(Press-News.org) A parabolic dish on the EPFL campus is easily overlooked, resembling a satellite dish or other telecommunications infrastructure. But this dish is special, because it works like an artificial tree. After concentrating solar radiation nearly 1,000 times, a reactor above the dish uses that sunlight to convert water into valuable and renewable hydrogen, oxygen, and heat.
“This is the first system-level demonstration of solar hydrogen generation. Unlike typical lab-scale demonstrations, it includes all auxiliary devices and components, so it gives us a better idea of the energy efficiency you can expect once you consider the complete system, and not just the device itself,” says Sophia Haussener, head of the Laboratory of Renewable Energy Science and Engineering (LRESE) in the School of Engineering.
“With an output power of over 2 kilowatts, we’ve cracked the 1-kilowatt ceiling for our pilot reactor while maintaining record-high efficiency for this large scale. The hydrogen production rate achieved in this work represents a really encouraging step towards the commercial realization of this technology.”
The work builds on preliminary research demonstrating the concept on the laboratory scale, using LRESE’s high-flux solar simulator, which was published in Nature Energy in 2019. Now, the team has published the results of their scaled-up, efficient, and multi-product process under real-world conditions in the same journal.
Waste not, want not
Hydrogen production from water using solar energy is referred to as artificial photosynthesis, but the LRESE system is unique for its ability to also produce heat and oxygen at scale.
After the dish concentrates the sun’s rays, water is pumped into its focus spot, where an integrated photoelectrochemical reactor is housed. Within this reactor, photoelectrochemical cells use solar energy to electrolyze, or split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. Heat is also generated, but instead of being released as a system loss, this heat is passed through a heat exchanger so that it can be harnessed – for ambient heating, for example.
In addition to the system’s primary outputs of hydrogen and heat, the oxygen molecules released by the photo-electrolysis reaction are also recovered and used.
“Oxygen is often perceived as a waste product, but in this case, it can also be harnessed – for example for medical applications,” Haussener says.
Industrial and residential energy
The system is suitable for industrial, commercial, and residential applications; in fact, LRESE-spinoff SoHHytec SA is already deploying and commercializing it. The EPFL start-up is working with a Swiss-based metal production facility to build a demonstration plant at the multi-100-kilowatt scale that will produce hydrogen for metal annealing processes, oxygen for nearby hospitals, and heat for the factory’s hot-water needs.
“With the pilot demonstration at EPFL, we have achieved a major milestone by demonstrating unprecedented efficiency at high output power densities. We are now scaling up a system in an artificial garden-like setup, where each of these ‘artificial trees’ is deployed in a modular fashion,” says SoHHytec co-founder and CEO Saurabh Tembhurne.
The system could be used to provide residential and commercial central heating and hot water, and to power hydrogen fuel cells. At an output level of about half a kilogram of solar hydrogen per day, the EPFL campus system could power around 1.5 hydrogen fuel cell vehicles driving an average annual distance; or meet up to half the electricity demand and more than half of the annual heat demand of a typical four-person Swiss household.
With their artificial photosynthesis system well on its way to scale-up, Haussener is already exploring new technological avenues. In particular, the lab is working on a large-scale solar-powered system that would split carbon dioxide instead of water, yielding useful materials like syngas for liquid fuel, or the green plastic precursor ethylene.
END
A solar hydrogen system that co-generates heat and oxygen
EPFL researchers have built a pilot-scale solar reactor that produces usable heat and oxygen, in addition to generating hydrogen with unprecedented efficiency for its size.
2023-04-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Methane from megafires: more spew than we knew
2023-04-17
Using a new detection method, UC Riverside scientists found a massive amount of methane, a super-potent greenhouse gas, coming from wildfires — a source not currently being accounted for by state air quality managers.
Methane warms the planet 86 times more powerfully than carbon dioxide over the course of 20 years, and it will be difficult for the state to reach its required cleaner air and climate goals without accounting for this source, the researchers said.
Wildfires emitting methane ...
Salmonella solution
2023-04-17
McMaster University researchers have developed a rapid and inexpensive test for Salmonella contamination in chicken and other food – one that’s easier to use than a home COVID test.
The test, described in a new paper in the journal Angewandte Chemie, could improve food safety, reduce the cost of processing fresh poultry and other foods, and help to limit broad recalls to batches that have specifically been identified as contaminated.
The researchers have shown that the test provides accurate results in an hour or less without the need for accessories or a power source, compared ...
New genetic target for male contraception identified
2023-04-17
PULLMAN, Wash. – Discovery of a gene in multiple mammalian species could pave the way for a highly effective, reversible and non-hormonal male contraceptive for humans and animals.
Washington State University researchers identified expression of the gene, Arrdc5, in the testicular tissue of mice, pigs, cattle and humans. When they knocked out the gene in mice, it created infertility only in the males, impacting their sperm count, movement and shape. The researchers detailed their findings in the journal Nature Communications.
“The study identifies this gene for the first time as being expressed ...
The annual report on antisemitism worldwide – 2022: Haredi Jews – The main target of antisemitic assaults
2023-04-17
Embargoed until Monday, April 17th at 11AM (Israel time)
On the eve of Holocaust Remembrance Day
Tel Aviv University in cooperation with the Anti-Defamation League (ADL) presents
The Annual Report on Antisemitism Worldwide – 2022:
Haredi Jews – The Main Target of Antisemitic Assaults
2002 saw another sharp increase in the number of antisemitic incidents in the United States and other Western countries, alongside a decline in several other countries, including France, Germany, and the United Kingdom.
The report found that Haredi Jews are the main victims of antisemitic assaults in the West. Physical attacks, which ...
8.8 million euros for accelerated drug repurposing for rare neurological disorders
2023-04-17
The SIMPATHIC Consortium, led by the Radboud University Medical Center and Amsterdam UMC, has developed a new approach to expedite the use of existing drugs for groups of patients with rare neurological disorders. The consortium has been awarded an 8.8-million-euro grant from the Horizon Europe program to further develop this innovative method.
Traditionally, drugs are developed one disease at a time, which is costly and time-consuming. It often takes a long time before patients can use a new drug. The international ...
Does depression affect the care and survival of patients with breast cancer?
2023-04-17
Study’s findings suggest that detecting and treating depression are critical to patient health.
In a recent study, having depression before or after a breast cancer diagnosis was associated with a lower likelihood of survival. The findings are published by Wiley online in CANCER, a peer-reviewed journal of the American Cancer Society.
For the study, Bin Huang, DrPH, of the University of Kentucky Markey Cancer Center, and his colleagues analyzed data from the Kentucky Cancer Registry to identify adult women diagnosed with primary invasive breast cancer in 2007–2011. Utilizing the health claims–linked cancer registry data, the ...
Teen jobs: Some parents cautious about negative impact on grades, sleep and social life
2023-04-17
For many teens, that first formal job as a fast-food cashier, barista or lifeguard is a rite of passage.
And while some families tout the positives of job experiences, such as improving their teen’s money management skills and self-esteem, others worry about the potential to negatively impact sleep, schedules and grades, according to the University of Michigan Health C.S. Mott Children’s Hospital National Poll on Children’s Health.
But finding a job that meets logistical considerations – with schedules and transportation topping the list ...
ARRS Annual Meeting: 4D flow MRI, 3D phantoms benefit atrial fibrillation patients
2023-04-17
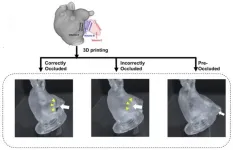
Honolulu, HI | April 17, 2023—Findings from an award-winning Scientific Online Poster presented during the 2023 ARRS Annual Meeting at the Hawaiian Convention Center suggest that correctly occluded left atrial appendages (LAAs) could present maximal reduction in left atrial (LA) flow stasis and thrombogenicity, offering a clinical goal for the procedure in patients with atrial fibrillation.
Pointing out the paucity of knowledge in atrial fibrillation (AF) populations regarding the actual flow dynamic changes before and after percutaneous left atrial appendage occlusion (LAAO), “we aimed to evaluate LA flow dynamics for pre-occluded, correctly occluded, and incorrectly ...
American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS) Global Partners honor Jeong Min Lee, Korean Society of Radiology (KSR) President, with ARRS membership
2023-04-17
Honolulu, HI | April 17, 2023—The Global Partner Society Program of the American Roentgen Ray Society (ARRS) is proud to announce that Jeong Min Lee, President of the Korean Society of Radiology (KSR) and professor of radiology at South Korea’s Seoul National University Hospital, will receive Honorary Membership in ARRS during the opening ceremony of the 2023 ARRS Annual Meeting in Honolulu, HI.
As per Section 6 of the ARRS bylaws, honorary members of the ARRS shall be those who have rendered valuable service ...
Over 1 million lives saved across Europe by COVID-19 vaccines since the end of 2020
2023-04-17
**Note: the release below is from the European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID 2023, Copenhagen, 15-18 April). Please credit the conference if you use this story**
COVID-19 vaccination directly saved at least 1,004,927 lives across Europe between December 2020 and March 2023, according to new research being presented at this year’s European Congress of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases (ECCMID) in Copenhagen, Denmark (15-18 April).
The new estimates by WHO/Europe and presented at the conference by Dr Margaux Meslé, Epidemiologist at WHO/Europe highlight the striking ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
attexis RCT shows clinically relevant reduction in adult ADHD symptoms and is published in Psychological Medicine
Cellular changes linked to depression related fatigue
First degree female relatives’ suicidal intentions may influence women’s suicide risk
Specific gut bacteria species (R inulinivorans) linked to muscle strength
Wegovy may have highest ‘eye stroke’ and sight loss risk of semaglutide GLP-1 agonists
New African species confirms evolutionary origin of magic mushrooms
Mining the dark transcriptome: University of Toronto Engineering researchers create the first potential drug molecules from long noncoding RNA
IU researchers identify clotting protein as potential target in pancreatic cancer
Human moral agency irreplaceable in the era of artificial intelligence
Racial, political cues on social media shape TV audiences’ choices
New model offers ‘clear path’ to keeping clean water flowing in rural Africa
Ochsner MD Anderson to be first in the southern U.S. to offer precision cancer radiation treatment
Newly transferred jumping genes drive lethal mutations
Where wells run deep, biodiversity runs thin
Q&A: Gassing up bioengineered materials for wound healing
From genetics to AI: Integrated approaches to decoding human language in the brain
Leora Westbrook appointed executive director of NR2F1 Foundation
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
[Press-News.org] A solar hydrogen system that co-generates heat and oxygenEPFL researchers have built a pilot-scale solar reactor that produces usable heat and oxygen, in addition to generating hydrogen with unprecedented efficiency for its size.