Random matrix theory approaches the mystery of the neutrino mass!
2023-04-06
(Press-News.org)
When any matter is divided into smaller and smaller pieces, eventually all you are left with—when it cannot be divided any further—is a particle. Currently, there are 12 different known elementary particles, which in turn are made up of quarks and leptons each of which come in six different flavors. These flavors are grouped into three generations—each with one charged and one neutral lepton—to form different particles, including the electron, muon, and tau neutrinos. In the Standard Model, the masses of the three generations of neutrinos are represented by a three-by-three matrix.
A research team led by Professor Naoyuki Haba from the Osaka Metropolitan University Graduate School of Science, analyzed the collection of leptons that make up the neutrino mass matrix. Neutrinos are known to have less difference in mass between generations than other elementary particles, so the research team considered that neutrinos are roughly equal in mass between generations. They analyzed the neutrino mass matrix by randomly assigning each element of the matrix. They showed theoretically, using the random mass matrix model that the lepton flavor mixings are large.
“Clarifying the properties of elementary particles leads to the exploration of the universe and ultimately to the grand theme of where we came from!” Professor Haba explained. “Beyond the remaining mysteries of the Standard Model, there is a whole new world of physics.”
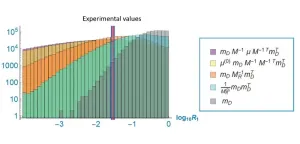
After studying the neutrino mass anarchy in the Dirac neutrino, seesaw, double seesaw models, the researchers found that the anarchy approach requires that the measure of the matrix should obey the Gaussian distribution. Having considered several models of light neutrino mass where the matrix is composed of the product of several random matrices, the research team was able to prove, as best they could at this stage, why the calculation of the squared difference of the neutrino masses are closest with the experimental results in the case of the seesaw model with the random Dirac and Majorana matrices.
“In this study, we showed that the neutrino mass hierarchy can be mathematically explained using random matrix theory. However, this proof is not mathematically complete and is expected to be rigorously proven as random matrix theory continues to develop,” said Professor Haba. “In the future, we will continue with our challenge of elucidating the three-generation copy structure of elementary particles, the essential nature of which is still completely unknown both theoretically and experimentally.”
Their findings were published in Progress of Theoretical and Experimental Physics.
###
About OMU
Osaka Metropolitan University is a new public university established by a merger between Osaka City University and Osaka Prefecture University in April 2022. For more science news, see https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/, and follow @OsakaMetUniv_en, or search #OMUScience.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-04-06
Researchers at Tufts University have successfully bulk-produced fat tissue in the lab that has a similar texture and make-up to fat tissue naturally occurring in animals. The results, described in a study published today in eLife, could be applied to the production of cultured meat grown entirely from cells, giving it a more realistic texture and flavor.
Startup companies around the world are developing cultivated meat—cell-grown chicken, beef, pork, and fish. Most are in early stages of development, not ready for large-scale production and, with a ...
2023-04-06
Analysis of official Ukraine health data reveals a perfect storm of rising infectious diseases cases and falling levels of childhood vaccination and case detection in the frontline eastern region of Kharkiv.
Between January and September 2022, new cases of rubella were 23 times higher among children living in the Kharkiv region than average rates across Ukraine, while shigellosis (diarrhoeal disease) and viral meningitis incidence was around 6 times higher, and whooping cough 5 times greater.
But registration of infectious disease cases halved in Kharkiv ...
2023-04-06
Key points:
This meta-analysis, which includes the most recent studies evaluating the link between air pollution and dementia, is the first to include studies based on active case ascertainment and to evaluate studies using a new, more powerful bias assessment tool.
The findings support the public health importance of a proposal, currently under consideration by the Environmental Protection Agency, to strengthen regulations on PM2.5
Boston, MA—Exposure to fine particulate air pollutants (PM2.5) may increase the risk of developing dementia, according to a new meta-analysis from Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health.
“This is a big step in providing actionable ...
2023-04-06
Exposure to fine particulate matter (PM2.5) air pollution is linked to a heightened risk of dementia, even at levels below current US, UK and European air quality standards, finds research published by The BMJ.
More limited data suggests that exposure to nitrogen dioxide and nitrogen oxide might also be a risk factor for dementia.
Many uncertainties remain, so caution is needed when interpreting these findings, but the researchers say the results “strengthen the evidence that air pollutants are risk factors for dementia.”
More than 57 million people worldwide are living with dementia and the global ...
2023-04-06
Experts recommend reducing consumption of added (“free”) sugars to around six teaspoons a day and limiting sugar-sweetened drinks to less than one serving a week after a comprehensive evidence review published by The BMJ today.
They found significant harmful associations between sugar consumption and 45 outcomes, including asthma, diabetes, obesity, heart disease, depression, some cancers and death.
It’s widely known that excessive sugar intake can have negative effects on health and this has prompted the World Health Organization (WHO) and others to suggest reducing consumption of free or added sugars ...
2023-04-06
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – April 05, 2023) A report from the Childhood Cancer Survivor Study (CCSS) provides strong evidence of the importance of a healthy lifestyle for adults who were treated for cancer as children. The study is the first to find that the specific primary causes of death in long term survivors are many of the same leading causes of death in the U.S. population, often occurring at younger than expected ages. It also found that adult survivors of childhood cancer experience four times the risk of late mortality as the general population, even 40 years after diagnosis. However, ...
2023-04-06
Up to two-thirds of patients with Tourette syndrome (TS), a tic disorder characterized by sudden uncontrollable physical movements, also suffer from obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), a psychiatric condition characterized by intrusive thoughts and repetitive behaviors. Unfortunately, many of these dual-diagnosis patients are resistant to conventional treatments such as medications or behavioral therapy. While deep brain stimulation (DBS) has been approved for compassionate use by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for OCD, this promising procedure is under investigational use for ...
2023-04-06
Russia’s invasion of Ukraine has struck a major blow to global markets for vital commodities – particularly grains like wheat and maize. Shortages and price increases are contributing to the food insecurity crisis in certain parts of the world, according to the United Nations, and to more general economic uncertainty.
A new study led by Adam Rose, research professor at the USC Sol Price School of Public Policy and its Center for Risk and Economic Analysis of Threats and Emergencies (CREATE), estimates that disruption to exports of grain commodities during a projected one-year period of the war will result in a $1.6 billion loss for the global economy.
The study was recently ...
2023-04-06
Intramuscular administration of tranexamic acid (TXA), a drug used to target severe bleeding after childbirth, is safe and quickly reaches therapeutic concentrations in pregnant women, according to a study involving researchers from the London School of Hygiene & Tropical Medicine (LSHTM).
The findings, from the Woman-PharmacoTXA Phase 2 trial, highlight that intramuscular injection may be a potential alternative to current intravenous approaches, which are often unsuitable in home births or rural care settings.
Oral TXA was also well-tolerated, however, on average, took around one hour to reach therapeutic ...
2023-04-06
Scientists have developed new technology to help couples undergoing in-vitro fertilisation (IVF) due to male fertility problems to increase their chances of success in having a baby.
Approximately one in six people worldwide is affected by infertility, according to the World Health Organization, and one in every 22 children in Australia is born via assisted reproduction. With a 78% failure rate, each IVF cycle can be an emotional rollercoaster that often ends in heartbreak.
“Male infertility plays a role in around 30% of cases, due to problems such as low sperm count, reduced motility ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Random matrix theory approaches the mystery of the neutrino mass!