(Press-News.org) Researchers Ludovico Lami (QuSoft, University of Amsterdam) and Mark M. Wilde (Cornell) have made significant progress in quantum computing by deriving a formula that predicts the effects of environmental noise. This is crucial for designing and building quantum computers capable of working in our imperfect world.
The choreography of quantum computing
Quantum computing uses the principles of quantum mechanics to perform calculations. Unlike classical computers, which use bits that can be either 0 or 1, quantum computers use quantum bits, or qubits, which can be in a superposition of 0 and 1 simultaneously.
This allows quantum computers to perform certain types of calculations much faster than classical computers. For example, a quantum computer can factor very large numbers in a fraction of the time it would take a classical computer.
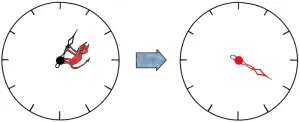
While one could naively attribute such an advantage to the ability of a quantum computer to perform numerous calculations in parallel, the reality is more complicated. The quantum wave function of the quantum computer (which represents its physical state) possesses several branches, each with its own phase. A phase can be thought of as the position of the hand of a clock, which can point in any direction on the clockface.
At the end of its computation, the quantum computer recombines the results of all computations it simultaneously carried out on different branches of the wave function into a single answer. “The phases associated to the different branches play a key role in determining the outcome of this recombination process, not unlike how the timing of a ballerina’s steps play a key role in determining the success of a ballet performance,” explains Lami.
Disruptive environmental noise
A significant obstacle to quantum computing is environmental noise. Such noise can be likened to a little demon that alters the phase of different branches of the wave function in an unpredictable way. This process of tampering with the phase of a quantum system is called dephasing, and can be detrimental to the success of a quantum computation.
Dephasing can occur in everyday devices such as optical fibres, which are used to transfer information in the form of light. Light rays travelling through an optical fibre can take different paths; since each path is associated to a specific phase, not knowing the path taken amounts to an effective dephasing noise.
In their new publication in Nature Photonics, Lami and Wilde analyse a model, called the bosonic dephasing channel, to study how noise affects the transmission of quantum information. It represents the dephasing acting on a single mode of light at definite wavelength and polarisation.
The number quantifying the effect of the noise on quantum information is the quantum capacity, which is the number of qubits that can be safely transmitted per use of a fibre. The new publication provides a full analytical solution to the problem of calculating the quantum capacity of the bosonic dephasing channel, for all possible forms of dephasing noise.
Longer messages overcome errors
To overcome the effects of noise, one can incorporate redundancy in the message to ensure that the quantum information can still be retrieved at the receiving end. This is similar to saying “Alpha, Beta, Charlie” instead of “A, B, C” when speaking on the phone. Although the transmitted message is longer, the redundancy ensures that it is understood correctly.
The new study quantifies exactly how much redundancy needs to be added to a quantum message to protect it from dephasing noise. This is significant because it enables scientists to quantify the effects of noise on quantum computing and develop methods to overcome these effects.
END
How to overcome noise in quantum computations
2023-04-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Archaeology: Evidence of drug use during Bronze Age ceremonies
2023-04-06
An analysis of strands of human hair from a burial site in Menorca, Spain, indicates that ancient human civilisations used hallucinogenic drugs derived from plants, reports a new paper published in Scientific Reports. These findings are the first direct evidence of ancient drug use in Europe, which may have been used as part of ritualistic ceremonies.
Previous evidence of prehistoric drug use in Europe has been based on indirect evidence such as the detection of opium alkaloids in Bronze Age containers, the ...
New test could help identify type 2 diabetes risk
2023-04-06
Analysing changes to DNA in the blood can improve the ability to predict a person’s risk of developing type 2 diabetes within a decade.
Scientists looked at the influence of these changes – known as DNA methylation – alongside other risk factors in almost 15,000 people to predict the likelihood of developing the condition years in advance of any symptoms developing.
The findings could lead to preventative measures being put in place earlier, reducing the economic and health burden caused by type 2 diabetes.
Methylation is a chemical process in the body in which a small molecule called a methyl group is added to DNA.
Current ...
Akili Labs and BGI Genomics to deliver their first commercial clinical sequencing facility in Africa
2023-04-06
JOHANNESBURG, SOUTH AFRICA and SHENZHEN, CHINA - 31.03.23
Akili Labs (Pty) Ltd, a pioneer of cost-effective molecular diagnostics and secure genomic data storage solutions, and BGI Genomics Co. Ltd, the world’s leading integrated solutions provider of precision medicine, today announced the signing of a technology transfer agreement that will provide the Southern region of Africa with clinical-grade sequencing solutions.
"Improving the cost and turnaround time of genetic sequencing services will play a major role in the expansion of precision medicine-driven healthcare in Africa," said Charles F.J. Faul, co-founder ...
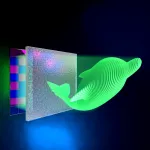
Technology advance paves way to more realistic 3D holograms for virtual reality and more
2023-04-06
WASHINGTON — Researchers have developed a new way to create dynamic ultrahigh-density 3D holographic projections. By packing more details into a 3D image, this type of hologram could enable realistic representations of the world around us for use in virtual reality and other applications.
“A 3D hologram can present real 3D scenes with continuous and fine features,” said Lei Gong, who led a research team from the University of Science and Technology of China. “For virtual reality, our method could be used with headset-based holographic displays to greatly improve the viewing angles, which would enhance the 3D viewing experience. ...
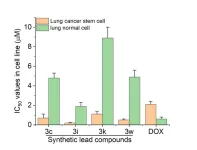
Novel tridimensional anticancer agents developed to fight against drug-resistant cancer cells
2023-04-06
A research team co-led by chemists from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) recently discovered novel, highly effective anticancer agents with tridimensional structures, which have high anticancer activity, low toxicity and the ability to overcome drug resistance in cancer cells. The findings help provide a new direction for anticancer drug development.
Cancer has long been a devastating disease, which affects millions of people worldwide. Despite advances in treatment, current anticancer drugs often have limited effectiveness, lack of cancer ...
ASBMB urges NIAID to prioritize DEAI
2023-04-06
The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology sent recommendations March 30 to the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases on expanding the institute’s diversity, equity, accessibility and inclusivity activities.
The society recommended, broadly, that the NIAID expand the use of diversity and re-entry grant supplements and better support disabled, LGBTQ+ and other underrepresented scientists.
“Because NIAID is one of the largest NIH institutes, they have ...
How to make better consistency and availability trade-offs in networks
2023-04-06
Imagine you want to withdraw some cash from an ATM. You expect it to show your account balance correctly and process your request quickly. However, network delays make it hard for the system to meet both of these simple expectations at the same time. If an ATM system tries to achieve high “consistency,” meaning that it displays the latest account balance by checking a remote database, it could make you wait or even prevent you from accessing your accounts during busy times. On the other hand, if an ATM system favors “availability,” it could let you access your accounts fast, but risk showing inaccurate information. To avoid undesired results, ...
Science journals integrate Dryad to simplify data deposition and strengthen scientific reproducibility
2023-04-06
The Science family journals have announced a partnership with the nonprofit data repository Dryad that simplifies the process by which authors deposit data underlying new work – a critical step to facilitating data’s routine reuse. The partnership is yet another step taken by the Science journals to ensure data the scientific community requires to verify, replicate and reanalyze new research is openly available.
“Addressing public access to data at scale is a critical challenge,” said Holden Thorp, Editor-in-Chief of the Science family ...
Men and women have different obesity drivers, pointing to the need for tailored interventions
2023-04-06
A new study from UCLA researchers finds sex-specific brain signals that appear to confirm that different drivers lead men and women to develop obesity. The study, appearing in the peer-reviewed journal Brain Communications, combined data from several modes of MRI with patients’ clinical features and personal histories to identify sex-specific mechanisms in the brain underlying obesity.
“We found differences in several of the brain’s networks associated with early life adversity, mental ...
Disparities identified among patients receiving advanced pulmonary support
2023-04-06
Some adults with severe respiratory illness, including women, those with public insurance, and people with fewer financial resources, may be less likely to receive an advanced form of life support known as extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO). A research team supported by the National Institutes of Health found that adults who received ECMO appeared to skew toward men, people with private health insurance, and those who came from areas with higher median incomes. ECMO helps patients with life-threatening illness or injury breathe by simulating the function of the heart and/or lungs, while giving those organs a chance to rest.
The study published in the Annals of the American ...