Inositol is a type of sugar that is essential for the viability of eukaryotic cells. Myo-inositol is the precursor of all inositol compounds, which play pivotal roles in cell signaling and metabolism. Consistent with its importance, a disturbance of inositol homeostasis or balance within the body is associated with health issues as diverse as neurological and psychiatric illnesses, myopathies, cancer, and diabetes. Inositol depletion is a hypothesized therapeutic mechanism of action of drugs used to treat bipolar disorder, a devastating psychiatric illness that affects approximately 2% of the population. The identification of specific pathways that are perturbed as a result of inositol deprivation will provide insights into the tumor-suppressive effects of upregulating inositol synthesis and may suggest candidates for new mood-stabilizing, inositol-depleting drugs for the treatment of bipolar disorder.
The study, “Regulation of inositol biosynthesis and consequences of inositol depletion,” will be led by Miriam Greenberg, Ph.D., professor of biological sciences in the College of Liberal Arts and Sciences. According to Greenberg, very little is known about inositol homeostasis in human cells.
“This research project seeks to determine how inositol synthesis is regulated and how its deprivation affects essential cellular functions in human cells,” said Greenberg. “My lab has identified the first negative transcriptional regulator of inositol synthesis in mammalian cells known as inositol hexakisphosphate kinase 1, or IP6K1. IP6K1 represses expression of ISYNA1, the gene coding for the rate-limiting enzyme of inositol synthesis, myo-inositol-3-P synthase (MIPS).”
Successful completion of Greenberg’s proposed studies may lead to the first molecular model of regulation of inositol synthesis in mammalian cells and demonstrate how inositol deprivation affects the cellular stress response and mitochondrial function.
In January, Greenberg was named an American Association for the Advancement of Science Fellow for her distinguished contributions to the field of lipid function, particularly for elucidating the role of cardiolipin in Barth syndrome and identifying molecular mechanisms of control of inositol homeostasis. Greenberg has received numerous grants from the National Institutes of Health and other organizations since 1995 and has been featured in multiple publications. Along with her research, Greenberg has an impressive academic history. She attended Harvard University for her post-doctorate, Albert Einstein College of Medicine for her Ph.D., Loyola University for her M.S. and Reed College for her B.A. in biology.
The project number for this National Institute of General Medical Sciences award is R35GM149271.
About Wayne State University
Wayne State University is one of the nation’s pre-eminent public research universities in an urban setting. Through its multidisciplinary approach to research and education, and its ongoing collaboration with government, industry and other institutions, the university seeks to enhance economic growth and improve the quality of life in the city of Detroit, state of Michigan and throughout the world. For more information about research at Wayne State University, visit research.wayne.edu.
END
Wayne State researcher receives $1.95 million NIH grant to study impact of inositol homeostasis on essential cellular functions
2023-04-14
(Press-News.org) DETROIT – A researcher from Wayne State University’s Department of Biological Sciences has received a five-year, $1.95 million grant from the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health to identify mechanisms that regulate inositol synthesis in mammalian cells and determine the cellular consequences of inositol depletion.
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Head and neck, breast cancer research highlights University of Cincinnati AACR abstracts
2023-04-14
University of Cincinnati Cancer Center researchers will present more than a dozen abstracts at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2023, held in Orlando, Florida, April 14-19, including findings that could advance treatments for head and neck and breast cancers.
Enzyme shows promise as target to treat HPV negative head and neck cancer
Vinita Takiar’s lab in UC’s Department of Radiation Oncology studies how to improve radiation therapy for head and neck cancer patients.
Julianna Korns, a doctoral student working in Takiar’s lab, and her colleagues study an enzyme called Plk1 that allows healthy cells to divide ...
Scientists develop new way to measure wind
2023-04-14
Wind speed and direction provide clues for forecasting weather patterns. In fact, wind influences cloud formation by bringing water vapor together. Atmospheric scientists have now found a novel way of measuring wind – by developing an algorithm that uses data from water vapor movements. This could help predict extreme events like hurricanes and storms.
A study published by University of Arizona researchers in the journal Geophysical Research Letters provides, for the first time, data on the vertical distribution of horizontal winds ...
Ancient DNA reveals the multiethnic structure of Mongolia’s first nomadic empire
2023-04-14
Long obscured in the shadows of history, the world’s first nomadic empire - the Xiongnu - is at last coming into view thanks to painstaking archaeological excavations and new ancient DNA evidence. Arising on the Mongolian steppe 1,500 years before the Mongols, the Xiongnu empire grew to be one of Iron Age Asia’s most powerful political forces - ultimately stretching its reach and influence from Egypt to Rome to Imperial China. Economically grounded in animal husbandry and dairying, the Xiongnu were famously nomadic, building their empire on the backs of horses. ...
2022 Tongan volcanic explosion was largest natural explosion in over a century, new study finds
2023-04-14
The 2022 eruption of a submarine volcano in Tonga was more powerful than the largest U.S. nuclear explosion, according to a new study led by scientists at the University of Miami Rosenstiel School of Marine, Atmospheric, and Earth Science and the Khaled bin Sultan Living Oceans Foundation.
The 15-megaton volcanic explosion from Hunga Tonga-Hunga Ha'apai, one of the largest natural explosions in more than a century, generated a mega-tsunami with waves up to 45-meters high (148 feet) along the coast of Tonga’s Tofua Island and waves up to 17 meters (56 feet) on Tongatapu, ...
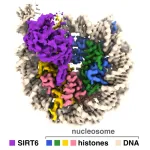
How does an aging-associated enzyme access our genetic material?
2023-04-14
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — New research provides insight into how an enzyme that helps regulate aging and other metabolic processes accesses our genetic material to modulate gene expression within the cell. A team led by Penn State researchers have produced images of a sirtuin enzyme bound to a nucleosome—a tightly packed complex of DNA and proteins called histones—showing how the enzyme navigates the nucleosome complex to access both DNA and histone proteins and clarifying how it functions in humans and other animals.
A paper describing the results appears April 14 in the journal ...
Aston University develops software to untangle genetic factors linked to shared characteristics among different species
2023-04-14
Has potential to help geneticists investigate vital issues such as antibacterial resistance
Will untangle the genetic components shared due to common ancestry from the ones shared due to evolution
The work is result of a four-year international collaboration.
Aston University has worked with international partners to develop a software package to help scientists answer key questions about genetic factors associated with shared characteristics among different species.
Called CALANGO (comparative analysis with annotation-based genomic ...
Single-use surgical items contribute two-thirds of carbon footprint of products used in common operations
2023-04-14
A new analysis of the carbon footprint of products used in the five most common surgical operations carried out in the NHS in England shows that 68% of carbon contributions come from single-use items, such as single-use gowns, patient drapes and instrument table drapes. Published by the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, the analysis highlights significant carbon contributors were the production of single use items and their waste disposal, together with processes for decontaminating reusable products.
Researchers ...
Study: Anti-obesity medications could be sold for lower prices
2023-04-14
ROCKVILLE, Md.—New research shows that several anti-obesity medications could be manufactured and profitability sold worldwide at far lower estimated lower prices compared to their high costs, according to a new study in Obesity, The Obesity Society’s (TOS) flagship journal.
“Access to medicine is a fundamental element of the human right to health. While the obesity pandemic grows, especially amongst low-income communities, effective medical treatments remain inaccessible for millions in need. Our study highlights the inequality in pricing that exists for effective anti-obesity medications, ...
Offering medications for opioid addiction to incarcerated individuals leads to decrease in overdose deaths
2023-04-14
BOSTON – New research from Boston Medical Center concluded that offering medications to treat opioid addiction in jails and prisons leads to a decrease in overdose deaths. Published in JAMA Network Open, the study also found that treating opioid addiction during incarceration is cost-effective in terms of healthcare costs, incarceration costs, and deaths avoided.
Overdoses kill more than 100,000 people per year in America and this number continues to increase every year. People with addiction are more likely to be incarcerated than treated, with those from communities of color who use drugs more likely to be incarcerated than ...
SIAM Conference on Financial Mathematics and Engineering (FM23)
2023-04-14
The objective of the Activity Group on Financial Mathematics and Engineering is to advance fundamental research and implementation of practices in financial engineering, computation, and operations. The group aims at fostering collaborations among applied mathematicians, applied probabilists, statisticians, computer and data scientists, economists, as well as industry practitioners. The conference will expose state-of-art mathematical and computational tools in quantitative finance, including its uses in the public and private sector. The activity group promotes and supports the development of financial mathematics and engineering as an academic discipline. END ...