Study finds record-breaking rates of sea-level rise along the U.S. Southeast and Gulf coasts
Tulane researchers found rates of sea-level rise of about a half an inch per year since 2010 — three times higher than the global average over the same period
2023-04-10
(Press-News.org)
Sea levels along the U.S. Southeast and Gulf coasts have been rapidly accelerating, reaching record-breaking rates over the past 12 years, according to a new study led by scientists at Tulane University.
In the study, published in Nature Communications, researchers said they had detected rates of sea-level rise of about a half an inch per year since 2010. They attribute the acceleration to the compounding effects of man-made climate change and natural climate variability.
“These rapid rates are unprecedented over at least the 20th century and they have been three times higher than the global average over the same period,” says Sönke Dangendorf, lead author and the David and Jane Flowerree Assistant Professor in the Department of River-Coastal Science and Engineering at Tulane.
The authors studied a combination of field and satellite measurements since 1900, pinpointing the individual contributors to the acceleration.
“We systematically investigated the different causes, such as vertical land motion, ice-mass loss, and air pressure, but none of them could sufficiently explain the recent rate,” said Noah Hendricks, co-author and undergraduate student in Dangendorf’s team at his former institution, Old Dominion University in Norfolk, Virginia.
“Instead, we found that the acceleration is a widespread signal that extends from the coasts of the Gulf of Mexico up to Cape Hatteras in North Carolina and into the North Atlantic Ocean and Caribbean Seas, which is indicative for changes in the ocean’s density and circulation.”
Over the past 12 years this entire area, known as the Subtropical Gyre, has been expanding primarily due to changing wind patterns and continued warming. Warmer water masses need more space and thus lead to a rise in sea level.
The scientists suggest that the recent acceleration was an unfortunate superposition of man-made climate change signals and a peak in weather-related variability that lasted over several years. They conclude that the rates will likely return to the more moderate values as predicted by climate models in the coming decades.
“However, this is no reason to give the all clear,” said Torbjörn Törnqvist, co-author and the Vokes Geology Professor in the Department of Earth and Environmental Sciences at Tulane. “These high rates of sea-level rise have put even more stress on these vulnerable coastlines, particularly in Louisiana and Texas where the land is also sinking rapidly.”
Dangendorf said the “results, once again, demonstrate the urgency of the climate crisis for the Gulf region. We need interdisciplinary and collaborative efforts to sustainably face these challenges.”
Also collaborating on the study were Qiang Sun from Tulane, John Klinck and Tal Ezer from Old Dominion University, Thomas Frederikse from the Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, California , Francisco M. Calafat from the National Oceanography Centre in Liverpool, UK, and Thomas Wahl from the University of Central Florida in Orlando.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-04-10
For the first time, the British Association for Psychopharmacology (BAP) has produced a guideline on catatonia. Catatonia is a severe psychiatric disorder that has been associated with a wide range of medical complications. Yet recognition and management remain poor.
Twenty-two experts from across three continents examined the latest research on this important condition and have developed a series of recommendations ranging from diagnosis and investigation to treatment. According to the lead author, Dr Jonathan Rogers of University ...
2023-04-10
**Note: the release below is a special early release from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April). Please credit the conference if you use this story**
Embargo: 2301H UK time Sunday 9 April
**Note – the press release is available in Spanish and Portuguese, see links below**
Targeted testing for HIV in emergency departments has great potential for increasing diagnoses, this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) in Copenhagen, Denmark, (15-18 April), will ...
2023-04-10
By using precision gene engineering techniques, researchers at the Earlham Institute in Norwich have been able to turn tobacco plants into solar-powered factories for moth sex pheromones.
Critically, they’ve shown how the production of these molecules can be efficiently managed so as not to hamper normal plant growth.
Pheromones are complex chemicals produced and released by an organism as a means of communication. They allow members of the same species to send signals, which includes letting others know they’re looking for love.
Farmers can hang pheromone dispersers among their crops to mimic the signals ...
2023-04-08
**Note: the release below is a special early release from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April). Please credit the conference if you use this story**
Embargo: 2301H UK time Friday 7 April
New research being presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) in Copenhagen, Denmark, (15-18 April) has identified several gold-based compounds with the potential to treat multidrug-resistant “superbugs”.
With ...
2023-04-07
It feels like a classical paradox: How do you see the invisible? But for modern astronomers, it is a very real challenge: How do you measure dark matter, which by definition emits no light?
The answer: You see how it impacts things that you can see. In the case of dark matter, astronomers watch how light from distant galaxies bends around it.
An international team of astrophysicists and cosmologists have spent the past year teasing out the secrets of this elusive material, using sophisticated computer simulations and the observations from the one of the most powerful astronomical cameras in the world, the Hyper Suprime-Cam (HSC). The team is led by astronomers from Princeton ...
2023-04-07
People with autism spectrum disorder can be classified into four distinct subtypes based on their brain activity and behavior, according to a study from Weill Cornell Medicine investigators.
The study, published March 9 in Nature Neuroscience, leveraged machine learning to analyze newly available neuroimaging data from 299 people with autism and 907 neurotypical people. They found patterns of brain connections linked with behavioral traits in people with autism, such as verbal ability, social affect, and repetitive or stereotypic behaviors. They confirmed that the four autism subgroups could also be replicated in a separate dataset ...
2023-04-07
“[...] DPE analysis may have an important role in improving the diagnosis and management of CRC.”
BUFFALO, NY- April 7, 2023 – A new editorial paper was published in Oncoscience (Volume 10) on March 23, 2023, entitled, “New method of clustering colorectal cancer patients using differential presence of exons (DPE) sequencing.”
Colorectal cancer (CRC) is a heterogeneous disease that occurs in the colon and the rectum, parts of the gastrointestinal system. CRC is the third leading cause of cancer-related ...
2023-04-07
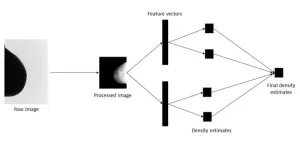
Breast cancer is the most common cancer to affect women worldwide. According to the American Cancer Society, about 1 in 8 women in the United States will develop breast cancer in their lifetime. While it is not possible to entirely prevent breast cancer, various medical organizations advise regular screening to detect and treat cases at the early stage. The breast density, defined as the proportion of fibro-glandular tissue within the breast, is often used to assess the risk of developing breast cancer. While various methods are available to estimate this measure, studies have shown that subjective assessments conducted by radiologists based on visual analogue scales ...
2023-04-07
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender and queer people who experienced intimate partner violence in their current relationship before COVID-19 had an increase in the frequency of victimization after the pandemic began, according to a Rutgers study.
While national emergencies, crises and pandemics increase the frequency of health risks and intimate partner violence few studies have considered the nuances of social and psychological factors, such as socioeconomic characteristics and mental health, in explaining the increase in intimate partner violence during times of crisis.
“To date, most programs on intimate ...
2023-04-07
Irvine, Calif., April 7, 2023 — Human activities emit many kinds of pollutants into the air, and without a molecule called hydroxide (OH), many of these pollutants would keep aggregating in the atmosphere.
How OH itself forms in the atmosphere was viewed as a complete story, but in new research published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, a research team that includes Sergey Nizkorodov, a University of California, Irvine professor of chemistry, report that a strong electric field that exists at the surface between airborne water droplets and ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Study finds record-breaking rates of sea-level rise along the U.S. Southeast and Gulf coasts
Tulane researchers found rates of sea-level rise of about a half an inch per year since 2010 — three times higher than the global average over the same period