(Press-News.org) The Forex market operates 24 hours a day, five days a week, and its participants include central banks, commercial banks, financial institutions, hedge funds, multinational corporations, retail traders, and individual investors. Transactions in this market are carried out through an over-the-counter (OTC) network, which means that trading takes place directly between parties, without a centralized exchange.
In the Forex market, currencies are traded in pairs, with each pair representing the value of one currency relative to the other. The first currency in a pair is referred to as the base currency, while the second currency is called the quote or counter currency. The exchange rate between two currencies represents the amount of the quote currency needed to buy one unit of the base currency.
Some of the most traded currency pairs in the Forex market include the EUR/USD (Euro/US Dollar), USD/JPY (US Dollar/Japanese Yen), GBP/USD (British Pound/US Dollar), and USD/CHF (US Dollar/Swiss Franc). These major currency pairs are known as the "majors" and account for a significant portion of the trading volume in the market.
Forex trading can be speculative, as traders attempt to profit from fluctuations in exchange rates. Factors that can influence these fluctuations include economic indicators, political events, central bank policies, and global market sentiment. Participants use various trading strategies, such as technical analysis, fundamental analysis, and algorithmic trading, to identify potential opportunities and manage risk.
Leverage is a common feature in Forex trading, which allows traders to control large positions with a small amount of capital. While leverage can magnify potential profits, it can also lead to significant losses if the market moves against a trader's position.
In summary, the Forex market is a vast, liquid, and decentralized global marketplace where currencies are traded 24 hours a day, five days a week. Its primary purpose is to facilitate international trade and investment, but it also attracts a diverse range of participants seeking to profit from currency fluctuations. The Forex market offers opportunities for traders with various trading strategies and risk appetites, but it also entails significant risks due to its highly leveraged nature.
The Forex market's size and global reach make it an attractive destination for traders and investors. However, to better understand the market, it's essential to delve deeper into its characteristics, participants, and key concepts:
Market structure: Unlike stock markets, which have centralized exchanges such as the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) or London Stock Exchange (LSE), the Forex market operates through an interbank network. This decentralized structure comprises a network of computers connecting major banks, financial institutions, and brokers worldwide. Trades are executed electronically via trading platforms, which has led to increased efficiency, transparency, and reduced transaction costs.
Participants: The Forex market consists of a diverse range of participants. Some of the key players include:
a. Central banks: They regulate their respective countries' money supply and interest rates, directly impacting currency values. Their interventions in the Forex market, such as adjusting interest rates or engaging in quantitative easing, can cause significant market fluctuations.
b. Commercial banks and financial institutions: They facilitate currency transactions for their clients and engage in proprietary trading to profit from currency fluctuations.
c. Corporations: Multinational companies need to exchange currencies for international trade, investment, and repatriation of profits. They may also engage in currency hedging strategies to minimize the impact of exchange rate fluctuations on their financial performance.
d. Hedge funds and investment managers: These institutions trade currencies as part of their investment portfolios, often employing sophisticated trading strategies and algorithms.
e. Retail traders: Individual investors trade currencies through online platforms offered by brokers, typically using margin accounts and leverage to enhance their trading capacity.
Forex sessions: The Forex market operates 24 hours a day, from Sunday evening to Friday evening, covering different trading sessions across the globe. These sessions are typically divided into four main regions: Sydney, Tokyo, London, and New York. As each session overlaps with another, the Forex market experiences periods of heightened liquidity and volatility, offering trading opportunities for participants.
Spot market, futures, and options: The majority of currency transactions occur in the spot market, where trades are settled immediately at the prevailing exchange rate. However, the Forex market also includes futures and options contracts, which are standardized agreements to buy or sell a specific currency at a predetermined price on a future date. These derivatives can be used for hedging or speculative purposes.
Risks: Forex trading carries several risks, such as market risk, leverage risk, interest rate risk, and counterparty risk. Market risk arises from fluctuations in exchange rates, while leverage risk stems from using borrowed funds to amplify potential profits or losses. Interest rate risk arises from changes in interest rates affecting currency values, and counterparty risk refers to the possibility of one party defaulting on its obligations in a transaction.
In conclusion, the Forex market's complexity, diversity, and continuous operation make it a dynamic and challenging environment for traders and investors. Understanding the market's structure, participants, and key concepts is crucial for those looking to navigate the world of currency trading successfully.
What is foreign exchange market or simply Forex?
2023-03-31
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Can cities make room for woodpeckers?
2023-03-31
Researchers are deploying the latest mapping techniques to identify the most important suburban habitat for North America’s largest woodpecker.
University of Cincinnati doctoral student Ruijia Hu said wildlife habitat in congested places like southwest Ohio is becoming increasingly fragmented as forests give way to new construction. Eventually, this could spell trouble to an animal with specific habitat needs like Ohio’s pileated woodpecker.
Pileated woodpeckers are crow-sized birds with colorful red crests and striking white facial stripes. They are found in forests from British Columbia to Florida. They have the ...
Study: ChatGPT has potential to help cirrhosis, liver cancer patients
2023-03-31
A new study by Cedars-Sinai investigators describes how ChatGPT, an artificial intelligence (AI) chatbot, may help improve health outcomes for patients with cirrhosis and liver cancer by providing easy-to-understand information about basic knowledge, lifestyle and treatments for these conditions.
The findings, published in the peer-reviewed journal Clinical and Molecular Hepatology, highlights the AI system’s potential to play a role in clinical practice.
“Patients with cirrhosis and/or liver cancer and their caregivers often have unmet needs and insufficient knowledge about managing and preventing complications of their disease,” ...
A healthy microbiome may prevent deadly infections in critically ill people
2023-03-31
Twenty to 50 per cent of all critically ill patients contract potentially deadly infections during their stay in the intensive care unit or in hospital after being in the ICU – markedly increasing the risk of death.
“Despite the use of antibiotics, hospital-acquired infections are a major clinical problem that persists to be a huge issue for which we don’t have good solutions,” says Dr. Braedon McDonald, MD, PhD, an intensive care physician at the Foothills Medical Centre (FMC) and assistant professor at the ...
Academic institutions receive lower financial returns from biotechnology licenses than commercial firms
2023-03-31
BENTLEY UNIVERSITY
The financial terms of biotechnology licenses from academic institutions are significantly less favorable than those of comparable licenses between commercial firms according to a new study from Bentley University’s Center for Integration of Science and Industry. The study, published in the journal PLOS ONE, shows that the royalties and payments to academic institutions are significantly lower than those to commercial firms for similar licenses and products at the same stages of development.
The article, titled “Comparing the economic terms of biotechnology licenses from academic institutions with those ...
Harnessing nature to promote planetary sustainability
2023-03-31
As Earth’s population grows, the demands of modern lifestyles place mounting strain on the global environment. Proposed solutions to preserve and promote planetary sustainability can sometimes prove more harmful than helpful. However, technologies that harness natural processes could be more successful.
Such technologies are the focus of the latest issue of the open access journal PLOS Biology, which features a special collection publishing March 31st of papers highlighting biology-based solutions that could be applied to reduce carbon dioxide emissions, eliminate non-degradable plastics, produce food or energy ...
Study examines how social rank affects response to stress
2023-03-31
Can an individual’s social status have an impact on their level of stress? Researchers at Tulane University put that question to the test and believe that social rank, particularly in females, does indeed affect the stress response.
In a study published in Current Biology, Tulane psychology professor Jonathan Fadok, PhD, and postdoctoral researcher Lydia Smith-Osborne looked at two forms of psychosocial stress — social isolation and social instability — and how they manifest themselves based on social rank.
They conducted their research on adult female mice, putting them in pairs and allowing them to form a stable ...
The stars in the brain may be information regulators
2023-03-31
Long thought of as “brain glue,” the star-shaped cells called astrocytes—members of a family of cells found in the central nervous system called glial that help regulate blood flow, synaptic activity, keep neurons healthy, and play an important role in breathing. Despite this growing appreciation for astrocytes, much remains unknown about the role these cells play in helping neurons and the brain process information.
“We believe astrocytes can add a new dimension to our understanding of how external and internal information is merged in the ...
The Institut Pasteur and the University of São Paulo sign articles of association to establish the Institut Pasteur in São Paulo
2023-03-31
On Friday March 31st, 2023 at a ceremony in Paris, the Institut Pasteur President, Professor Stewart Cole, and the University of São Paulo (USP) Rector, Carlos Gilberto Carlotti Junior, signed articles of association for the Institut Pasteur in São Paulo, a private non-profit organization under Brazilian law. The mission of the institute, an associate member of the Pasteur Network, is to conduct research in the field of biology that contributes to the development of human health, and to promote outreach, education, innovation and knowledge transfer activities and public health measures.
The Institut Pasteur ...
Mathematical model provides bolt of understanding for lightning-produced X-rays
2023-03-31
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — In the early 2000s, scientists observed lightning discharge producing X-rays comprising high energy photons — the same type used for medical imaging. Researchers could recreate this phenomenon in the lab, but they could not fully explain how and why lightning produced X-rays. Now, two decades later, a Penn State-led team has discovered a new physical mechanism explaining naturally occurring X-rays associated with lightning activity in the Earth’s atmosphere.
They published their ...
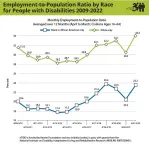
nTIDE March 2023 Deeper Dive: Intersection of race and disability perpetuate inequalities in employment impacting Black/African American people with disabilities
2023-03-31
East Hanover, NJ – March 31, 2023 – Since the pandemic, gains in the labor market have been slower to materialize for black/African American people with disabilities compared to their white counterparts, according to experts speaking last Friday during the nTIDE Deeper Dive Lunch & Learn Webinar. They discussed potential factors underlying why the disability employment gap is wider among members of the black/African American population when compared to the white population and how to integrate measures to effect change.
Using data from the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) for persons ages 16-64, the monthly employment-to-population ratio averaged ...