using existing methods.
UT-Battelle manages ORNL for the Department of Energy’s Office of Science, the single largest supporter of basic research in the physical sciences in the United States. The Office of Science is working to address some of the most pressing challenges of our time. For more information, please visit energy.gov/science.
SAGE can advance fundamental biology as well as bioengineering, Guss said. “As a national lab, enabling science everywhere is part of our mission. SAGE is a tool that can speed the work of industry and academic researchers in their own organisms of interest.”
END
Story tip: A wise tool for modifying microbes
SAGE enables high-throughput engineering for bioenergy, plastics recycling, medical therapies
2023-03-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
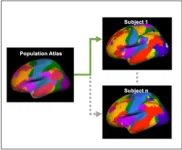
Individualized brain fingerprints can help to uncover early signs of Alzheimer’s disease
2023-03-28
Neuroscientists from the Medical University of South Carolina (MUSC) report in Brain Connectivity that they have detected subtle differences in the way the brain functions in older adults with preclinical Alzheimer’s disease (AD).
Adults with preclinical AD have the earliest signs of disease, such as buildup of amyloid-beta proteins in their brains. However, they have no noticeable symptoms of cognitive decline.
The research team, led by Andreana Benitez, Ph.D., and Stephanie Fountain-Zaragoza, Ph.D., used a novel brain imaging analysis technique to construct individualized maps of brain function. They then looked to see if there were ...
Tax on sugary drinks helps health during pregnancy
2023-03-28
Taxes on sugary drinks reduce the risk of gestational diabetes and unhealthy weight gain in pregnant women, reports a new UC San Francisco study of more than 5 million women.
Published by the American Journal of Preventive Medicine, this is the first study to examine how sugar-sweetened beverage (SSB) taxes affect the health of mothers and children immediately before and after birth. Researchers compared mothers who were living in cities that had SSB taxes in effect while they were pregnant to mothers in cities with no SSB taxes. In addition to significantly lowering the risk of diabetes and unhealthy weight gain ...
Technology to protect bioactive compounds from food during digestion
2023-03-28
Bioactive compounds present mostly in fruit and vegetables perform different bodily functions relating to health and well-being. Their effects are considered antioxidant, antidiabetic, antiaging and anticancer, among others.
Many studies are looking for ways to optimize absorption of bioactive compounds by the organism and increase their bioavailability – the proportion that enters the bloodstream after absorption. One way is to coat the compounds with another material and package them on the nanometric scale (a nanometer is a billionth of a meter). Nanoencapsulation, as this technique is known, assures slow release of the compounds so that they take longer to digest and can survive ...
New drug combination holds unusually positive results for HPV-negative patients with advanced head and neck cancer
2023-03-28
WASHINGTON (March 28, 2023)— A new combination drug treatment showed promising results in patients with pan-refractory, recurrent/metastatic head and neck cancer, according to a study published today in the Journal of Clinical Oncology.
Head and neck cancer is a deadly form of cancer that arises in the lining of the mouth and throat. Worldwide more than 700,000 people were diagnosed with head and neck cancer in 2021. The disease is caused by the human papillomavirus (HPV) or environmental carcinogens, including the regular use of tobacco or alcohol. When the cancer comes back after curative ...
NASA wallops supports second rocket lab electron launch
2023-03-28
NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility supported the successful launch of a Rocket Lab Electron rocket at 6:39 p.m. EDT, Thursday, March 16, from Virginia’s Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport on Wallops Island, Virginia.
The mission, named “Stronger Together,” carried two, 100-kilogram commercial satellites to low-Earth orbit for Capella Space.
“I’m extremely proud of the NASA team that helped ensure a safe and successful launch operation today,” said ...
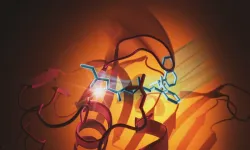
Researchers find new molecule that shows promise in slowing SARS-CoV-2
2023-03-28
Researchers have designed a molecule that slows the effects of one of SARS-CoV-2's more dangerous components – an enzyme called a protease that cuts off the immune system's communications and helps the virus replicate.
While much more needs to happen to develop a drug, scientists can begin to imagine what that drug could look like – thanks to new images of the molecule bound to the protease.
“We have been searching for an effective molecule like this one for a while,” said Suman Pokhrel, a Stanford University graduate student in chemical and systems biology and one of the paper’s lead authors. “It is ...
Rural educators find solutions to support multilingual learners
2023-03-28
A new study found a professional development program helped teachers in a rural school district in the Southeast to collaborate and identify innovative solutions to serve multilingual learners, or students learning English as a second language.
The study, published in the Journal of Research in Rural Education, suggests professional development can help prepare teachers in rural districts that have fewer resources and a growing need to support multilingual learners.
“Professional development is essential in rural communities, where you might not have resources for specialists like a literacy coach, bilingual school psychologist, or bilingual family engagement specialist,” ...
Retinal scans: A non-invasive, inexpensive method to track human aging
2023-03-28
Buck Institute professor Pankaj Kapahi thinks the eye is a window to aging. His lab, in collaboration with Google Health and Zuckerberg San Francisco General Hospital, has shown how imaging of the fundus, the blood vessel-rich tissue in the retina, can be used to track human aging, in a way that is noninvasive, less expensive and more accurate than other aging clocks that are currently available. Publishing in eLife, researchers also did a genome-wide association study (GWAS) to establish the genetic basis for such a clock, which they call eyeAge.
“This type of imaging could be really ...
New additives could turn concrete into an effective carbon sink
2023-03-28
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Despite the many advantages of concrete as a modern construction material, including its high strength, low cost, and ease of manufacture, its production currently accounts for approximately 8 percent of global carbon dioxide emissions.
Recent discoveries by a team at MIT have revealed that introducing new materials into existing concrete manufacturing processes could significantly reduce this carbon footprint, without altering concrete’s bulk mechanical properties.
The findings are published today in the ...
Fluorescent visualization and evaluation of NPC1L1-mediated cholesterol absorption at the levels of endocytic vesicles
2023-03-28
Excessive cholesterol absorption from intestinal lumen contributes to the pathogenesis of hypercholesterolemia, which is a well-established risk factor for atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. The absorption of intestinal cholesterol is primarily mediated by Niemann-Pick C1-like 1 (NPC1L1) protein, which is responsible for about 70% cholesterol absorption. NPC1L1-deficient mice are resistant to diet-induced hypercholesterolemia, which provides a compelling strategy for intervention the related diseases through inhibiting NPC1L1 expression or activity.
NPC1L1 protein is expressed in the brush border membrane of small intestine. The protein is extensively N-glycosylated ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
New molecular switch that boosts tooth regeneration discovered
Jeonbuk National University researchers track mineral growth on bioorganic coatings in real time at nanoscale
Convergence in the Canopy: Why the Gracixalus weii treefrog sounds like a songbird
Subway systems are uncomfortably hot — and worsening
Granular activated carbon-sorbed PFAS can be used to extract lithium from brine
How AI is integrated into clinical workflow lowers medical liability perception
New biotech company to accelerate treatments for heart disease
One gene makes the difference: research team achieves breakthrough in breeding winter-hardy faba beans
Predicting brain health with a smartwatch
How boron helps to produce key proteins for new cancer therapies
Writing the catalog of plasma membrane repair proteins
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
[Press-News.org] Story tip: A wise tool for modifying microbesSAGE enables high-throughput engineering for bioenergy, plastics recycling, medical therapies