(Press-News.org) As a four-day work week is trialled in countries across the globe, health researchers at the University of South Australia say they’re ‘all in’ when it comes to a long weekend, especially as new empirical research shows that the extra time off is good for our health.
Assessing changes in daily movements before, during and after holidays, researchers found that people displayed more active, healthy behaviours when they were on holiday, even when they only had a three-day break.
Across the 13-month study period, people generally took an average two to three holidays, each being around 12 days. The most common holiday type was ‘outdoor recreation’ (35 per cent), followed by ‘family/social events’ (31 per cent), ‘rest and relaxation’ (17 per cent) and ‘non-leisure pursuits’ such as caring for others or home renovations (17 per cent).
Specifically, it showed that on holiday people:
engaged in 13 per cent more moderate-to-vigorous physical activity (MVPA) each day (or five min/day more)
were five per cent less sedentary each day (or 29 min/day less)
slept four per cent more each day (or 21 min/day more).
UniSA researcher Dr Ty Ferguson says that the research indicates that people display healthier behaviours when they are on holiday.
“When people go on holiday, they’re changing their everyday responsibilities because they’re not locked down to their normal schedule,” Dr Ferguson says.
“In this study, we found that movement patterns changed for the better when on holiday, with increased physical activity and decreased sedentary behaviour observed across the board.
“We also found that people gained an extra 21 minutes of sleep each day they were on holiday, which can have a range of positive effects on our physical and mental health. For example, getting enough sleep can help improve our mood, cognitive function, and productivity. It can also help lower our risk of developing a range of health conditions, such as obesity, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and depression.
“Interestingly, the size of these changes increased in line with the length of the holiday – so the longer the holiday, the better the health benefits.”
The study used data from the Annual rhythms in adults’ lifestyle and health (ARIA) study where 308 adults (mean age 40.4 years) wore fitness trackers 24 hours a day for 13 months. Minute-by-minute
movement behaviour data were aggregated into daily totals to compare movement behaviours pre-holiday, during holiday and post-holiday.
Senior researcher UniSA’s Prof Carol Maher says that the study offers support for the growing movement for a four-day week.
“A shorter working week is being trialled by companies all over the world. Not surprisingly, employees reported less stress, burnout, fatigue, as well as better mental health and improved work-life balance,” Prof Maher says.
“This study provides empirical evidence that people have healthier lifestyle patterns when they have a short break, such as a three-day weekend. This increase in physical activity and sleep is expected to have positive effects on both mental and physical health, contributing to the benefits observed with a four-day work week.
“Importantly, our study also showed that even after a short holiday, people’s increased sleep remained elevated for two weeks, showing that the health benefits of a three-day break can have lasting effects beyond the holiday itself.
“As the world adapts to a new normal, perhaps it's time to embrace the long weekend as a way to boost our physical and mental health.”
…………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
Contact for interview: Dr Ty Ferguson E: Ty.Ferguson@unisa.edu.au
Media contact: Annabel Mansfield M: +61 479 182 489 E: Annabel.Mansfield@unisa.edu.au
END
Time out: We all need a three-day weekend
2023-04-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
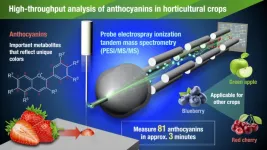
Using a new technique, PESI/MS/MS, to analyze the nutritional compounds in crops
2023-04-13
Anthocyanins are compounds related to the color of plants. They also have beneficial effects on human health and are used as a supplement. Various species of anthocyanins, divided by their molecular shape, are present in plants. Therefore, simple, and rapid, analytical techniques that can distinguish among these species in crops are necessary for breeding and quality assessment. A team of Nagoya University researchers in Japan has used a technique called probe electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (PESI/MS/MS) to analyze anthocyanins in crops. ...
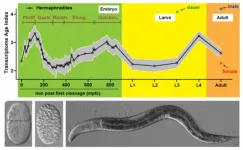
HKU biologists determine the evolutionary age of individual cell types providing critical insights for animal development
2023-04-13
A research team led by Dr Chaogu ZHENG from the School of Biological Sciences at The University of Hong Kong (HKU) has recently made a significant discovery about the evolutionary age of different type of cells in a small animal called Caenorhabditis elegans (C. elegans). By using single-cell transcriptomic data and refined phylostratigraphy, the team determines the transcriptomic age of individual cells, which means they are able to estimate the evolutionary origin of different cells based on the age of the genes expressed in the ...
Coral-eating fish poo may act as ‘probiotics’ for reefs
2023-04-13
Until recently, fish that eat coral — corallivores — were thought to weaken reef structures, while fish that consume algae and detritus — grazers — were thought to keep reefs healthy. But scientists have discovered that feces from grazers leave large lesions on coral, possibly because they contain coral pathogens. By contrast, feces from corallivores may provide a source of beneficial microbes that help coral thrive.
“Corallivorous fish are generally regarded as harmful because they bite the corals,” said Dr Carsten Grupstra of Rice University, ...
New study demonstrates hospital safety climate and organizational characteristics predict healthcare-associated infections and occupational health outcomes
2023-04-13
Arlington, Va., April 13, 2023 – New data published today in the American Journal of Infection Control (AJIC) provide the first published evidence that a positive safety climate and adherence to standard precautions predict key healthcare-associated infection (HAI) and occupational health outcomes among patients and health care workers, respectively. The findings highlight features within hospitals’ organizations and safety climates that could be modified to improve these outcomes.
“Despite the infection prevention and safety benefits associated with standard precautions, generating consistent adherence in the healthcare setting has been ...
Selenium as a predictor of metabolic syndrome in middle age women
2023-04-12
“Recently, optimizing selenium intake in the population to prevent diseases [...] has been an important issue in modern health care worldwide.”
BUFFALO, NY- April 12, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 6, entitled, “Selenium as a predictor of metabolic syndrome in middle age women.”
Metabolic syndrome (MetS) is a widespread clinical entity that has become almost a global epidemic. Selenium plays an important role in metabolic homeostasis. It has been suggested that it ...
A new vision for soybean meal: designer tempeh
2023-04-12
In a novel effort to create the next generation of plant-based, protein-rich environmentally sustainable and savory alternatives to animal meat, a University of Massachusetts Amherst food scientist has turned his attention to soybean meal.
Globally, this byproduct of soybean oil extraction is used almost exclusively for animal feed. In the U.S. alone, some 48 million metric tons of soybean meal was produced in 2022, according to the USDA.
“After the oil extraction, the majority of the protein is in the meal, not the oil,” says Hang ...
Riluzole and Sorafenib in patients with advanced solid tumors: a Phase I trial
2023-04-12
“Our phase I study determined the tolerable dose of this combination and investigated its biologic effects.”
BUFFALO, NY- April 12, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on April 10, 2023, entitled, “A phase I trial of riluzole and sorafenib in patients with advanced solid tumors: CTEP #8850.”
Overexpression of metabotropic glutamate receptor 1 (GRM1) has been implicated in the pathogenesis of multiple cancers. Riluzole, an inhibitor of glutamate release, showed synergistic antitumor activity in combination with the multi-kinase inhibitor sorafenib ...
COVID-19 increased weekday screentime for children: study
2023-04-12
The COVID-19 pandemic led to increased weekday screentime for school-aged children says a new study involving the University of Ottawa published in JAMA Pediatrics.
Researchers examined the change in children’s screen time from prior to the pandemic to three separate pandemic waves between 2020 and 2021. Researchers found a boost of up to 1.35 hours per day during the weekdays compared to prior to the pandemic, particularly with school closures at the onset of the pandemic.
While the weekend time was on par with pre-pandemic levels, ...
In search of a better semiconductor chip
2023-04-12
A University of Texas at Arlington materials science and engineering researcher is working on a project to determine when failure happens in electronic device circuits. The research ultimately will help manufacturers design better semiconductor chips.
Choong-Un Kim, professor in the Department of Materials Science and Engineering, was awarded a $285,0000 grant from the Semiconductor Research Corporation (SRC) for the project “Enabling Electromigration Solver for Solder Joint With Various Packaging Structures and Alloys.” This is the latest in a series of grants he has received from SRC that aims to answer the demand for improved device reliability.
The SRC ...
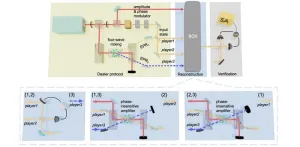
All-optical quantum state sharing via continuous variable system
2023-04-12
Quantum information is a powerful technology for increasing the amount of information that can be processed and communicated securely. Using quantum entanglement to securely distribute a secret quantum state among multiple parties is known as “quantum state sharing.” An important protocol in quantum networks and cryptography, quantum state sharing works like this (in simple terms): a secret quantum state is divided into n shares and given to n players. The secret state can only be reconstructed ...