(Press-News.org) There is a need for new drugs. For example, many of the antibiotics that we have been using for a long time are becoming less effective. Chemists and pharmaceutical scientists are frantically searching for new active substances, especially those that can penetrate cell membranes, as these are the only ones that patients can take orally in the form of a tablet or syrup. Only these active ingredients pass through the intestinal wall in the small intestine and enter the bloodstream to reach the affected area in the body. For active ingredients that cannot penetrate the cell membrane, physicians have no choice but to inject them directly into the bloodstream.
Large molecules with potential
That is why researchers are trying to understand which molecules can penetrate cell membranes and how exactly they do this. For one important and promising class of substances – cyclic peptides – chemists at ETH Zurich have now decoded additional details of the relevant mechanism. “The more we know about this mechanism and the properties a molecule must have, the earlier and more effectively researchers can take this into account when developing new drugs,” says Sereina Riniker, a professor in the Department of Chemistry and Applied Biosciences. She led the study, which has now been published in the Journal of Medicinal Chemistry.
Cyclic peptides are ring-shaped molecules that are much larger than the small molecules that make up the majority of today’s drugs. In some areas of application, however, chemists and pharmaceutical scientists are coming up against their limits with small molecules, which is why they are turning to larger molecules like the cyclic peptides. This substance class includes many pharmaceutically active natural substances, such as cyclosporine, an immunosuppressant that for decades has been used after organ transplants, and many antibiotics.
Possible only with computer modelling
Using computer modelling and a lot of supercomputer power, Riniker and her colleagues were able to elucidate how cyclic peptides similar to cyclosporine cross a membrane. “Only modelling allows us such detailed, high-resolution insights, as there are no experiments that would let us observe an individual molecule crossing a membrane,” Riniker says.
To understand the mechanism, one must know how cyclic peptides are structured: they consist of a central ring structure to which side chains are attached. The molecules are flexible and can dynamically change their structure to adapt to their environment.
Dance through the cell membrane
Riniker’s simulations reveal in detail how a cyclic peptide penetrates the membrane: First, the molecule anchor itself to the membrane’s surface, before penetrating it perpendicular to the membrane. It then changes its three-dimensional shape while passing through, rotating once about its longitudinal axis before reaching the other side of the membrane, where it exits again.
These changes in shape have to do with the different environments the molecule experiences as it moves through the membrane: The body consists largely of water. Both inside and outside of cells, biochemical molecules are mostly present in aqueous solution. Cell membranes, on the other hand, are made up of fatty acids, so water-repellent conditions prevail within them. “To enable it to cross the membrane, the cyclic peptide changes its three-dimensional shape to briefly become as hydrophobic as possible,” Riniker explains.
Changing molecular side chains
For the present study, the researchers investigated eight different cyclic peptides. These are model peptides with no medicinal effect – scientists at pharmaceutical giant Novartis developed them for basic research, which is why Riniker also collaborated with Novartis researchers for this study.
The new findings can now be used in discovering cyclic peptides as new drug candidates. However, Riniker points out a certain trade-off: there are side chains that provide ideal conditions for cyclic peptides to anchor to the membrane surface, but that make it difficult for the peptides to cross the membrane. This new knowledge helps researchers to give advance thought to which side chains they want to use and where on the molecule they are most helpful. All of this could speed up drug discovery and development by ensuring right from the outset that researchers are investigating potential active ingredients that can eventually be taken as a tablet.
END
How drugs get into the blood
2023-04-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
A novel robotic bronchoscope system for navigation and biopsy of pulmonary lesions
2023-04-14
Cancers are notoriously known for their high mortality rate and increasing incidence worldwide. Among them, lung cancer is arguably one of the most devastating ones. According to the World Cancer Research Fund International, lung cancer was the second most common cancer around the world in 2020, with more than 2.2 million new cases and 1.8 million deaths.
However, lung cancer, like other cancers, is easier to treat if caught earlier. “The reported 1-year survival rate for stage V is just 15% to 19% compared with 81% to 85% for stage I, which means that the early ...
Black cancer patients 71% more likely to experience heart damage following chemotherapy treatment
2023-04-14
Chemotherapy is associated with an increased risk of treatment-related heart damage, including heart failure and cerebrovascular disease, for many patients. But a new meta-analysis, presented at the American College of Cardiology’s Advancing the Cardiovascular Care of the Oncology Patient 2023 conference, finds that Black patients or patients of African ancestry have 71% higher odds of cardiotoxicity following cancer treatment compared to White patients.
Cardiotoxicity is any heart damage stemming from cancer treatment or drugs, including ...
Optica Publishing Group announces launch of Optica Quantum
2023-04-14
WASHINGTON—On World Quantum Day, Optica Publishing Group announced it will begin publishing a new journal in September 2023 dedicated to highly selective results in quantum information science and technology (QIST). The new journal, Optica Quantum, joins the Society’s portfolio of the most-cited journals in optics and photonics and will provide the community with articles of the same exceptional standards for quality, novelty, and significance as its parent journal, Optica.
The concept of quantum light serves as a foundation for many quantum technologies and ongoing ...
Farmer’ beetle finds suitable host trees by tracing scent of its fungus crop
2023-04-14
The alnus ambrosia beetle Xylosandrus germanus, also known as the black stem borer, was accidentally introduced by humans from its native east Asia to North America and Europe around the beginning of the 20th century. X. germanus is a so-called ambrosia beetle, which means that it farms its own food: a specialized fungal symbiont which it ‘sows’ and tends inside the galleries that it digs inside wood. It is a destructive invasive pest, known to attack more than 200 species from 51 families of broadleaf and conifer trees. While it prefers to colonize dead ...
Treasure hunt in hot springs?
2023-04-14
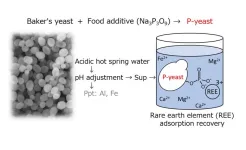
The demand for precious metals and rare earths is expected to continue increasing in the future. Due to limited production areas, recycling from precision equipment and recovering from seawater and hot spring water are needed to ensure a stable supply.
A research group led by Professor Masayuki Azuma and Associate Professor Yoshihiro Ojima of the Osaka Metropolitan University Graduate School of Engineering has successfully developed an adsorbent material that can selectively recover rare earth elements (REEs) using environmentally friendly and inexpensive baker’s yeast and trimetaphosphate, which is used as a food additive.
The research group conducted experiments using ...
Why did the mpox (monkeypox) epidemic wane? Belgian researchers propose theory
2023-04-14
**Note: the release below is from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April). Please credit the conference if you use this story**
Did the recent mpox (formerly known as monkeypox) outbreak end because of “network immunity”? That’s the theory being put forward by Belgian researchers at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) in Copenhagen, Denmark (15-18 April).
2022 saw a global outbreak of mpox, a viral ...
The Lancet Public Health: Hearing aids may protect against a higher risk of dementia associated with hearing loss, study suggests
2023-04-14
Peer-reviewed / Observational study / People
The Lancet Public Health: Hearing aids may protect against a higher risk of dementia associated with hearing loss, study suggests
Study of 437,704 people suggests those experiencing hearing loss and not using hearing aids may have a higher risk of dementia than people without hearing loss. Those using hearing aids did not appear to be at an increased risk of dementia.
After adjusting for other factors, study analysis suggests a 1.7% risk of dementia in people with hearing loss who are not using hearing aids, compared to 1.2% among those without hearing loss ...
One of first studies to assess new bivalent Covid-19 booster vaccine shows it is highly effective in reducing deaths and hospitalizations
2023-04-14
*Note: this is a joint press release from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) and The Lancet Infectious Diseases. Please credit both the congress and the journal in your stories*
Since September, 2022, bivalent mRNA vaccines – which contain elements from both the original wild type COVID strain and an updated component from the omicron strain – have replaced older style monovalent boosters in the USA, Israel, and other countries. These vaccines were designed to help improve vaccine-induced immunity against the omicron variant and subsequent subvariants.
A new study published in The Lancet Infectious Diseases and ...
A $1 million boost to UT’s venture culture
2023-04-14
Adding fuel to The University of Texas at Austin’s startup engine, alumnus William “Billy” Freed, BBA ’81, and his family have given $1 million to the Herb Kelleher Entrepreneurship Center in the McCombs School of Business.
The gift establishes the Freed Family Entrepreneurship Excellence Fund and endows the Freed Family Pitch Competition, previously called DisrupTexas. Freed’s wife Cheryl, BA ’82, JD ’84; sons Tyler, BS ’17, and Russell, BBA ’21; and daughter-in-law Leslie Lugrin Freed, BS ’17, ...
Data can now be processed at the speed of light!
2023-04-14
How can Marvel movie character Ant-Man produce such strong energy out of his small body? The secret lies in the “transistors” on his suit that amplify weak signals for processing. Transistors that amplify electrical signals in the conventional way lose heat energy and limit the speed of signal transfer, which degrades performance. What if it were possible to overcome such limitation and make a high-performance suit that is light and small but without loss of heat energy?
A POSTECH team of Professor Kyoung-Duck Park and Yeonjeong Koo from the Department of Physics and a team from ...