(Press-News.org) Study Title: Belzutifan plus cabozantinib for patients with advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma previously treated with immunotherapy: an open-label, single-arm, phase 2 study
Publication: The Lancet Oncology, March 31, 2023, 6:30pm ET, https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanonc/article/PIIS1470-2045(23)00097-9/fulltext
Dana-Farber Cancer Institute author: Toni K. Choueiri, MD
Summary:
Immunotherapies, such as anti-PD-1 and anti-PD-L1, have become standard first line therapies for patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma (kidney cancer). Most patients, however, eventually experience disease progression, with no consensus on what therapy to use next. In this open-label phase 2 study, led by Dana-Farber Cancer Institute’s Toni Choueiri, MD, researchers investigated for the first time the combination of cabozantinib, a VEGF TKI, plus belzutifan, a HIF-2α inhibitor. Belzutifan has shown antitumor activity and favorable safety in heavily pretreated advanced kidney cancer. The researchers previously reported results for cohort 1 of the trial, called LITESPARK-003. This study reports on cohort 2, which includes patients diagnosed with advanced clear cell renal cell carcinoma who have previously received immunotherapy and up to two systemic treatment regimens. After a median follow-up of 24 months, interim results of the combination show promising antitumor activity in this pre-treated patient group with a disease control rate of 92% and a manageable safety profile.
Impact:
While immunotherapy has changed the treatment landscape for advanced renal cell carcinoma, questions about what therapy to provide when patients experience disease progression on immunotherapy remain. In this study, interim results of the combination of cabozantinib, a VEGF TKI, plus belzutifan, a HIF-2α inhibitor, show promising anti-tumor activity in this pre-treated patient group. The results suggest that the combination might fill and unmet need and provides a rationale for further study of combining a VEGF TKI and a HIF-2 inhibitor.
Funding: Merck Sharp & Dohme (a subsidiary of Merck & Co) and the National Cancer Institute.
Contact: Victoria Warren, Victoria_Warren@dfci.harvard.edu, 617-939-5531
END
Combination therapy a promising option for advanced kidney cancer patients already treated with immunotherapy
2023-04-01
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Final Human Brain Project Summit closes with a vision for the future of digital brain research
2023-04-01
The ten-year European Flagship Human Brain Project (HBP) links brain research with computing and technology in a large-scale, interdisciplinary approach. During the HBP Summit, researchers presented the abundant scientific achievements of the project and the legacy that it will leave for the research community. With the project approaching its conclusion in September 2023, a focal point of the final HBP Summit in Marseille was the discussion of the future of digital brain research.
One of the lasting contributions of the project is the research infrastructure EBRAINS, which provides open access to advanced technologies, tools, data and services for brain research and will ...
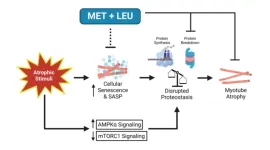
Metformin & leucine prevent cellular senescence & proteostasis disruption
2023-03-31
“Cellular senescence and disrupted proteostasis induced by myotube atrophy are prevented with low-dose metformin and leucine cocktail.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 31, 2023 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 6, entitled, “Cellular senescence and disrupted proteostasis induced by myotube atrophy are prevented with low-dose metformin and leucine cocktail.”
Aging coincides with the accumulation of senescent cells within skeletal muscle that produce inflammatory products, known as the senescence-associated secretory ...
Plastic transistor amplifies biochemical sensing signal
2023-03-31
Molecules in our body send faint biochemical signals when health issues arise
New technology boosts these signals by 1,000 times
New approach paves way for sensing signals in real-time in the body without sending blood or saliva samples to a lab
EVANSTON, Ill. — The molecules in our bodies are in constant communication. Some of these molecules provide a biochemical fingerprint that could indicate how a wound is healing, whether or not a cancer treatment is working or that a virus has invaded the body. If we could sense these signals in ...
Childhood asthma declines during COVID-19 pandemic
2023-03-31
Half as many children in the United States were diagnosed with asthma in the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic compared to previous years, and Rutgers researchers think fewer colds may be part of the reason.
In a new Rutgers study, published in Respiratory Research, researchers examined the rates of new asthma diagnoses in a large commercial insurance claims database during the first year of the pandemic compared with rates of new diagnoses during the previous three years.
Using the Health Core Integrated Research ...
Study shows ketamine could be beneficial for treating brain injury in children
2023-03-31
A common anesthesia drug could be beneficial in reducing pressure inside the skull of children with traumatic brain injuries (TBI), according to a study published in Critical Care Medicine.
Ketamine, a drug that has been used for anesthesia since the 1970s, has traditionally been avoided for patients with TBI due to early studies suggesting that it could raise the pressure inside of the skull, known as intracranial pressure (ICP).
More recent studies have suggested otherwise, said lead author Michael Wolf, MD, assistant professor of Pediatrics and Neurological ...
Yak milk consumption among Mongol Empire elites
2023-03-31
Photos
For the first time, researchers have pinpointed a date when elite Mongol Empire people were drinking yak milk, according to a study co-led by a University of Michigan researcher.
By analyzing proteins found within ancient dental calculus, an international team of researchers provides direct evidence for consumption of milk from multiple ruminants, including yak. In addition, they discovered milk and blood proteins associated with both horses and ruminants. The team's results are published in Communication Biology.
The study presents novel protein findings from an elite Mongol Era cemetery ...
Hope for salamanders? Illinois study recalibrates climate change effects
2023-03-31
URBANA, Ill. – For tiny salamanders squirming skin-to-soil, big-picture weather patterns may seem as far away as outer space. But for decades, scientists have mostly relied on free-air temperature data at large spatial scales to predict future salamander distributions under climate change. The outlook was dire for the mini ecosystem engineers, suggesting near elimination of habitat in crucial areas.
Now, University of Illinois researchers are tuning into the microclimates that really matter to the imperiled amphibians and forecasting a somewhat more hopeful future.
“The ...
Engineered E. coli delivers therapeutic nanobodies to the gut
2023-03-31
BOSTON-- Humans are colonized with thousands of bacterial strains. Researchers are now focused on genetically modifying such bacteria to enhance their intrinsic therapeutic properties.
One goal is to develop smart microbes that release therapeutic payloads at sites of disease, thus maintaining therapeutic efficacy while limiting many of the side effects that can be associated with the systemic administration of conventional drugs.
Investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of Mass General Brigham (MGB), have engineered a strain of the probiotic Escherichia ...
New type of friction discovered in ligand-protein systems
2023-03-31
An interdisciplinary research team of the Institutes of Physical Chemistry and Physics of the University of Freiburg and the Max Planck Institute of Biophysics in Frankfurt-am-Main has discovered a new, direction-dependent friction in proteins called anisotropic friction. “Until now, nobody had observed that friction in biomolecules was dependent on direction,” says physicist Dr. Steffen Wolf of the University of Freiburg. The results have been published as cover story in the scientific journal “Nano Letters.”
Experiments on model complex of protein-ligands
Proteins constitute the microscopic machinery of cells. They perform work during their functional cycles. Accordingly, ...
New UNC Chapel Hill study quantifies $562M in financial risk from Hurricane Florence using novel modeling approach that evaluates risk of mortgage default and property abandonment
2023-03-31
When Hurricane Florence made landfall on North Carolina’s coast in 2018, it brought record rainfall causing catastrophic flooding and damages to communities across the eastern portion of the state.
Estimating the financial impacts of household flooding is complex because direct damages often snowball into other financial risks, like a decrease in property value or loss of equity. Generally, post-disaster damage assessments focus on insured and uninsured losses, but these numbers do not account for the secondary impacts to households, lenders, local governments and other stakeholders who may also share in the financial consequences if a property owner defaults ...