(Press-News.org) Industrial cultivation of hemp is seeing a massive expansion in the United States due to new federal laws and consumer demand.
Because of these changes in regulation, part of the Agriculture Improvement Act of 2018, researchers are legally able to perform tests on hemp and growers can produce plants. In 2021, hemp, which has a THC concentration of less than 0.3 percent on a dry weight basis, was grown on 54,000 acres with a value of more than $824 million, according to the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
In partnership with York University in Ontario, Canada, and the Institute for Advanced Learning and Research in Danville, Virginia, researchers in the College of Agriculture and Life Sciences received a $600,000 grant to study the regulation of the genes that are responsible for cannabinoid biosynthesis.
“We’re interested in the regulation of the gene expression of the enzymes that are responsible for cannabinoid biosynthesis,” said Bastiaan Bargmann, an assistant professor in the School of Plant and Environmental Sciences. “We currently just don’t have a lot of knowledge about how the biosynthetic pathway is regulated.”
An improved understanding of those processes could allow for better selection or modification of plants with particular cannabinoid content, potentially increasing profits and reducing risk for growers, as crops with more than the allowed level of THC must be destroyed. Discoveries could also help the pharmaceutical industry as cannabinoids are becoming increasingly significant for the treatment of pain, anxiety, epilepsy, and cancer.
“We have a list of nine transcription factors that we want to investigate further and see if they regulate the expression of these genes that are involved in cannabinoid biosynthesis,” Bargmann said.
To understand the regulation of the cannabinoid synthesis pathway in hemp (Cannabis sativa L.), researchers will map the relationship between factors that turn on or off the genes for enzymes, measure the effect of manipulating these factors, and engineer hemp cells and plants with the modified profiles.
“If we can find ways to manipulate the biosynthesis so that, instead of these main ones (THC and CBD), we start to get other ones like CBG (Cannabigerol), CBN (Cannabinol), and others, then we can perhaps grow crops that have a greater economic value than the ones we currently have,” Bargmann said.
END
Virginia Tech researchers to investigate transcriptional regulation of cannabinoid synthesis in industrial hemp
2023-04-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Blood-based biomarkers accurately predict neuroendocrine tumor response to radiopharmaceutical therapy
2023-04-06
Reston, VA—A simple blood draw can provide physicians with valuable information that can determine if peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) is likely to be effective in a patient with neuroendocrine cancer. The blood-based biomarker PPQ can predict which patients will respond to PRRT with 96 percent accuracy; changes in another biomarker, NETest, correctly correlate with PRRT response in 90 percent of patients. The study, published in the April issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, ...
Fully recyclable printed electronics ditch toxic chemicals for water
2023-04-06
DURHAM, N.C. – Engineers at Duke University have produced the world’s first fully recyclable printed electronics that replace the use of chemicals with water in the fabrication process. By bypassing the need for hazardous chemicals, the demonstration points down a path industry could follow to reduce its environmental footprint and human health risks.
The research appeared online Feb. 28 in the journal Nano Letters.
One of the dominant challenges facing any electronics manufacturer is successfully securing several layers of components on ...
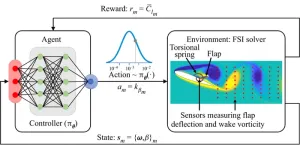
Model simulates variable flap stiffness for the best lift
2023-04-06
There is extensive research on how a fixed-position flap affects lift in the realm of fluid-structure interaction. However, taking the conversation in a new direction, researchers at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign conducted a bio-inspired study with a novel twist—variable stiffness—to learn more about how it affects lift.
The researchers wondered if they could model a flap on an airfoil, or wing, with varying stiffnesses over time much like a bird can tense, or stiffen, the musculature and tendons connected to covert feathers.
“We know from previous studies ...
Broccoli consumption protects gut lining, reduces disease, in mice
2023-04-06
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Broccoli is known to be beneficial to our health. For example, research has shown that increased consumption of the cruciferous vegetable decreases incidences of cancer and type 2 diabetes. In a recent study, researchers at Penn State found that broccoli contains certain molecules that bind to a receptor within mice and help to protect the lining of the small intestine, thereby inhibiting the development of disease. The findings lend support to the idea that broccoli truly is a ‘superfood.’
“We ...
UNLV, SNWA study makes case for Candida auris wastewater surveillance
2023-04-06
A rapid spike in cases of a potentially deadly, drug-resistant fungus has concerned public health officials across the nation. But a team of Southern Nevada researchers hope their new study applying wastewater surveillance can help health officials get a step ahead of this emerging global public health threat.
The Pathogen Problem
Candida auris is a fungus that can cause serious infections, particularly in patients who are immunocompromised, have pre-existing health conditions, are in long-term healthcare settings, or are undergoing treatment with invasive medical devices such as a catheter. Infection prevention ...
Giving pregnant women routine third trimester ultrasound scans could reduce rates of undetected breech pregnancy by 71%, enabling better care before and during labor and improved outcomes for newborns
2023-04-06
Giving pregnant women routine third trimester ultrasound scans could reduce rates of undetected breech pregnancy by 71%, enabling better care before and during labor and improved outcomes for newborns
In your coverage, please use this URL to provide access to the freely available paper in PLOS Medicine: http://journals.plos.org/plosmedicine/article?id=10.1371/journal.pmed.1004192
Article Title: Impact of point-of-care ultrasound and routine third trimester ultrasound on undiagnosed breech presentation and perinatal outcomes: An observational multicentre cohort study
Author Countries: United Kingdom, Turkey
Funding: The author(s) received no specific funding for this work. END ...
Implant treats dangerously low blood pressure in people with spinal cord injury
2023-04-06
An implant that delivers electrical stimulation to a select group of spinal neurons can treat dangerously low blood pressure in people with spinal cord injuries, addressing an often “invisible” consequence of paralysis.
For his work in developing this treatment, called the neuroprosthetic baroreflex, Jordan W. Squair is the winner of the 2023 BioInnovation Institute & Science Prize for Innovation. The prize seeks to reward scientists who deliver research at the intersection of the life sciences and entrepreneurship.
“Dr. Squair’s prize-winning research on epidural electrical stimulation restores blood pressure control in patients ...
Editorial: Share SARS-CoV-2 data immediately
2023-04-06
In an editorial, Maria Van Kerkhove – who serves as the technical lead for the COVID-19 response at the World Health Organization (WHO) – outlines how earlier this month (March 2023), WHO learned that scientists in China possessed data on viral samples from Wuhan that had been gathered in January 2020. “These should have been shared immediately—not 3 years later,” she writes. “The lack of data disclosure is simply inexcusable.” WHO continues to call on China and all countries to share any data on the origins of SARS-CoV-2 immediately. “China has advanced technical capabilities,” Van ...
Uncovered: A new mode of reproduction that produces chimeric males in yellow crazy ants
2023-04-06
Male yellow crazy ants (Anoplolepis gracilipes) are chimeras of two separate genetic lineages, researchers report in a study that reveals a unique mode of reproduction in this species – one previously unknown to science. While most multicellular organisms develop from a single-cell zygote into a collection of genetically identical cells – a hallmark of biological inheritance – the new findings show that yellow crazy ants deviate from this expectation. According to the study, all male yellow crazy ants are instead composed ...
Bushmeat consumption unchanged by COVID-19 in Kenya and Tanzania border towns, new study reveals
2023-04-06
First ever study looking at disease risks of wild meat activities in rural communities.
Nearly 70% of rural respondents at Kenya-Tanzania border said that COVID-19 did not impact their levels of wild meat consumption, with some even reporting increased consumption.
Ungulates were found to be the most consumed species, followed by birds, rodents and shrews.
Governments need to focus on better controlling zoonotic disease transmission risks through community engagements on behavior change interventions, improving hygiene and standards of informal markets, supporting wildlife conservation ...