(Press-News.org) A University of Texas at Arlington computer security researcher has received a prestigious federal grant to determine what technologies and methods work best to attain and retain online security and privacy.
Shirin Nilizadeh, assistant professor in the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, received a $200,000 National Science Foundation grant to study social media discussions and better understand what concerns are about online security and privacy, what technologies and tools they suggest to each other to use and whether they are effective. Nilizadeh called this a “worldwide challenge.”
“People care about their online security and privacy everywhere,” she said. “And sometimes, due to societal and political movements, they become more cautious or aware of the problems, where they go online and on social media, and proactively discuss their concerns and ask for tools and methods that can help protect them.
“We can help as a research community to see what’s working and what isn’t. We can take these research findings to design and develop better online safeguards and to improve the existing security and privacy-preserving systems if they are not secure, effective and efficient.”
Hong Jiang, chair of the Department of Computer Science and Engineering, said Nilizadeh’s research could further the security of social network tools.
“Everyone is connected to social networks,” Jiang said. “Studying social networks’ discussions and understanding what security measures people are looking for and using allow researchers to develop and provide such measures to improve online security and privacy.”
Previous Nilizadeh work showed that social media users extensively discussed the security and privacy threats of video communication tools more people started working from home due to the COVID-19 pandemic. This work showed how misinformation about security and privacy spread on social media platforms.
Nilizadeh previously did work on how job applicants can “hack” hiring systems and improve their standing by using certain words on their applications. She also has studied whether security and privacy applications like content moderation tools are fair toward users from various demographics and backgrounds.
END
Computer scientist confronts worldwide challenge of online security and privacy
UTA researcher aims to improve online safeguards that protect user privacy
2023-04-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Requirement to wear masks in hospitals may have little impact on COVID-19 transmission during Omicron wave, UK study suggests
2023-04-07
**Note: the release below is a special early release from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April). Please credit the congress if you use this story**
Embargo: 2301H UK time Thursday 6 April
Requirements to wear surgical masks in a large London hospital during the first 10 months of Omicron activity (December 2021 to September 2022) made no discernible difference to reducing hospital-acquired SARS-CoV-2 infections, according to new research being presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) in Copenhagen, ...
Omicron appears more deadly than seasonal influenza, study suggests
2023-04-07
**Note: the release below is a special early release from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April). Please credit the congress if you use this story**
Embargo: 2301H UK time Thurs 6 April
Adults hospitalised with the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron variant have a higher death rate than those hospitalised with seasonal influenza, even though Omicron is considered less virulent with lower case fatality rates than the delta and alpha strains, new research being presented at this year’s ...
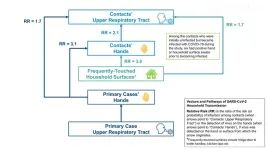
Spread of COVID-19 in households is linked to virus on hands and surfaces, say researchers
2023-04-07
IMPERIAL COLLEGE LONDON PRESS RELEASE
Under STRICT EMBARGO until:
Thursday 6 April 2023
23:30 UK TIME / 19:30 ET
Peer-reviewed / Observational study / People
Spread of COVID-19 in households is linked to virus on hands and surfaces, say researchers
A new Imperial College London-led study provides the first empirical evidence for transmission of SARS-CoV-2 via people’s hands and frequently touched household surfaces.
The research sheds new light on the spread of COVID-19 in households, where most transmission of SARS-CoV-2 occurs, and it is the first to link the presence ...
Environmental impact reports hugely underestimate consequences for wildlife
2023-04-07
Environmental Impact Assessments may hugely underestimate the effect that new developments have on wildlife, according to new research from the University of East Anglia.
This is because they don’t take into account how birds and other animals move around between different sites.
A study published today shows how a new airport development planned in Portugal could affect more than 10 times the number of Black-tailed Godwits estimated in a previous Environmental Impact Assessment.
The research team have been studying these Godwits across Europe for over 30 years but they say that any species that moves around is likely to be under-represented ...
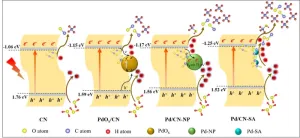
Effect of palladium chemical states on CO2 photocatalytic reduction over g-C3N4: Distinct role of single-atomic state in boosting CH4 production
2023-04-07
Using solar energy and photocatalysts to convert CO2 into high value-added chemicals can simultaneously alleviate the greenhouse effect and energy shortage, being recognized to be a promising alternative to achieve sustainable social development. Single atom cocatalysts decoration has been demonstrated to be effective strategy to improve the CO2 photocatalytic reduction efficiency. Unfortunately, when unraveling the mechanism behind performance promotion, most studies mainly focused on clarifying the superior ...
Physicians should be on alert for group A strep as cases experience historic rise, study finds
2023-04-06
The U.S. experienced an unprecedented number of group A streptococcal infections in children from October to December of 2022, which should alert physicians to check for the potentially deadly infectious disease as the country moves out of the pandemic, according to research published by UTHealth Houston.
The study, led by senior author Anthony R. Flores, MD, PhD, MPH, associate professor and chief of pediatric infectious diseases at McGovern Medical School at UTHealth Houston, was published this month in Clinical Infectious Diseases.
During the COVID-19 pandemic, the rate of other infectious diseases dropped due to safety measures such as social distancing and mask-wearing, according ...
Chemistry’s Michael Schulz awarded National Science Foundation CAREER award
2023-04-06
Michael Schulz, assistant professor of chemistry within the Virginia Tech College of Science, has received a National Science Foundation Faculty Early Career Development (CAREER) award. The award, which begins in May, comes on the heels of Schulz receiving a U.S. Department of Energy 2022 Early Career Research Program Award.
Schulz received the foundation's five-year $725,000 for the project titled "CAREER: Novel Approaches to Hyperbranched Polymers" to develop ruthenium-catalyzed self-condensing Ring-Opening Metathesis Polymerization to prepare hyperbranched polymers. The award comes ...
Virginia Tech researchers to investigate transcriptional regulation of cannabinoid synthesis in industrial hemp
2023-04-06
Industrial cultivation of hemp is seeing a massive expansion in the United States due to new federal laws and consumer demand.
Because of these changes in regulation, part of the Agriculture Improvement Act of 2018, researchers are legally able to perform tests on hemp and growers can produce plants. In 2021, hemp, which has a THC concentration of less than 0.3 percent on a dry weight basis, was grown on 54,000 acres with a value of more than $824 million, according to the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
In partnership with York University in Ontario, Canada, and the ...
Blood-based biomarkers accurately predict neuroendocrine tumor response to radiopharmaceutical therapy
2023-04-06
Reston, VA—A simple blood draw can provide physicians with valuable information that can determine if peptide receptor radionuclide therapy (PRRT) is likely to be effective in a patient with neuroendocrine cancer. The blood-based biomarker PPQ can predict which patients will respond to PRRT with 96 percent accuracy; changes in another biomarker, NETest, correctly correlate with PRRT response in 90 percent of patients. The study, published in the April issue of The Journal of Nuclear Medicine, ...
Fully recyclable printed electronics ditch toxic chemicals for water
2023-04-06
DURHAM, N.C. – Engineers at Duke University have produced the world’s first fully recyclable printed electronics that replace the use of chemicals with water in the fabrication process. By bypassing the need for hazardous chemicals, the demonstration points down a path industry could follow to reduce its environmental footprint and human health risks.
The research appeared online Feb. 28 in the journal Nano Letters.
One of the dominant challenges facing any electronics manufacturer is successfully securing several layers of components on ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
[Press-News.org] Computer scientist confronts worldwide challenge of online security and privacyUTA researcher aims to improve online safeguards that protect user privacy