(Press-News.org) A research model of dietary intake in 184 countries, developed by researchers at the Friedman School of Nutrition Science and Policy at Tufts University, estimates that poor diet contributed to over 14.1 million cases of type 2 diabetes in 2018, representing over 70% of new diagnoses globally. The analysis, which looked at data from 1990 and 2018, provides valuable insight into which dietary factors are driving type 2 diabetes burden by world region. The study was published April 17 in the journal Nature Medicine.
Of the 11 dietary factors considered, three had an outsized contribution to the rising global incidence of type 2 diabetes: Insufficient intake of whole grains, excesses of refined rice and wheat, and the overconsumption of processed meat. Factors such as drinking too much fruit juice and not eating enough non-starchy vegetables, nuts, or seeds, had less of an impact on new cases of the disease.
“Our study suggests poor carbohydrate quality is a leading driver of diet-attributable type 2 diabetes globally, and with important variation by nation and over time,” says senior author Dariush Mozaffarian, Jean Mayer Professor of Nutrition and dean for policy at the Friedman School. “These new findings reveal critical areas for national and global focus to improve nutrition and reduce devastating burdens of diabetes.”
Type 2 diabetes is characterized by the resistance of the body’s cells to insulin. Of the 184 countries included in the Nature Medicine study, all saw an increase in type 2 diabetes cases between 1990 and 2018, representing a growing burden on individuals, families, and healthcare systems.
The research team based their model on information from the Global Dietary Database, along with population demographics from multiple sources, global type 2 diabetes incidence estimates, and data on how food choices impact people living with obesity and type 2 diabetes from multiple published papers.
The analysis revealed that poor diet is causing a larger proportion of total type 2 diabetes incidence in men versus women, in younger versus older adults, and in urban versus rural residents at the global level.
Regionally, Central and Eastern Europe and Central Asia —particularly in Poland and Russia, where diets tend to be rich in red meat, processed meat, and potatoes —had the greatest number of type 2 diabetes cases linked to diet. Incidence was also high in Latin America and the Caribbean, especially in Colombia and Mexico, which was credited to high consumption of sugary drinks, processed meat, and low intake of whole grains.
Regions where diet had less of an impact on type 2 diabetes cases included South Asia and Sub-Sharan Africa —though the largest increases in type 2 diabetes due to poor diet between 1990 and 2018 were observed in Sub-Saharan Africa. Of the 30 most populated countries studied, India, Nigeria, and Ethiopia had the fewest case of type 2 diabetes related to unhealthy eating.
“Left unchecked and with incidence only projected to rise, type 2 diabetes will continue to impact population health, economic productivity, health care system capacity, and drive heath inequities worldwide,” says first author Meghan O’Hearn. She conducted this research while a PhD candidate at the Friedman School and currently works as Impact Director for Food Systems for the Future, a non-profit institute and for-profit fund that enables innovative food and agriculture enterprises to measurably improve nutrition outcomes for underserved and low-income communities. “These findings can help inform nutritional priorities for clinicians, policymakers, and private sector actors as they encourage healthier dietary choices that address this global epidemic.”
Other recent studies have estimated that 40% of type 2 diabetes cases globally are attributed to suboptimal diet, lower than the 70% reported in the Nature Medicine paper. The research team attributes this to the new information in their analysis, such as the first ever inclusion of refined grains, which was one of the top contributors to diabetes burdens; and updated data on dietary habits based on national individual-level dietary surveys, rather than agricultural estimates. The investigators also note that they presented the uncertainty of these new estimates, which can continue to be refined as new data emerges.
Research reported in this article was supported by the Bill and Melinda Gates Foundation. Complete information on authors, funders, methodology, and conflicts of interest is available in the published paper. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the funders.
END
Study links poor diet to 14 million cases of type 2 diabetes globally
Researchers from Tufts University estimate 7 out of 10 cases of type 2 diabetes worldwide in 2018 linked to food choices
2023-04-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
SpyLigation uses light to switch on proteins
2023-04-17
Scientists can now use light to activate protein functions both inside and outside of living cells. The new method, called light-activated SpyLigation, can turn on proteins that are normally off to allow researchers to study and control them in more detail. This technology has potential uses in tissue engineering, regenerative medicine, and understanding how the body works.
Proteins perform nearly every important task in biology, including processing DNA, metabolizing nutrients, and fighting off infections. When, where, and how proteins become active is important for a variety of biological processes. Increasingly, ...
Dexamethasone for inpatients with COVID-19 in a national cohort
2023-04-17
About The Study: In this national multicenter cohort study of inpatients with COVID-19, early administration of dexamethasone was associated with significantly reduced odds of mortality or discharge to hospice in those requiring supplemental oxygen or mechanical ventilation and/or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation but not in those requiring no supplemental oxygen or noninvasive positive pressure ventilation. These results support the continued use of systemic dexamethasone in patients hospitalized with COVID-19.
Authors: Laine ...
Investigational drug may improve stem cell transplantation for multiple myeloma patients
2023-04-17
The standard treatment for patients with multiple myeloma often includes stem cell transplantation in which the patient’s own stem cells are harvested and stored while the patient receives intensive chemotherapy to kill the cancer. Then, the patient’s stem cells are returned to the patient to help with recovery. But for a significant proportion of patients, the number of stem cells that can be harvested is not optimal for transplant and negatively affects patient outcomes.
However, an international phase 3 clinical trial led by physicians at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis has shown that the investigational ...
University of Rochester researchers discover how to steer army of immune cells toward cancer
2023-04-17
Immunotherapy, particularly CAR T-Cell treatment for cancer, is extending the lives of many patients. But sometimes the therapy randomly migrates to places it shouldn’t go, tucking into the lungs or other noncancerous tissue and causing toxic side effects. A University of Rochester/Wilmot Cancer Institute team discovered the molecule responsible for guiding T cells toward tumors, setting the stage for scientists to improve upon the groundbreaking treatment.
The next step is to find a drug that can manipulate the ...
Poverty is the fourth greatest cause of U.S. deaths, analysis published in JAMA finds.
2023-04-17
Poverty has long been linked to shorter lives. But just how many deaths in the United States are associated with poverty? The number has been elusive – until now.
UC Riverside paper published Monday in the Journal of the American Medical Association associated poverty with an estimated 183,000 deaths in the United States in 2019 among people 15 years and older.
This estimate is considered conservative because the data is from the year just prior to the COVID-19 pandemic, which caused spikes in deaths worldwide and continues to take its toll.
The analysis found that only heart disease, ...
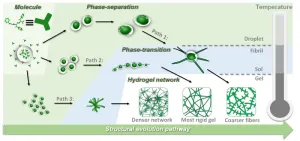
Steering phase-separated droplets to control mechanical properties of supramolecular peptide hydrogels
2023-04-17
Self-assembled peptide supramolecular hydrogels have shown great application prospects in various areas, including tissue engineering, drug delivery, and biosensing.
Precisely and flexibly controlling the mechanical properties of peptide hydrogels to match the targeted applications is important. The common methods to regulate the mechanical properties of supramolecular hydrogels generally include: changing the formula (different peptide sequences, adding cross-linking agents) or changing the environmental conditions (concentration, temperature, pH and ions), both of which inevitably change the chemical composition of the ...
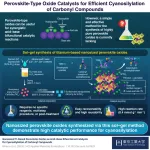
Facile synthesis of high-performance perovskite oxides for acid–base catalysis
2023-04-17
Bifunctional acid−base catalysts are highly desirable for industrially relevant chemical processes. Owing to their ability to activate electrophiles and nucleophiles simultaneously, they allow the catalysis to proceed synergistically and cooperatively. Solid acid−base catalysts are particularly advantageous since they are reusable and result in no waste products. However, controlling the structure of such catalysts for cooperatively workable active sites is challenging. Simple and effective methods that enable the synthesis of high-performance solid acid−base ...
Quantum light source goes fully on-chip, bringing scalability to the quantum cloud
2023-04-17
An international team of researchers from Leibniz University Hannover (Germany), the University of Twente (Netherlands), and the start-up company QuiX Quantum has presented an entangled quantum light source fully integrated for the first time on a chip. “Our breakthrough allowed us to shrink the source size by a factor of more than 1000, allowing reproducibility, stability over a longer time, scaling, and potentially mass-production. All these characteristics are required for real-world applications such as quantum processors,” says Prof. Dr. Michael Kues, head of the Institute ...
Lipid molecules help to get stroke therapies into the brain
2023-04-17
Researchers from Tokyo Medical and Dental University (TMDU) find that, when a stroke therapy is linked to a specific kind of lipid and injected into the blood, it is taken up preferentially in the stroke-lesioned brain
Tokyo, Japan – To get therapies into the brain after a stroke, researchers are increasingly making use of the blood–brain barrier, which allows only certain molecules to pass from the blood into the brain. In a study published earlier this year in Molecular Therapy, ...
Ben-Gurion University researcher and colleagues pen 10 simple rules for socially responsible science
2023-04-17
BEER-SHEVA, Israel, April 17, 2023 – Scientific research must meet clear ethical guidelines to prevent harm to participants. However, research can also indirectly harm individuals and social groups, for example by shaping social perceptions and inspiring policy. Researchers receive little to no training on how to consider and minimize such harm.
To that end, Ben-Gurion University of the Negev's Dr. Niv Reggev and his international colleagues have published ten simple rules for socially responsible science. The ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Research alert: Understanding substance use across the full spectrum of sexual identity
Pekingese, Shih Tzu and Staffordshire Bull Terrier among twelve dog breeds at risk of serious breathing condition
Selected dog breeds with most breathing trouble identified in new study
Interplay of class and gender may influence social judgments differently between cultures
Pollen counts can be predicted by machine learning models using meteorological data with more than 80% accuracy even a week ahead, for both grass and birch tree pollen, which could be key in effective
Rewriting our understanding of early hominin dispersal to Eurasia
Rising simultaneous wildfire risk compromises international firefighting efforts
Honey bee "dance floors" can be accurately located with a new method, mapping where in the hive forager bees perform waggle dances to signal the location of pollen and nectar for their nestmates
Exercise and nutritional drinks can reduce the need for care in dementia
Michelson Medical Research Foundation awards $750,000 to rising immunology leaders
SfN announces Early Career Policy Ambassadors Class of 2026
Spiritual practices strongly associated with reduced risk for hazardous alcohol and drug use
Novel vaccine protects against C. diff disease and recurrence
An “electrical” circadian clock balances growth between shoots and roots
Largest study of rare skin cancer in Mexican patients shows its more complex than previously thought
Colonists dredged away Sydney’s natural oyster reefs. Now science knows how best to restore them.
Joint and independent associations of gestational diabetes and depression with childhood obesity
Spirituality and harmful or hazardous alcohol and other drug use
New plastic material could solve energy storage challenge, researchers report
Mapping protein production in brain cells yields new insights for brain disease
Exposing a hidden anchor for HIV replication
Can Europe be climate-neutral by 2050? New monitor tracks the pace of the energy transition
Major heart attack study reveals ‘survival paradox’: Frail men at higher risk of death than women despite better treatment
Medicare patients get different stroke care depending on plan, analysis reveals
Polyploidy-induced senescence may drive aging, tissue repair, and cancer risk
Study shows that treating patients with lifestyle medicine may help reduce clinician burnout
Experimental and numerical framework for acoustic streaming prediction in mid-air phased arrays
Ancestral motif enables broad DNA binding by NIN, a master regulator of rhizobial symbiosis
Macrophage immune cells need constant reminders to retain memories of prior infections
Ultra-endurance running may accelerate aging and breakdown of red blood cells
[Press-News.org] Study links poor diet to 14 million cases of type 2 diabetes globallyResearchers from Tufts University estimate 7 out of 10 cases of type 2 diabetes worldwide in 2018 linked to food choices