(Press-News.org) Newborns of non-refugee immigrant females are at overall lower risk of serious illness and death than those of Canadian-born females in low-income neighbourhoods in Ontario, according to new research published in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.221711.
Previous research has looked at the risk of adverse outcomes for newborns in low- v. high-income neighbourhoods, but there is little evidence on the respective risks for immigrant and nonimmigrant mothers living in similar low-income neighbourhoods. Both immigration status and living in a low-income neighbourhood have been associated with poorer neonatal outcomes.
To understand the risk of severe neonatal morbidity and mortality (SNMM) in infants born to immigrants compared with nonimmigrants, researchers looked at data on all live, in-hospital births of single babies (singleton) at 20–42 weeks' gestation between 2002 and 2019 in Ontario. Ontario, Canada's largest province, receives about 53% of female immigrants entering the country.
Indicators of severe neonatal morbidity included breathing support, intravenous fluid use, early birth (before 32 weeks' gestation), very low birth weight and respiratory distress.
During the study period, there were 414 241 singleton births to 312 124 females aged 15 years and older living in low-income urban neighbourhoods. Of live births, 148 050 were to immigrants and 266 191 to Canadian-born females. The risk of SNMM for newborns of immigrant females was significantly lower than for newborns of Canadian-born females (49.7 per 1000 live births compared with 65.6 per 1000 live births). However, risk varied depending on the country of origin, with a higher risk of SNMM in newborns of immigrants from Jamaica and Ghana and in those with longer residence in Ontario.
The Healthy Immigrant Effect may explain some of these differences.
"Immigrant females who are healthier and more resilient may be most capable of migration; the immigration policy of a host country may preferentially select healthy immigrants," writes Dr. Joel Ray, a physician at St. Michael's Hospital, a site of Unity Health, and scientist at ICES, with coauthors.
"Another explanation may be that some immigrants have greater net income, educational achievement and health literacy than the average for a low-income neighbourhood," adds Dr. Patricia O'Campo, co-author and epidemiologist, St. Michael's Hospital and the University of Toronto, Toronto, Ontario.
The research underscores the importance of looking at trends at neighbourhood levels and that there is variability within areas.
"Efforts should be aimed at improving the overall health and well-being of all females residing in low-income areas, and at determining if the risk of adverse birth outcomes can be equitably reduced among immigrant and nonimmigrant groups," concludes Jennifer Jairam, a PhD candidate from the University of Toronto.
END
Lower risk of severe illness and death in newborns of low-income immigrant than Canadian-born females
2023-04-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Income rank linked to experience of physical pain, irrespective of whether in a rich or poor country, study suggests
2023-04-17
A new study of worldwide polling data suggests that a person’s income rank relative to their peers is linked to their experience of physical pain, with a lower income rank linked to a higher likelihood of experiencing pain. It is the first time such a relationship has been shown.
The study found the link to persist, to the same degree, irrespective of whether the person lives in a rich country or a poor country.
Income rank is the position of an individual’s absolute personal income amount in a list of those amounts ordered from lowest to highest. The higher the position in the list, the higher the income ...
Treatment with immunotherapy alone produces ‘exceptional’ response rates in some melanoma patients
2023-04-16
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Data from a national clinical trial shows that a striking 89% of patients with desmoplastic melanoma responded to immunotherapy (pembrolizumab) alone, suggesting that many patients could avoid the risk for toxicity from combination therapies and achieve cancer control with this approach to treatment.
Desmoplastic melanoma is a subset of melanoma skin cancer that is caused by high levels of ultraviolet (UV) radiation damage and, therefore, a high number of tumor mutations that all contribute to aggressive ...
SWOG S1512 trial sees high response rate to pembrolizumab in patients with unresectable desmoplastic melanoma
2023-04-16
Close to 90 percent of patients with unresectable (inoperable) desmoplastic melanoma, a rare form of skin cancer, saw their cancer improve after treatment with the immunotherapy drug pembrolizumab in a recent clinical trial.
These results from the S1512 trial conducted by the SWOG Cancer Research Network, a group funded by the National Cancer Institute (NCI), are being delivered in an oral presentation at the clinical trials plenary session of the 2023 annual meeting of the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) in Orlando, Florida, on April 16th.
The S1512 ...
AACR: YAP/TEAD inhibitor VT3989 is well tolerated and shows antitumor activity in advanced mesothelioma and NF2-mutant cancers
2023-04-16
ABSTRACT: CT006
ORLANDO, Fla. ― The first-in-class YAP/TEAD inhibitor VT3989 was well tolerated with durable antitumor responses in patients with advanced malignant mesothelioma and other tumors with NF2 mutations, according to results of a Phase I trial led by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center. The first-in-human study was presented today at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2023.
Seven of 69 patients had radiological partial responses that persisted up to at least 21 months, indicating tumor shrinkage, while 34 had stable disease. Patient benefit was observed in patients with both mesothelioma ...
AACR: Penn Medicine preclinical study identifies new target for recurrent ovarian cancer
2023-04-16
ORLANDO – Despite recent advances, ovarian cancer remains the fifth leading cause of cancer-related deaths among women, and there’s a critical need for new treatment options, especially for advanced cancers that grow back after standard of care treatment. Results from a preclinical study, led by researchers from the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania, verified a new target for drug-resistant ovarian cancer and provided data to support a treatment approach that is already making its way into clinical trials.
Sarah Gitto, PhD, an instructor of Pathology and Laboratory ...
Adding new vaccine type to leading immunotherapy dramatically reduced melanoma recurrence
2023-04-16
VIDEO OF RESEARCHER AND PATIENT COMMENTARY IS AVAILABLE AT:
https://bcove.video/3mxxASq
The combination of an experimental mRNA vaccine with an immunotherapy reduced the likelihood of melanoma recurring or causing death by 44% when compared to immunotherapy alone, a new clinical trial shows.
Led by researchers at NYU Langone Health and its Perlmutter Cancer Center, the randomized phase 2b trial involved men and women who had surgery to remove melanoma from lymph nodes or other organs and were at high risk of the disease returning in sites distant from the original cancer. ...
AACR: Lung cancer outcomes significantly improved with immunotherapy-based treatment given before and after surgery
2023-04-16
ABSTRACT: CT005
ORLANDO, Fla. ― A regimen of pre-surgical immunotherapy and chemotherapy followed by post-surgical immunotherapy significantly improved event-free survival (EFS) and pathologic complete response (pCR) rates compared to chemotherapy alone for patients with operable non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC), according to Phase III trial results presented today by researchers from The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2023.
The ...
A new breakthrough in Alzheimer disease research - visualizing reactive astrocyte-neuron interaction
2023-04-16
Recently, a team of South Korean scientists led by Director C. Justin LEE of the Center for Cognition and Sociality within the Institute for Basic Science made a new discovery that can revolutionize both the diagnosis and treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. The group demonstrated a mechanism where the astrocytes in the brain uptake elevated levels of acetates, which turns them into hazardous reactive astrocytes. They then went on further to develop a new imaging technique that takes advantage of this mechanism to directly observe the astrocyte-neuron interactions.
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), one of ...
Statin use is associated with lower risk of stroke in patients with atrial fibrillation
2023-04-16
Barcelona, Spain – 16 April 2023: A region-wide study in more than 50,000 patients with atrial fibrillation has found reduced risks of stroke and transient ischaemic attack in those who started statins within a year of diagnosis compared with those who did not. The findings are presented at EHRA 2023, a scientific congress of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC).1
“Our study indicates that taking statins for many years was even more protective against stroke than short-term use,” said study author Ms. Jiayi Huang, a PhD student at the University of Hong Kong, China.
Atrial fibrillation is the most common ...
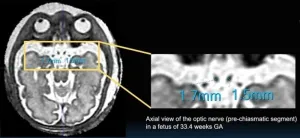
ARRS Annual Meeting: 3D SVR MRI helps delineate fetal optic nerve pathway
2023-04-16
Honolulu, HI | April 16, 2023—An award-winning Scientific Online Poster presented during the 2023 ARRS Annual Meeting on the island of Oahu explained how the novel technique of three-dimensional (3D) slice-to-volume (SVR) MRI allows for precise delineation and measurement of the fetal optic pathway (FOP).
Noting the limited fetal presentation and low reproducibility of ultrasound-based techniques, as well as conventional MRI’s inconsistencies in FOP visualization due to low resolution (i.e., large slice thickness), “our preliminary results nevertheless demonstrate the promises and utility of this technique,” said Eric Juang, MS, of Creighton University ...