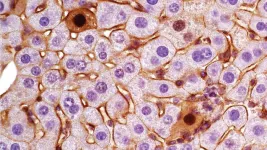
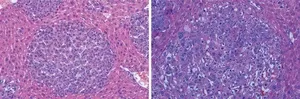
(Press-News.org) Mutations in our genes can lead to severe problems, like colon or liver cancer. But cancer is very complex. Mutations in the same genes can lead to different subtypes of tumors in different people. Currently, scientists don’t have a good way to produce such tumor subtypes for study in the lab.
Now, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Assistant Professor Semir Beyaz has created a new method to model certain liver cancer tumor subtypes using the gene-editing tool CRISPR-Cas9.
Genes contain the information our bodies need to create proteins. Highly similar proteins produced from the same gene are called isoforms. Different isoforms generate different tumors. This process is known as exon skipping, where multiple parts of a gene are stitched together to make a different version of a protein.
“Everyone thinks that cancer is just one type,” Beyaz explains. “But with different isoforms, you can end up with cancer subtypes that have different characteristics.”
Beyaz and his colleagues produced two distinct tumor subtypes by targeting a single section of the mouse gene, Ctnnb1, with CRISPR. The tool is mostly used to inhibit gene function. This is the first time CRISPR has been used to generate different cancer-causing gain-of-function mutations in mice. These mutations enhance protein activity to promote tumor growth. The team sequenced each tumor subtype to figure out which isoform was associated with the differences they observed.
“We were able to define those isoforms that associated with different cancer subtypes,” Beyaz says. “That was, for us, a surprising discovery.”
Next, to confirm that these isoforms actually caused the variances, they produced them in the mouse without using CRISPR. They found that they were indeed able to generate the two different tumor subtypes with their respective characteristics. Both of these liver tumor subtypes are also found in humans.
The mutations Beyaz targeted can lead to colon and liver cancers. Targeting exon skipping has emerged as a potential therapeutic approach for treating cancer and other diseases. Beyaz’s new study method allows researchers to investigate this phenomenon in living mice cells using CRISPR. The platform could someday help researchers develop new therapeutic interventions. “Ultimately,” Beyaz explains, “what we want to do is find the best models to study the biology of cancer so that we can find a cure.”
END
Identifying cancer genes’ multiple personalities
2023-04-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Recent advances in mushroom research
2023-04-10
So, mushroom-zombies recently took over a fictional world, but in real life, they’re really not so scary. These fungi range in shape from broad, plate-like portobellos and gangly enokis to a version resembling a giant, shaggy lion’s mane. And now scientists are finding ways to grow mushrooms on new materials, as well as incorporate them in more sustainable products. Below are some recent papers published in ACS journals that report insights into additional applications for mushrooms. Reporters can request free access to these ...
Giant, swimming mouths: Oral dimensions of extant sharks do not accurately predict body size in Dunkleosteus terrelli (Placodermi: Arthrodira)
2023-04-10
A new study by Case Western Reserve University PhD student Russell Engelman published in PeerJ Life & Environment attempts to address a persistent problem in paleontology – what were the size of Dunkleosteus and other late Devonian arthrodire placoderms. Arthrodire placoderms are extinct fishes with had armor covering their head and part of their torso, but like sharks the rest of their skeleton was made of cartilage, meaning most of their body did not preserve when they became fossilized.
Previous size estimates for Dunkleosteus were ...
Scheduled childbirth may greatly reduce preeclampsia, a leading cause of maternal death
2023-04-10
Research Highlights:
Analysis found that more than half of preeclampsia cases that occur during weeks 37-42 of pregnancy (called at-term preeclampsia) may be prevented with timed birth, such as a scheduled induction or Cesarean delivery.
Planned labor inductions and Cesarean deliveries are already widely practiced for a range of reasons, however, they are seldom considered as an intervention to prevent at-term preeclampsia, which may be life-threatening.
Embargoed until 4 a.m. CT/5 a.m. ET Monday, April 10, 2023
DALLAS, April ...
Non-biological factors and social determinants of health important in women’s CVD risk assessment
2023-04-10
Statement Highlights:
A new American Heart Association scientific statement reviews research about racial and ethnic differences in cardiovascular risk factors among women in the U.S.
In addition to traditional risk factors, women of underrepresented races or ethnicities experience challenges in the diagnosis and treatment of cardiovascular conditions due to language barriers, discrimination, difficulties in acculturation or assimilation, lack of financial resources or health insurance, or lack of access to health care.
Women of racial and ethnic backgrounds other than white have been underrepresented ...
Study finds record-breaking rates of sea-level rise along the U.S. Southeast and Gulf coasts
2023-04-10
Sea levels along the U.S. Southeast and Gulf coasts have been rapidly accelerating, reaching record-breaking rates over the past 12 years, according to a new study led by scientists at Tulane University.
In the study, published in Nature Communications, researchers said they had detected rates of sea-level rise of about a half an inch per year since 2010. They attribute the acceleration to the compounding effects of man-made climate change and natural climate variability.
“These rapid rates are unprecedented over at least the 20th century and they have been three times higher than the global average over the same period,” says Sönke ...
New guidelines on catatonia aim to create a step-change in management
2023-04-10
For the first time, the British Association for Psychopharmacology (BAP) has produced a guideline on catatonia. Catatonia is a severe psychiatric disorder that has been associated with a wide range of medical complications. Yet recognition and management remain poor.
Twenty-two experts from across three continents examined the latest research on this important condition and have developed a series of recommendations ranging from diagnosis and investigation to treatment. According to the lead author, Dr Jonathan Rogers of University ...
Targeted testing for HIV in hospital emergency departments has great potential, Spanish researchers say
2023-04-10
**Note: the release below is a special early release from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April). Please credit the conference if you use this story**
Embargo: 2301H UK time Sunday 9 April
**Note – the press release is available in Spanish and Portuguese, see links below**
Targeted testing for HIV in emergency departments has great potential for increasing diagnoses, this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) in Copenhagen, Denmark, (15-18 April), will ...
Engineered plants produce sex perfume to trick pests and replace pesticides
2023-04-10
By using precision gene engineering techniques, researchers at the Earlham Institute in Norwich have been able to turn tobacco plants into solar-powered factories for moth sex pheromones.
Critically, they’ve shown how the production of these molecules can be efficiently managed so as not to hamper normal plant growth.
Pheromones are complex chemicals produced and released by an organism as a means of communication. They allow members of the same species to send signals, which includes letting others know they’re looking for love.
Farmers can hang pheromone dispersers among their crops to mimic the signals ...
Future is bright for gold-based antibiotics
2023-04-08
**Note: the release below is a special early release from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April). Please credit the conference if you use this story**
Embargo: 2301H UK time Friday 7 April
New research being presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) in Copenhagen, Denmark, (15-18 April) has identified several gold-based compounds with the potential to treat multidrug-resistant “superbugs”.
With ...
How to see the invisible: Using the dark matter distribution to test our cosmological model
2023-04-07
It feels like a classical paradox: How do you see the invisible? But for modern astronomers, it is a very real challenge: How do you measure dark matter, which by definition emits no light?
The answer: You see how it impacts things that you can see. In the case of dark matter, astronomers watch how light from distant galaxies bends around it.
An international team of astrophysicists and cosmologists have spent the past year teasing out the secrets of this elusive material, using sophisticated computer simulations and the observations from the one of the most powerful astronomical cameras in the world, the Hyper Suprime-Cam (HSC). The team is led by astronomers from Princeton ...