(Press-News.org) Cosmologists have found new evidence for the standard model of cosmology – this time, using data on the structure of galaxy clusters.
In a recent study, a team led by physicists at the Department of Energy's SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory and Stanford University made detailed measurements of the X-ray emission from galaxy clusters, which revealed the distribution of matter within them. In turn, the data helped the scientists test the prevailing theory of the structure and evolution of the universe, known as Lambda-CDM.
Getting there wasn’t an easy task, however.
Here's the trouble: Inferring the mass distributions of galaxy clusters from their X-ray emission is most reliable when the energy in the gas within clusters is balanced by the pull of gravity, which holds the whole system together. Measurements of the mass distributions in real clusters therefore focus on those that have settled down to a "relaxed" state. When comparing to theoretical predictions, it is therefore essential to take this selection of relaxed clusters into account.
Keeping this in mind, Stanford physics graduate student Elise Darragh-Ford and her colleagues examined computer-simulated clusters produced by the The Three Hundred Project. First, they computed what the X-ray emission for each simulated cluster should look like. Then, they applied the same observational criteria used to identify relaxed galaxy clusters from real data to the simulated images to winnow the set down.
The researchers next measured the relationships between three properties – the cluster mass, how centrally concentrated this mass is, and the redshift of the clusters, which reflects how old the universe was when the light we observe was emitted – for both the simulated Three Hundred Project clusters and 44 real clusters observed with NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory.
The team found consistent results from both data sets: overall, clusters have become more centrally concentrated over time, while at any given time, less massive clusters are more centrally concentrated than more massive ones. "The measured relationships agree extremely well between observation and theory, providing strong support for the Lambda-CDM paradigm," said Darragh-Ford.
In the future, the scientists hope to be able to expand the size of both the observed and simulated galaxy cluster data sets in their analysis. SLAC-supported projects coming online in the next few years, including the Rubin Observatory's Legacy Survey of Space and Time and the fourth-generation cosmic microwave background experiment (CMB-S4), will help identify a much larger number of galaxy clusters, while planned space missions, such as the European Space Agency's ATHENA satellite, can follow up with X-ray measurements. SLAC cosmologists are also working to expand the size and accuracy of computer simulations of the cosmos, making it possible to study galaxy clusters in greater detail and place stringent limits on alternative cosmological scenarios.
The research was supported by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration and the DOE Office of Science.
END
Galaxy clusters yield new evidence for standard model of cosmology
2023-04-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New UH project combats food insecurity through AI
2023-04-03
One in eight Texans experiences food insecurity, according to the non-profit agency Feeding America. That means 1.4 million Texas households are food insecure, with limited or inconsistent access to nutritious food for an active, healthy life. The USDA's most recent survey on the issue reported that Texas is among the top nine U.S. states with a higher prevalence of food insecurity than the national average.
To address this issue, a University of Houston-led team is developing an artificial intelligence-based platform that can support the food charity ecosystem through data-driven technologies.
"The commitment of our team is to help our fellow ...
Generosity is left-wing
2023-04-03
Is the tendency to share with other people linked to political orientation? And in which way? In a new study, researchers from the IMT School for Advanced Studies Lucca, Ca’ Foscari University of Venice, and University of Milan Bicocca show that around the world left-leaning people are more inclined to be altruistic, in general and towards the international community. On the other hand, conservative and right people tend to be more altruistic towards their country. What might sound like the confirmation of a prejudice, is in reality a tendency observed worldwide through a ...
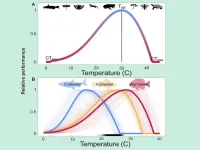
Innovative method predicts the effects of climate change on cold-blooded animals
2023-04-03
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — In the face of a warming climate that is having a profound effect on global biodiversity and will change the distribution and abundance of many animals, a Penn State-led research team has developed a statistical model that improves estimates of habitat suitability and extinction probability for cold-blooded animals as temperatures climb.
Cold-blooded animals — a diverse group including fish, reptiles, amphibians and insects — comprise most species on Earth. The body temperature of cold-blooded animals is strongly influenced by the temperature of their environment. Because their growth, reproductive success ...
Gulf offshore oil and gas production has double the climate impact as inventories report
2023-04-03
Images
By directly measuring greenhouse gas emissions from an airplane flying over the Gulf of Mexico, a University of Michigan-led team found that the nation's largest offshore fossil fuel production basin has twice the climate warming impact as official estimates.
The work could have bearing on future energy production in the gulf, as decisions about expanding oil and gas harvesting depend on calculations of the climate impact.
While a gap between reported and measured methane emissions in the basin has been noted in the past, this study is believed ...
Squash bees flourish in response to agricultural intensification
2023-04-03
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — While pollinator populations of many species have plummeted worldwide, one bee species is blowing up the map with its rapid population expansion. The key to this insect’s success? Its passion for pumpkins, zucchinis, and other squashes, and the massive increase in cultivation of these crops across North America over the last 1,000 years.
A new study led by Penn State found that the squash bee (Eucera pruinosa) has evolved in response to intensifying agriculture — namely squashes in the genus ...
Strong ultralight material could aid energy storage, carbon capture
2023-04-03
HOUSTON – (April 3, 2023) – 2D materials get their strength from their atom-thin, sheetlike structure. However, stacking multiple layers of a 2D material will sap it of the qualities that make it so useful.
Rice University materials scientist Jun Lou and collaborators at the University of Maryland showed that fine-tuning interlayer interactions in a class of 2D polymers known as covalent organic frameworks (COFs) can determine the materials’ loss or retention of desirable ...
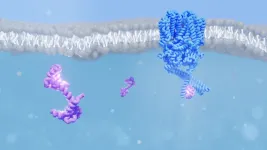
Calcium sensor helps us to see the stars
2023-04-03
Using cryo-electron microscopy and mass spectrometry, researchers from PSI have deciphered the structure of an ion channel found in the eye while it interacts with the protein calmodulin – a structure that has eluded scientists for three decades. They believe that this interaction could explain how our eyes can achieve such remarkable sensitivity to dim light. Their results are published in the journal PNAS.
As you look at the bright screen of your phone or computer, ion channels in your eyes close in response to the light. This is the final step of a biochemical ...
New research could spur broader use of 2D materials
2023-04-03
They’re considered some of the strongest materials on the planet, but tapping that strength has proved to be a challenge.
2D materials, thinner than the most delicate onionskin paper, have attracted intense interest because of their incredible mechanical properties. Those properties, however, dissipate when the materials are stacked in multiple layers, thus limiting their usefulness.
“Think of a graphite pencil,” says Teng Li, Keystone Professor at the University of Maryland’s (UMD) Department of Mechanical Engineering. “Its core is made of graphite, and graphite ...
April issues of American Psychiatric Association journals cover genetic underpinnings of common disorders, a digital intervention for depression and anxiety in youth, and more
2023-04-03
WASHINGTON, D.C., April 3, 2023 — The latest issues of three of the American Psychiatric Association’s journals, The American Journal of Psychiatry, Psychiatric Services, and The American Journal of Psychotherapy, are now available online.
The April issue of The American Journal of Psychiatry features genetic, neuroimaging, and behavioral neuroscience studies that focus on the underpinnings of mood disorders, psychotic disorders, autism, and stress-related disorders. Highlights from the issue:
Lower Availability of Mitochondrial Complex I in Anterior Cingulate Cortex in ...
Royal reception on Commonwealth Day 2023 for Sri Lankan PhD researcher
2023-04-03
A PhD researcher from the University of Huddersfield’s Global Disaster Resilience Centre (GDRC) was invited by His Majesty The King and The Queen Consort to attend a special reception at Buckingham Palace and more, in celebration of Commonwealth Day 2023.
Malith Senevirathne is a PhD student at the GDRC, within the University’s School of Applied Sciences and a Research Assistant for the CORE project (sCience and human factOr for Resilient sociEty), funded by the European Commission. As ...