(Press-News.org) Combined long-term survival results from nonrandomized phase II trial NRG Oncology RTOG 0630 and the ancillary analysis of the combined NRG-RTOG 0630/9514 trials indicate that pathologic complete response (pCR) is associated with improved survival outcomes for patients with localized soft tissue sarcoma (STS) who receive preoperative chemoradiotherapy or radiotherapy. This data suggests that pCR can be used as a prognostic factor for clinical outcomes in future STS research. These results were recently published in the JAMA Oncology.
NRG-RTOG 0630 and 9514 both evaluated STS patients who were receiving either preoperative image-guided radiotherapy (IGRT; 0630) or neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (9514). The primary objective of the combined ancillary analysis was to correlate percentage tumor viability after surgery with survival and disease outcomes for this patient population on these two studies.
“Previously, all information that researchers had regarding the prognostic impact of pCR to therapy for STS patients was limited, unclear, and often offered conflicting results. In this analysis, we strived to connect the treatment-induced pCR of STS patients receiving these relatively uniformed treatment regimens to their recently reported long-term outcomes,” stated Dian Wang, MD, PhD, FASTRO, of the Rush University Medical Center and the Lead Author of the NRG-RTOG 0630/9514 manuscript.
The long-term results of NRG-RTOG 0630 analyzed 79 patients with STS at a median follow-up of 6 years for surviving patients. The results, published in this manuscript, indicate the estimated 5-year overall survival (OS) is 62.1% (95% confidence interval [CI] 51.2-73.0) and the estimated 5-year local failure (LF) rate is 12.7% (95% CI 6.5-21.1). The 5-year distant failure rate is 45.3% (95% CI 33.8-56.0) and the 5-year disease-free survival (DFS) and distant disease-free survival rates are 47.5% (95% CI 36.4-58.6) and 52.1% (95% CI 40.9-63.3), respectively. These results have also established that the reduced target volumes that were used during this study are appropriate for preoperative IGRT.
NRG-RTOG 0630 and 9514 combined included 123 patients that were evaluable for pCR as 14 out of 51 (27.5%) on 9514 and 14 out of 72 (19.4%) on 0630 had pCR. The 5-year OS rate is 100% for patients with pCR versus 76.5% (95% CI 62.3-90.8) and 56.4% (95% CI 43.3-69.5) for patients with <pCR in 9514 and 0630, respectively and pCR is associated with improved OS (p=0.01) and DFS [hazard ratio (HR) 4.91, 95% CI 1.51-15.93; p=0.008] relative to <pCR. Five-year LF rate was 0% in patients with pCR vs. 11.7% (95% CI 3.6-25.1) and 9.1% (95% CI 3.3-18.5) for patients with <pCR in 9514 and 0630, respectively. Histologic types other than leiomyosarcoma, liposarcoma, and myxofibrosarcoma are associated with worse OS [HR 2.24, 95% CI 1.12-4.45].
Further research should consider an analysis of a larger population of STS patients, delving into the correlation between hyalinization/fibrosis to oncologic outcomes, assessing imaging and pCR in relation to disease outcomes, and clarifying specific histologic types that may benefit from treatment intensification and personalized therapy to help strengthen the findings of this study.
This project was supported by grants U10CA180868 (NRG Oncology Operations) and U10CA180822 (NRG Oncology SDMC) from the National Cancer Institute (NCI).
Citation
Wang D, Harris J, Kraybill WG, et al. Pathologic Complete Response and Clinical Outcomes in Patients With Localized Soft Tissue Sarcoma Treated With Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy or Radiotherapy: The NRG/RTOG 9514 and 0630 Nonrandomized Clinical Trials. JAMA Oncol. Published online March 30, 2023. doi:10.1001/jamaoncol.2023.0042
About NRG Oncology
NRG Oncology conducts practice-changing, multi-institutional clinical and translational research to improve the lives of patients with cancer. Founded in 2012, NRG Oncology is a Pennsylvania-based nonprofit corporation that integrates the research of the legacy National Surgical Adjuvant Breast and Bowel Project (NSABP), Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG), and Gynecologic Oncology Group (GOG) programs. The research network seeks to carry out clinical trials with emphases on gender-specific malignancies, including gynecologic, breast, and prostate cancers, and on localized or locally advanced cancers of all types. NRG Oncology’s extensive research organization comprises multidisciplinary investigators, including medical oncologists, radiation oncologists, surgeons, physicists, pathologists, and statisticians, and encompasses more than 1,300 research sites located world-wide with predominance in the United States and Canada. NRG Oncology is supported primarily through grants from the National Cancer Institute (NCI) and is one of five research groups in the NCI’s National Clinical Trials Network.
END
NRG Oncology combined trial long-term results indicate that pathologic complete response is prognostic of outcomes for soft tissue sarcoma patients
2023-03-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Pensoft joins Advisory Panel to further develop the Journal Comparison Service by cOAlition S
2023-03-31
Back in December, we announced that Pensoft joined 27 other publishers in sharing prices and services via the Journal Comparison Service developed by cOAlition S, in order to boost transparency in scholarly publishing.
Now, we are up to another challenge: we have joined the Advisory Panel appointed by cOAlition S to help further the improvement and development of this important service. The Advisory Panel consists of twelve members (six publishers and six end-users) representing different stakeholders in the scholarly communication ecosystem.
Journal Comparison Service (JSC) is an initiative by cOAlition S aimed to improve ...
Scallop eyes as inspiration for new microscope objectives
2023-03-31
Some species of mussels can see. Scallops, for example, have up to 200 eyes that help them detect predators such as an approaching starfish. However, the eyes of scallops differ significantly from the human eye. While in our eyes the combination of cornea and lens creates an image on the retina, in scallop eyes light is focused by a hemispherical mirror.
Optical imaging with lenses or mirrors
Creating images with mirrors instead of lenses is especially common in astronomical telescopes, in order to capture as much light as possible from planets, stars and galaxies. In the Schmidt telescope developed in the 1930s by Bernhard Schmidt (1879-1935) and still in use in many observatories today, ...
Path to net-zero carbon capture and storage may lead to ocean
2023-03-31
Lehigh Engineering researcher Arup SenGupta has developed a novel way to capture carbon dioxide from the air and store it in the “infinite sink” of the ocean.
The approach uses an innovative copper-containing polymeric filter and essentially converts CO2 into sodium bicarbonate (aka baking soda) that can be released harmlessly into the ocean. This new hybrid material, or filter, is called DeCarbonHIX (i.e., decarbonization through hybrid ion exchange material), and is described in a paper recently published in the journal Science Advances.
The research, which demonstrated a 300 percent increase in the amount of carbon captured ...
Association between daily alcohol intake and risk of all-cause mortality
2023-03-31
About The Study: In this updated systematic review and meta-analysis of 107 studies involving more than 4.8 million participants, daily low or moderate alcohol intake was not significantly associated with all-cause mortality risk, while increased risk was evident at higher consumption levels, starting at lower levels for women than men.
Authors: Jinhui Zhao, Ph.D., of the University of Victoria in Victoria, British Columbia, Canada, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.6185)
Editor’s ...
Racial, ethnic differences in insurance after job loss during COVID-19
2023-03-31
About The Study: While the decline in employer-sponsored insurance in 2020 was offset by an increase in Medicaid coverage among newly unemployed white working-age adults, there was no such rise among newly unemployed Black and Hispanic workers.
Authors: Peter J. Huckfeldt, Ph.D., of the University of Minnesota School of Public Health in Minneapolis, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2023.0168)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including ...
Pictures inside a cell: USC researchers develop new tool to provide greater insight into biological processes
2023-03-31
A groundbreaking technique developed by researchers affiliated with the USC Michelson Center for Convergent Bioscience presents a new way of gathering and organizing highly detailed information about organic tissues in record time.
The methods could someday be used to rapidly process tissue biopsies in cancer care or detecting bacteria in food processing plants.
Tissues emit signals, or intrinsic fields, that while detectable are very weak and hard to differentiate. The technique, detailed in a pair of papers published in Nature Methods ...
Vaginal microbiome does not influence babies’ gut microbiome
2023-03-31
New University of British Columbia research is challenging a longstanding assumption that a baby’s gut microbiome is primarily shaped by their mother’s vaginal microbiome, while shedding new light on the factors that do influence its development.
When babies are born, their gut is a nearly sterile environment. But that quickly changes as the infant’s digestive tract becomes home to trillions of microbial cells throughout their early development. This gut microbiome is an important part of overall health and alterations early in life have been associated with negative health outcomes later on, including asthma and obesity.
It has ...
Green technologies for a greener environment
2023-03-31
About Book:
Green tech refers to materials and technology that are used to reduce adverse human impact on Earth. It encompasses a wide area of scientific research, including energy, atmospheric science, agriculture, material science, and hydrology.
Using sustainable resources to produce energy for a better greener tomorrow has been at the epicentre of man’s thought since 1987, in the United Nations Brundtland Report was published, which defined sustainable development as “needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs”.
It has real-world examples some ...
Novel supercapacitor for energy storage applications
2023-03-31
Researchers at the Department of Instrumentation and Applied Physics (IAP), Indian Institute of Science (IISc), have designed a novel ultramicro supercapacitor, a tiny device capable of storing an enormous amount of electric charge. It is also much smaller and more compact than existing supercapacitors and can potentially be used in many devices ranging from streetlights to consumer electronics, electric cars and medical devices.
Most of these devices are currently powered by batteries. However, over time, these batteries lose their ability to store charge and therefore have a limited shelf-life. Capacitors, on the other hand, can store electric charge for much ...
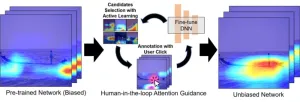
Click away the bias: New system to make AI training easier and more accurate
2023-03-31
Ishikawa, Japan -- In the past few years, “AI” has become a major buzzword in technology. The prospect of a computer being able to do tasks which only a human could perform is a captivating thought indeed! AIs can be created using multiple different methods, but one of the most popular ones right now involves the use of deep neural networks (DNNs). These structures try to mimic the neural connections and function of the brain and are generally trained on a dataset before they are deployed in the real world. By training them on a dataset beforehand, ...