(Press-News.org) JUPITER, FL, December 28, 2010 – Scientists from the Florida campus of The Scripps Research Institute have identified a molecular interaction between a structural hepatitis C virus protein (HCV) and a protein critical to viral replication. This new finding strongly suggests a novel method of inhibiting the production of the virus and a potential new therapeutic target for hepatitis C drug development.
The study was published in the January 2010 issue (Volume 92, Part 1) of the Journal of General Virology.
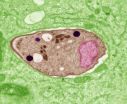
These new data underline the essential role of the viral protein known as "core" as a primary organizer of the infectious HCV particle assembly and support a new molecular understanding of the formation of the viral particle itself.
"While our finding that the HCV core interacts with the non-structural helicase protein was not totally unexpected, this had not really been confirmed until this study," said Scripps Florida Professor Donny Strosberg, who led the study. "But the most exciting part is that small molecule inhibitors of dimerization [the joining of two identical subunits] of core actually inhibit interaction between core and helicase, thus possibly preventing production of an infectious viral particle."
A Viral Plague
Hepatitis C virus infects between 130 and 170 million people worldwide and is the cause of an epidemic of liver cirrhosis and cancer. Because current HCV treatments are only partially effective, a number of alternative molecular mechanisms are actively being pursued as possible drug targets.
One of the critical problems of finding inhibitors for the hepatitis C virus is that it mutates at such prodigious rates. An RNA virus such as hepatitis C can mutate at a rate estimated as high as one million times that of DNA viruses such as the herpes virus.
With this in mind, Strosberg has been examining the core protein, the most conserved protein among all HCV genotypes. Core plays several essential roles in the viral cycle in the host cell. It is particularly important in the assembly of the hepatitis C nucleocapsid or capsid, an essential step in the formation of infectious viral particles; the nucleocapsid is the virus genome protected by a protein coat. By interacting with various structural and non-structural viral proteins, core plays an essential role in the HCV cycle during assembly and release of the infectious virus as well as disassembly of viral particles upon entering host cells. Core also interacts with a number of cellular proteins, possibly contributing to the disarmament of several host defense mechanisms and to the activation of oncogenic pathways.
Last year, Strosberg developed a novel quantitative test for monitoring these protein-protein interactions with the specific goal of identifying inhibitors of the core dimerization, which would block virus production. Strosberg and his colleagues uncovered peptides derived from the core protein of hepatitis C that inhibit not only dimerization of the core protein, but also production of the actual virus.
That earlier study led to the discovery of non-peptidic small organic molecules that strongly inhibited HCV production, one of which, SL201, was used in the new study.
In the new study, Strosberg and his colleagues focused on non-structural proteins that provide functions relating to HCV production, in particular NS3 helicase. The scientists' findings support a growing body of evidence that this protein participates in the assembly and production of infectious viral particles. The interaction of the core protein with this non-structural protein also confirms core as a key organizer of virus assembly and suggests it acts to facilitate the packaging and integration of the newly synthesized viral RNA.
INFORMATION:
The first author of the study, "Dimerization-Driven Interaction of Hepatitis C Virus Core Protein with Ns3 Helicase," is Guillaume Mousseau of Scripps Research. Additional authors include Smitha Kota, S. and Virginia Takahashi of Scripps Research, and David Frick of the University of Wisconsin, Milwaukee. For more information, see http://vir.sgmjournals.org/cgi/content/abstract/92/1/101 .
The study was supported by the state of Florida, The Factor Foundation, and the National Institutes of Health.
About The Scripps Research Institute
The Scripps Research Institute is one of the world's largest independent, non-profit biomedical research organizations, at the forefront of basic biomedical science that seeks to comprehend the most fundamental processes of life. Scripps Research is internationally recognized for its discoveries in immunology, molecular and cellular biology, chemistry, neurosciences, autoimmune, cardiovascular, and infectious diseases, and synthetic vaccine development. An institution that evolved from the Scripps Metabolic Clinic founded by philanthropist Ellen Browning Scripps in 1924, Scripps Research currently employs approximately 3,000 scientists, postdoctoral fellows, scientific and other technicians, doctoral degree graduate students, and administrative and technical support personnel. Headquartered in La Jolla, California, the institute also includes Scripps Florida, whose researchers focus on basic biomedical science, drug discovery, and technology development. Scripps Florida is located in Jupiter, Florida. For more information, see www.scripps.edu.
END
LEXINGTON, KY – Polyethylene mulches, used widely in commercial vegetable production to improve crop yields and produce quality, have distinct disadvantages. Disposal options are limited, and plastic mulches often end up in landfills, being burned, or disposed of illegally. Recycling polyethylene mulches is also a challenge; the mulches used in large-scale vegetable production are contaminated with too much dirt and debris to be recycled directly from the field in most power plants and incinerators. Timothy Coolong from the University of Kentucky's Department of Horticulture ...
QUEBEC, CANADA – A study in HortTechnology featured a new technology that improved greenhouse climates by reducing solar heat radiation and temperatures during the hot summer season. The study, published by a team of Canadian researchers, was the first investigation into the effects of application of the liquid foam technology as a shading method. Results showed that the technology improved greenhouse and plant microclimates and decreased air temperature more than conventional shading curtains traditionally used by greenhouse growers.
Excess temperature, solar radiation, ...
CORVALLIS, OR – Diseases caused by a species of fungus called Phytophthora syringae are responsible for significant economic losses on a wide range of plants, including pear. In the Pacific Northwest region of the United States, disease occurs during the winter in nursery stock, especially on trees that are harvested and stored in coolers or in outdoor sawdust beds. Recent field observations by growers suggest that increased nitrogen content in nursery trees resulting from foliar sprays with urea in the autumn increases tree susceptibility to infection by Phytophthora syringae. ...
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have learned why changes in a single gene, ROP18, contribute substantially to dangerous forms of the parasite Toxoplasma gondii. The answer has likely moved science a step closer to new ways to beat Toxoplasma and many other parasites.
In a study published in Cell Host & Microbe, scientists show that the ROP18 protein disables host cell proteins that would otherwise pop a protective bubble the parasite makes for itself. The parasite puts the bubble on like a spacesuit by forming a membrane around itself ...
STORRS, CT – Woody ornamental plants with colorful or unusually shaped stems, buds, flowers, or fruits represent a growing specialty niche in cut flower production markets. These unique plants can be good prospects for off-season production, offering distinct benefits such as extended growing seasons, respectable financial returns, hardiness, and the ability to produce multiple harvests from single plantings.
A research team from the Department of Plant Science and Landscape Architecture at the University of Connecticut recently published the results of a poll of North ...
DALLAS – Dec. 29, 2010 – Patients with diabetes, kidney disease and anemia who don't respond to treatment with an anti-anemia drug have a higher risk of cardiovascular disease or death, researchers at UT Southwestern Medical Center have found.
The results suggest that testing such patients' responsiveness to the drug and keeping blood iron levels a little low might reduce their risk, said Dr. Robert Toto, professor of internal medicine and clinical sciences and a senior author of the study, which appeared in the New England Journal of Medicine.
"These patients required ...
To succeed in the global business arena, companies that manufacture and distribute products must be agile, efficient and operationally adept at marketing in unique local geographies. At the center of this formidable challenge is the often complex process of translating and localizing high-quality product-related content ¨C typically under intense time pressures. Combined with an ever-expanding list of markets and languages, these multilingual projects can become overwhelming. This requires companies to treat translation as a critical path event, not merely an afterthought, ...
Staging Diva, Debra Gould, is helping new and aspiring home stagers to make 2011 the year they finally follow their dream of earning a good living from their decorating talents by throwing a huge year end sale. From December 26 until midnight EST on December 31, every item in the Staging Diva Store is marked down and the Staging Diva Program is priced lower than it's ever been before as Gould encourages stagers to 'Make 2011 Your Own.'
"2010 has been a challenging year for many of us and everyone's sick of hearing negative headlines about the economy," says Gould. She ...
iFunia, a professional developer of Mac multimedia applications, today launches an ultimate video and DVD package, MediaConverter Suite for Mac, which provides Mac users with an integrated solution to video conversion and DVD ripping In the holiday season, MediaConverter Suite for Mac will be priced at 49, saving $21 from the full price $70.
iFunia MediaConverter Suite for Mac is bundled by two programs: iFunia DVD Ripper Pro for Mac and iFunia Video Converter Pro for Mac. With this MediaConverter Suite, Mac users can easily convert all video files and DVD movie collections ...
Thanks to a number of American and British sitcoms that have gained popularity in Italy, kids today are better placed in understanding English. In fact TV advertisements are now being made with short English phrases as slogans to their products. With the internet making inroads in Italy, almost every Italian finds it imperative to learn English. This has led to a number of people starting tutorials for 'corsi di inglese Roma' or learning English in Rome.
English is the gateway for people all over the world to succeed. No other language has single handedly influenced ...