Terna and Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia together for innovation and research
The agreement aims to design and implement innovative solutions in the field of robotics for the management of electricity grids and electrical substations by the company
2023-04-07
(Press-News.org)
Rome (Italy), 7th April 2023 - Terna, the company led by Stefano Donnarumma that manages the national transmission grid, and Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT- Italian Institute of Technology) have signed a five-year collaboration agreement aimed at studying and implementing innovative solutions in the field of robotics to support the company's field activities.
The agreement was signed on April 6th in Rome by Massimiliano Garri, Terna's Head of Innovation & Market Solutions, and Giorgio Metta, IIT Scientific Director.
"We are proud to start the collaboration with an excellence on the Italian research and innovation scene," said Massimiliano Garri, Terna's Head of Innovation & Market Solutions. "The robotic solutions we will implement with the IIT will support our people, ensuring an even higher level of safety in the operations they carry out every day throughout Italy. The partnership that begins today will allow us to evolve, innovate and make our operations even more efficient, with important benefits for the entire national electricity grid”.
The Scientific Director of Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia, Giorgio Metta, said: "We were established with the aim of putting the technologies developed in our laboratories at the service of the country's economy and its production system. The agreement signed today with Terna fully achieves this important vocation of the Institute, confirming us as an instrument of innovation and underlining our commitment to the development of technologies that support human beings and make work safer."
The development of new solutions is crucial to Terna, which, as a director and enabler of the energy transition, is daily engaged in researching and adopting innovative technologies to meet the main challenges posed by national and international decarbonisation targets.
Thanks to the collaboration with the IIT and the Institute's know-how in the field of automation and robotics, Terna will thus be able to develop new technological solutions to support consolidated operations and maintenance in the daily management of approximately 75,000 km of high and extra-high voltage power lines and over 900 electrical substations throughout Italy.
The Italian Institute of Technology and Terna have already identified some initial, specific cases to be developed and tested together, such as, for instance: autonomous robots capable of carrying out operations on pylons supporting overhead power lines, advanced systems for monitoring electrical substations in the absence of human operators, and devices such as exoskeletons to support the work of field personnel. During the collaboration, Terna and IIT will also consider taking steps to protect intellectual property with the aim of protecting and enhancing research results.
Terna's innovation plan aims to manage the evolution of the electricity system, increase the performance and resilience of the transmission grids, increase efficiency and minimise the risks arising from maintenance, as well as to better cope with new ways of working by helping to create a company where people are increasingly at the centre; all this with a focus on sustainability and energy transition as key factors in the company's business, in favour of a just transition that creates value and benefits for the company, its stakeholders and the surrounding system.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-04-07
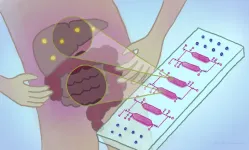
A new chip that holds different cell types in tiny, interconnected chambers could allow scientists to better understand the physiological and disease interactions between organs. The integrated-gut-liver-on-a-chip (iGLC) platform was designed by scientists at Kyoto University’s Institute for Integrated Cell-Material Sciences (iCeMS), to improve understanding of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD). The researchers, together with colleagues in Japan, published their findings in the journal Communications ...
2023-04-07
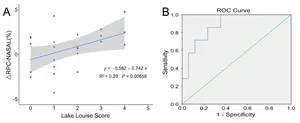
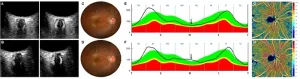
This study is led by Dr.Ningli Wang and Dr.Yuan Xie (Beijing Tongren Hospital, Capital Medical University), they provide evidence that retinal microvasculature is a potential biomarker for cerebral microvasculature changes and acute mountain sickness(AMS) development during risk assessment of individuals at high altitudes.
Since the retinal and cerebral vasculature share many morphological and physiological characteristics, direct evaluation of the more accessible retinal vasculature should theoretically provide insights into the cerebral circulation. Therefore, the role of retinal imaging ...
2023-04-07
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Glioblastoma is the most common type of brain tumor in adults. The disease is 100% fatal and there are no cures, making it the most aggressive type of cancer. Such a poor prognosis has motivated researchers and neurosurgeons to understand the biology of tumors with the goal of creating better therapies.
Dominique Higgins, MD, PhD, an assistant professor in the Department of Neurosurgery, has heeded the call. Higgins and a team of researchers at Columbia University have found ...
2023-04-07
INDIANAPOLIS—For centuries, people have suspected a full moon in the sky to cause mysterious changes in people. Now, psychiatrists at Indiana University School of Medicine have found deaths by suicide increase during the full moon.
“We wanted to analyze the hypothesis that suicides are increased during the period around full moons and determine if high-risk patients should be followed more closely during those times,” said Alexander Niculescu, MD, PhD.
Niculescu and his team looked at data from the Marion County coroner’s ...
2023-04-07
Imagine if you could ask a machine to “smell” something for you with just a click of a button. That’s what electronic noses, or e-noses, are for. They are systems that combine chemical gas sensors, signal processing and machine learning algorithms to mimic the sense of smell. E-noses can be used for many purposes, such as checking food quality, monitoring air pollution, diagnosing diseases and detecting explosives. How do they work? What are the challenges and opportunities in this field? A team led by Jingdong Chen of Northwestern Polytechnical University in Xi’an, China and ...
2023-04-07
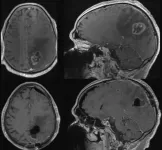
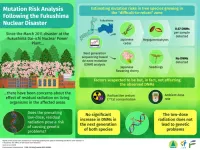
Ionizing radiation from nuclear disasters are known to be harmful to the natural environment. The Fukushima Dai-ichi Nuclear Power Plant meltdown that occurred in 2011 is a prominent example of such a disaster in recent memory. Even a decade after the incident, concerns remain about the long-term effects of the radiation. In particular, it is not clear how the residual low-dose radiation might affect living organisms at the genetic level.
The brunt of the disaster is usually borne by the floras inhabiting the contaminated areas since they cannot move. This, however, makes them ideal for ...
2023-04-07
A team led by Masaya Hagiwara of RIKEN national science institute in Japan has developed an ingenious device, using layers of hydrogels in a cube-like structure, that allows researchers to construct complex 3D organoids without using elaborate techniques. The group also recently demonstrated the ability to use the device to build organoids that faithfully reproduce the asymmetric genetic expression that characterizes the actual development of organisms. The device has the potential to revolutionize the way we test drugs, and could also provide insights into how tissues develop and lead to ...
2023-04-07
Dan Răzvan Popoviciu new book New Worlds: Colonizing Planets, Moons and Beyond (published by Bentham Science) explores the possibilities of transforming humanity into a multi-planetary species, while also sounding an alarm about our long-term future. It emphasizes the importance of efficiently using Earth's resources and expanding beyond the planet's borders.
In the book, Popoviciu discusses how various planets, moons, and asteroids in the Solar System can provide important resources and become potential new home worlds for humans. The author goes beyond simple colonization and discusses solutions for terraforming ...
2023-04-07
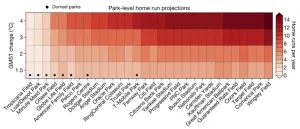
In the history of Major League Baseball, first came the low-scoring dead-ball era, followed by the modern live-ball era characterized by power hitters such as Babe Ruth and Henry "Hank" Aaron. Then, regrettably, was the steroid era of the 1990s and early 2000s.
Now, could baseball be on the cusp of a "climate-ball" era where higher temperatures due to global warming increasingly determine the outcome of a game?
A new Dartmouth College study suggests it may be. A report in the Bulletin of the ...
2023-04-07
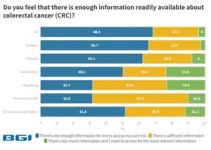
To uncover attitudes and the biggest challenges facing colorectal cancer (CRC) awareness and screening, BGI Genomics today released its State of Colorectal Cancer Awareness Report, marking the first-ever global survey report on the world's third most common cancer. This report is released on World Health Day, April 07, 2023, in line with achieving Health For All, and seeks to motivate action to tackle the health challenges of today and tomorrow.
This ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Terna and Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia together for innovation and research
The agreement aims to design and implement innovative solutions in the field of robotics for the management of electricity grids and electrical substations by the company