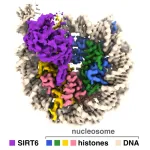
(Press-News.org) UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — New research provides insight into how an enzyme that helps regulate aging and other metabolic processes accesses our genetic material to modulate gene expression within the cell. A team led by Penn State researchers have produced images of a sirtuin enzyme bound to a nucleosome—a tightly packed complex of DNA and proteins called histones—showing how the enzyme navigates the nucleosome complex to access both DNA and histone proteins and clarifying how it functions in humans and other animals.
A paper describing the results appears April 14 in the journal Science Advances.
Sirtuins are a type of enzyme found in organisms ranging from bacteria to humans that play important roles in aging, sensing DNA damage, and suppressing tumors in various cancers. Because of these varied roles, pharmaceutical companies are exploring their potential for biomedical applications. Much effort has focused on the ability of some sirtuins to decrease gene expression by removing a chemical flag from histone proteins.
“In our cells, DNA is not naked like we see it in textbooks; it is spooled around proteins called histones within a large complex called the nucleosome,” said Song Tan, Verne M. Willaman Professor of Molecular Biology at Penn State and an author of the paper. “This packaging can also contribute signals for turning on or turning off genes: Adding an ‘acetyl’ chemical flag to the histone packaging material turns on a gene, while removing the acetyl flag turns the gene off. Sirtuins can silence gene activity by removing the acetyl flag from histones packaged into nucleosomes. Understanding how sirtuins interact with the nucleosome to remove this flag could inform future drug discovery efforts.”
Previous studies have focused on how sirtuins interact with short segments of histones in isolation, in part because such histone “tail” peptides are much easier to work with in the lab. According to Tan, the nucleosome is a hundred times larger than typical histone peptides used in these studies and are consequently much more complicated to work with.
“We have visualized a sirtuin enzyme called SIRT6 on its physiologically relevant substrate—the entire nucleosome,” said Jean-Paul Armache, assistant professor of biochemistry and molecular biology at Penn State and an author of the paper. “And we found that SIRT6 interacts with multiple parts of the nucleosome, not only the histone where the acetyl flag is to be modified”
Using a powerful type of imaging called cryo-electron microscopy with instruments at the Penn State Cryo-Electron Microscopy Facility, the National Cancer Institute and the Pacific Northwest Cryo-EM Center, the researchers identified how SIRT6 positions itself on the nucleosome in order to remove an acetyl group from the K9 position on the histone called H3. Following up with biochemical experiments—in collaboration with the lab of Craig Peterson at the University of Massachusetts Chan Medical School—helped confirm their results.
The researchers found that SIRT6 binds to the nucleosome using a type of connection called an “arginine anchor.” This type of binding—described by Tan’s lab in 2014—is used by a variety of proteins that target a particularly acidic patch on the nucleosome’s surface. In this case, a structural feature of SIRT6 called an extended loop nestles into a divot in the acidic patch, somewhat like a pipe sitting in a ditch.
“The arginine anchor is a common paradigm for how many chromatin proteins interact with the nucleosome,” said Tan. “When we mutated the SIRT6 arginine anchor, the activity at the K9 position was severely affected, supporting a critical role for the SIRT6’s arginine anchor. Surprisingly, this mutation also impacted SIRT6’s enzymatic activity at a different position, K56, located much further away.”
Instead of SIRT6 binding to the nucleosome in two different ways to access the two different histone positions, it is possible that SIRT6 binds to access K9 in a way that might also provide access to K56.
“SIRT6 binds to a partially unwrapped nucleosome, with DNA displaced from the end of the nucleosome” said Armache. “This exposes the K56 position, and it is possible that SIRT6 could essentially lean down to reach that position. We would like to validate this hypothesis in the future. We also hope to explore how SIRT6 works alongside other enzymes and to better understand its role in the response to DNA damage.”
In addition to Tan, Armache, and Peterson, the research team at Penn State includes postdoctoral scholars Un Seng Chio, Othman Rechiche, and Jiang Zhu and graduate student Erik Leith. The research team at the UMass Chan Medical School also includes Alysia Bryll and Jessica Feldman. This research was supported by the U.S. National Institutes of Health and the Pennsylvania Department of Health using Tobacco CURE funds.
END
How does an aging-associated enzyme access our genetic material?
2023-04-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Aston University develops software to untangle genetic factors linked to shared characteristics among different species
2023-04-14
Has potential to help geneticists investigate vital issues such as antibacterial resistance
Will untangle the genetic components shared due to common ancestry from the ones shared due to evolution
The work is result of a four-year international collaboration.
Aston University has worked with international partners to develop a software package to help scientists answer key questions about genetic factors associated with shared characteristics among different species.
Called CALANGO (comparative analysis with annotation-based genomic ...
Single-use surgical items contribute two-thirds of carbon footprint of products used in common operations
2023-04-14
A new analysis of the carbon footprint of products used in the five most common surgical operations carried out in the NHS in England shows that 68% of carbon contributions come from single-use items, such as single-use gowns, patient drapes and instrument table drapes. Published by the Journal of the Royal Society of Medicine, the analysis highlights significant carbon contributors were the production of single use items and their waste disposal, together with processes for decontaminating reusable products.
Researchers ...
Study: Anti-obesity medications could be sold for lower prices
2023-04-14
ROCKVILLE, Md.—New research shows that several anti-obesity medications could be manufactured and profitability sold worldwide at far lower estimated lower prices compared to their high costs, according to a new study in Obesity, The Obesity Society’s (TOS) flagship journal.
“Access to medicine is a fundamental element of the human right to health. While the obesity pandemic grows, especially amongst low-income communities, effective medical treatments remain inaccessible for millions in need. Our study highlights the inequality in pricing that exists for effective anti-obesity medications, ...
Offering medications for opioid addiction to incarcerated individuals leads to decrease in overdose deaths
2023-04-14
BOSTON – New research from Boston Medical Center concluded that offering medications to treat opioid addiction in jails and prisons leads to a decrease in overdose deaths. Published in JAMA Network Open, the study also found that treating opioid addiction during incarceration is cost-effective in terms of healthcare costs, incarceration costs, and deaths avoided.
Overdoses kill more than 100,000 people per year in America and this number continues to increase every year. People with addiction are more likely to be incarcerated than treated, with those from communities of color who use drugs more likely to be incarcerated than ...
SIAM Conference on Financial Mathematics and Engineering (FM23)
2023-04-14
The objective of the Activity Group on Financial Mathematics and Engineering is to advance fundamental research and implementation of practices in financial engineering, computation, and operations. The group aims at fostering collaborations among applied mathematicians, applied probabilists, statisticians, computer and data scientists, economists, as well as industry practitioners. The conference will expose state-of-art mathematical and computational tools in quantitative finance, including its uses in the public and private sector. The activity group promotes and supports the development of financial mathematics and engineering as an academic discipline. END ...
Ambrosia beetles can recognise their food fungi by their scents
2023-04-14
Certain ambrosia beetles species engage in active agriculture. As social communities, they breed and care for food fungi in the wood of trees and ensure that so-called weed fungi spread less. Researchers led by Prof. Dr. Peter Biedermann, professor of Forest Entomology and Forest Protection at the University of Freiburg, now demonstrate for the first time that ambrosia beetles can distinguish between different species of fungi by their scents. "The results can contribute to a better understanding of why beetles selectively colonise trees with conspecifics and how ...
Study snapshot: Following the letter of the law: 2020–2021 retention outcomes under Michigan’s Read by Grade Three Law
2023-04-14
Study: "Following the Letter of the Law: 2020–2021 Retention Outcomes Under Michigan’s Read by Grade Three Law"
Authors: Andrew Niel Utter (Michigan State University), John Westall (Michigan State University), Katharine O. Strunk (Michigan State University)
Embargoed until: 12:01 a.m. CT Friday, April 14
This study will be presented at the place-based component of the 2023 Annual Meeting of the American Educational Research Association.
Session: Minding the Gap in Accountability Policy Implementation
Date/Time: Friday, April 14, 2:50 p.m. – 4:20 p.m. CT
Main Findings:
Under Michigan’s “Read by Grade ...
The ACMG publishes statement on clinical, technical and environmental biases influencing equitable access to clinical genetics/genomics testing
2023-04-14
With the goal of fostering awareness and identifying strategies to reduce bias within the medical genetics field and to improve health equity, members of the ACMG’s Social, Ethical and Legal Issues (SELI) and Diversity, Equity and Inclusion (DEI) Committees collaborated to address factors in which bias can occur in clinical genetic testing in a just-published statement, “Clinical, technical, and environmental biases influencing equitable access to clinical genetics/genomics testing: A points to consider statement of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics (ACMG)”.
This is the first joint statement of the ACMG’s ...
Improving community outreach and engagement
2023-04-14
As researchers continue to make advances in new cancer prevention and treatment methods, it will not have much impact if the community is unaware and not engaged. For this reason, community outreach and engagement (COE) efforts are an important pillar of the University of Cincinnati Cancer Center’s mission.
Cancer Center researchers will present research abstracts on several COE initiatives at the American Association for Cancer Research Annual Meeting 2023, held in Orlando, Florida, April 14-19.
Encouraging ...
Healing the unhealable: New approach helps bones mend themselves
2023-04-14
Young babies and newborn mice can naturally heal damage to the bones that form the top of the skull, but this ability is lost in adults. In a new study published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, University of Pittsburgh researchers developed a novel approach that promoted bone regeneration in mice without implantation of bone tissue or biomaterials.
The technique uses a device similar to an orthodontic wire used to realign teeth to carefully stretch the skull along its sutures, activating ...