(Press-News.org) A new analysis shows that, compared to similarly high-income European countries, the US continues to have substantially higher death rates at all but the oldest ages, resulting in more “excess deaths,” and this gap widened during the Covid-19 pandemic. Patrick Heuveline, of the University of California, Los Angeles (UCLA), presents these findings in the open-access journal PLOS ONE on March 29, 2023.
Calculating excess death rates can be useful for comparing mortality between different countries or sub-populations, as well as before and after the onset of a health crisis. Prior research has documented a substantial widening of the mortality gap between the US and five high-income European countries between 2000 and 2017. Mounting evidence suggests that, compared to those countries, the US has experienced even higher Covid-19 mortality during the pandemic.
Building on those earlier studies, Heuveline calculated excess death rates in the US relative to the same five countries—England & Wales, France, Germany, Italy, and Spain—for 2017 through 2021. The calculations account for different population sizes between the countries.
Heuveline found that the number of excess deaths between the US and the five European countries did indeed increase between 2017 and 2021, and that Covid-19 mortality contributed to this increase. Between 2019 and 2021, the annual number of excess deaths in the US nearly doubled, however, 45 percent of this rise was due to causes other than Covid-19. In 2021, 25 percent of all excess deaths in the US were attributed to Covid-19, representing 223,266 deaths out of 892,491 total excess deaths from any cause.
Further research will be needed to identify specific underlying reasons for how, exactly, the Covid-19 pandemic helped to drive the widening excess deaths gap between the US and Europe. For instance, Heuveline suggests, such research could explore differences in vaccination rates or social conditions that place a disproportionate impact on minority populations.
Heuveline adds: “The mortality gap widened during the pandemic, but not just due to the US handling of the crisis mortality from Covid-19. The chronic toll of excess deaths due to causes other than Covid-19 continued to increase as well, further demonstrating the US health policy failure to integrate the social, psychological and economic dimensions of health, from a weak social security net and lack of health care access for all to poor health behaviors.”
#####
In your coverage please use this URL to provide access to the freely available article in PLOS ONE: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0283153
Citation: Heuveline P (2023) The Covid-19 pandemic and the expansion of the mortality gap between the United States and its European peers. PLoS ONE 18(3): e0283153. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0283153
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The author benefited from facilities and resources provided by the California Center for Population Research at UCLA (CCPR), which receives core support (P2C-HD041022) from the Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
END
Excess death gap widens between US and Europe
US has an increasingly high proportion of excess deaths compared to five European countries
2023-03-29
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
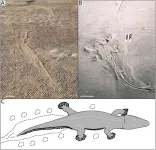
Ancient giant amphibians swam like crocodiles 250 million years ago
2023-03-29
Ancient 2m-long amphibians swam like crocodiles long before true crocodiles existed, according to a study published March 29, 2023 in the open-access journal PLOS ONE by David P. Groenewald of the University of the Witwatersrand, South Africa and colleagues.
During the Late Permian Period, just over 250 million years ago, South Africa was home to rhinesuchid temnospondyls, large predatory amphibians with bodies similar to crocodiles or big salamanders. These extinct animals are known mainly from skeletal remains, but in this study, researchers ...
In the very old, higher BMI is associated with more health complaints, and in overweight men, with mental health complaints too
2023-03-29
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0283089
Article Title: The impact of BMI on psychological health in oldest old individuals–Are there differences between women and men?
Author Countries: Germany
Funding: This study was funded by the @ktivPLUS study (German Federal Ministry of Education and Research, grant number 01GY2108) awarded to M. Löbner. Publication was funded by the Open Access Publishing Fund of Leipzig University, which is supported by the German Research ...
Drones could be used reliably to map how and why pedestrians use city streets, according to a pilot study in Santiago de Chile
2023-03-29
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0282024
Article Title: Pedestrian street behavior mapping using unmanned aerial vehicles. A case study in Santiago de Chile
Author Countries: Spain
Funding: OM has received funding from the Spanish Ministry of Science and Innovation of the Government of Spain (RyC RYC2020-029441-I). This research was also funded by the Ministry of Science and Innovation of the Government of Spain [grant number PID2019-104344RB-I00]. END ...
We are not yet approaching any maximum human lifespan, according to an examination of human mortality over time and across 19 countries
2023-03-29
###
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/plosone/article?id=10.1371/journal.pone.0281752
Article Title: Mortality postponement and compression at older ages in human cohorts
Author Countries: USA
Funding: The authors received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Stereotypes about senior employees lead to premature retirements
2023-03-29
Unproductive, inflexible, and less motivated... these are some of the most common stereotypes about senior employees. Even though the stereotypes are usually unfounded, they nevertheless influence how senior employees perceive themselves and their status in the workplace. And they thus become a key factor in many senior employees’ retirement decisions, conclude University of Copenhagen researchers in a new study published in PLOS ONE.
“In our study, we refer to the uncertainty that senior employees feel about their status as ‘the worn-out syndrome’, which ...
Earth prefers to serve life in XXS and XXL sizes: UBC research
2023-03-29
Life comes in all shapes in sizes, but some sizes are more popular than others, new research from the University of British Columbia has found.
In the first study of its kind published today in PLOS ONE, Dr. Eden Tekwa, who conducted the study as a postdoctoral fellow at UBC’s department of zoology, surveyed the body sizes of all Earth’s living organisms, and uncovered an unexpected pattern. Contrary to what current theories can explain, our planet’s biomass—the material that makes up all living organisms—is ...
Nature favors all creatures great and small over medium size
2023-03-29
Life may come in all shapes and sizes, but in nature the most extreme size ranges predominate, according to Rutgers researchers.
A survey of body sizes of Earth organisms, published Wednesday, March 29, in the science journal PLoS ONE, shows that the planet’s biomass – the material that makes up all living organisms – is concentrated in organisms at either end of the size spectrum.
“This conclusion – that life on earth comes packaged predominantly in the largest and smallest sizes – was a discovery that surprised us,” said Malin Pinsky, an associate professor ...
Sox9 protein enables molecular time travel that can lead to colorectal cancer
2023-03-29
Study Title: Aberrant cell state plasticity mediated by developmental reprogramming precedes colorectal cancer initiation
Publication: Science Advances: March 29, 2023, 2:00pm ET 10.1126/sciadv.adf0927
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute author: Pratyusha Bala, PhD, Jonathan P. Rennhack, PhD, Daulet Aitymbayev, MS, Matthew B. Yurgelun, MD, William C. Hahn, MD, PhD, Nilay S. Sethi, MD, PhD
Summary:
Normally the lining of the colon forms a series of steep hills and valleys. At the surface, where the hills peak, are functional colon cells that do the organ’s work of absorption and secretion. Deep in the valleys are stem cells that constantly ...
Ancient African empires’ impact on migration revealed by genetics
2023-03-29
Traces of ancient empires that stretched across Africa remain in the DNA of people living on the continent, reveals a new genetics study led by UCL researchers.
Published in Science Advances, the collaboration between UCL geneticists working alongside anthropologists, archaeologists, historians and linguists in Africa and beyond found evidence for when different peoples intermixed across the continent. Their findings indicate migration linked to vast empires such as the Kanem-Bornu and the kingdoms of Aksum and Makuria, ...
Method for improving seasonal flu vaccines also aids pandemic prediction
2023-03-29
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – March 29, 2023) Improving the seasonal influenza vaccine and public health specialists’ ability to predict pandemic potential in new flu strains may be possible due to new findings from scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital. The key is the stability of a viral protein that gains entry into human cells. The findings were published today in Science Advances.
“We found that the protein flu viruses use to enter cells, hemagglutinin, needs to be relatively stable and resistant to acid in an effective H3N2 flu vaccine,” said senior and co-corresponding ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Excess death gap widens between US and EuropeUS has an increasingly high proportion of excess deaths compared to five European countries