(Press-News.org)
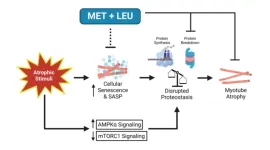
“Cellular senescence and disrupted proteostasis induced by myotube atrophy are prevented with low-dose metformin and leucine cocktail.”
BUFFALO, NY- March 31, 2023 – A new research paper was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 6, entitled, “Cellular senescence and disrupted proteostasis induced by myotube atrophy are prevented with low-dose metformin and leucine cocktail.”
Aging coincides with the accumulation of senescent cells within skeletal muscle that produce inflammatory products, known as the senescence-associated secretory phenotype, but the relationship of senescent cells to muscle atrophy is unclear. Previously, researchers found that a metformin + leucine (MET+LEU) treatment had synergistic effects in aged mice to improve skeletal muscle structure and function during disuse atrophy.
In this new study, researchers Jonathan J. Petrocelli, Naomi M.M.P. de Hart, Marisa J. Lang, Elena M. Yee, Patrick J. Ferrara, Dennis K. Fix, Amandine Chaix, Katsuhiko Funai, and Micah J. Drummond from the University of Utah aimed to determine the mechanisms by which MET+LEU exhibits muscle atrophy protection in vitro and if this occurs through cellular senescence.
“The purpose of this study was to identify the skeletal muscle cell-intrinsic effects of MET+LEU during an atrophy stimulus. Secondarily, we sought to determine the possible mechanisms underlying MET+LEU action on skeletal muscle cells with an emphasis on cellular senescence.”
C2C12 myoblasts differentiated into myotubes were used to determine MET+LEU mechanisms during atrophy. Additionally, aged mouse single myofibers and older human donor primary myoblasts were individually isolated to determine the translational potential of MET+LEU on muscle cells. MET+LEU (25 + 125 μM) treatment increased myotube differentiation and prevented myotube atrophy. Low concentration (0.1 + 0.5 μM) MET+LEU had unique effects to prevent muscle atrophy and increase transcripts related to protein synthesis and decrease transcripts related to protein breakdown. Myotube atrophy resulted in dysregulated proteostasis that was reversed with MET+LEU and individually with proteasome inhibition (MG-132).
Inflammatory and cellular senescence transcriptional pathways and respective transcripts were increased following myotube atrophy yet reversed with MET+LEU treatment. Dasatinib + quercetin (D+Q) senolytic prevented myotube atrophy similar to MET+LEU. Finally, MET+LEU prevented loss in myotube size in alternate in vitro models of muscle atrophy as well as in aged myofibers while, in human primary myotubes, MET+LEU prevented reductions in myonuclei fusion. These data support that MET+LEU has skeletal muscle cell-autonomous properties to prevent atrophy by reversing senescence and improving proteostasis.
“In conclusion, this study provides evidence of a possible link between cellular senescence and disrupted proteostasis that is targeted by MET+LEU in muscle cells to reverse the muscle atrophy phenotype.”
DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.204600
Corresponding Author: Micah J. Drummond - micah.drummond@hsc.utah.edu
Keywords: skeletal muscle atrophy, inflammation, senolytic, AMPK, protein breakdown
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.204600
About Aging-US:
Launched in 2009, Aging (Aging-US) publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
SoundCloud
Facebook
Twitter
Instagram
YouTube
LabTube
LinkedIn
Reddit
Pinterest
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
END
Molecules in our body send faint biochemical signals when health issues arise
New technology boosts these signals by 1,000 times
New approach paves way for sensing signals in real-time in the body without sending blood or saliva samples to a lab
EVANSTON, Ill. — The molecules in our bodies are in constant communication. Some of these molecules provide a biochemical fingerprint that could indicate how a wound is healing, whether or not a cancer treatment is working or that a virus has invaded the body. If we could sense these signals in ...
Half as many children in the United States were diagnosed with asthma in the first year of the COVID-19 pandemic compared to previous years, and Rutgers researchers think fewer colds may be part of the reason.
In a new Rutgers study, published in Respiratory Research, researchers examined the rates of new asthma diagnoses in a large commercial insurance claims database during the first year of the pandemic compared with rates of new diagnoses during the previous three years.
Using the Health Core Integrated Research ...
A common anesthesia drug could be beneficial in reducing pressure inside the skull of children with traumatic brain injuries (TBI), according to a study published in Critical Care Medicine.
Ketamine, a drug that has been used for anesthesia since the 1970s, has traditionally been avoided for patients with TBI due to early studies suggesting that it could raise the pressure inside of the skull, known as intracranial pressure (ICP).
More recent studies have suggested otherwise, said lead author Michael Wolf, MD, assistant professor of Pediatrics and Neurological ...
Photos
For the first time, researchers have pinpointed a date when elite Mongol Empire people were drinking yak milk, according to a study co-led by a University of Michigan researcher.
By analyzing proteins found within ancient dental calculus, an international team of researchers provides direct evidence for consumption of milk from multiple ruminants, including yak. In addition, they discovered milk and blood proteins associated with both horses and ruminants. The team's results are published in Communication Biology.
The study presents novel protein findings from an elite Mongol Era cemetery ...
URBANA, Ill. – For tiny salamanders squirming skin-to-soil, big-picture weather patterns may seem as far away as outer space. But for decades, scientists have mostly relied on free-air temperature data at large spatial scales to predict future salamander distributions under climate change. The outlook was dire for the mini ecosystem engineers, suggesting near elimination of habitat in crucial areas.
Now, University of Illinois researchers are tuning into the microclimates that really matter to the imperiled amphibians and forecasting a somewhat more hopeful future.
“The ...
BOSTON-- Humans are colonized with thousands of bacterial strains. Researchers are now focused on genetically modifying such bacteria to enhance their intrinsic therapeutic properties.
One goal is to develop smart microbes that release therapeutic payloads at sites of disease, thus maintaining therapeutic efficacy while limiting many of the side effects that can be associated with the systemic administration of conventional drugs.
Investigators at Massachusetts General Hospital (MGH), a founding member of Mass General Brigham (MGB), have engineered a strain of the probiotic Escherichia ...
An interdisciplinary research team of the Institutes of Physical Chemistry and Physics of the University of Freiburg and the Max Planck Institute of Biophysics in Frankfurt-am-Main has discovered a new, direction-dependent friction in proteins called anisotropic friction. “Until now, nobody had observed that friction in biomolecules was dependent on direction,” says physicist Dr. Steffen Wolf of the University of Freiburg. The results have been published as cover story in the scientific journal “Nano Letters.”
Experiments on model complex of protein-ligands
Proteins constitute the microscopic machinery of cells. They perform work during their functional cycles. Accordingly, ...
When Hurricane Florence made landfall on North Carolina’s coast in 2018, it brought record rainfall causing catastrophic flooding and damages to communities across the eastern portion of the state.
Estimating the financial impacts of household flooding is complex because direct damages often snowball into other financial risks, like a decrease in property value or loss of equity. Generally, post-disaster damage assessments focus on insured and uninsured losses, but these numbers do not account for the secondary impacts to households, lenders, local governments and other stakeholders who may also share in the financial consequences if a property owner defaults ...
The Forex market, also known as the foreign exchange market or simply Forex (short for "foreign exchange"), is a decentralized global market where various currencies are traded. It is the largest financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume exceeding $6 trillion. The primary purpose of the Forex market is to facilitate international trade and investment by allowing businesses, governments, and individuals to convert one currency into another.
Researchers are deploying the latest mapping techniques to identify the most important suburban habitat for North America’s largest woodpecker.
University of Cincinnati doctoral student Ruijia Hu said wildlife habitat in congested places like southwest Ohio is becoming increasingly fragmented as forests give way to new construction. Eventually, this could spell trouble to an animal with specific habitat needs like Ohio’s pileated woodpecker.
Pileated woodpeckers are crow-sized birds with colorful red crests and striking white facial stripes. They are found in forests from British Columbia to Florida. They have the ...