(Press-News.org) After three popular primetime medical dramas included storylines about health harms from using e-cigarettes, hundreds of people took to Twitter to comment – including some who said they planned to quit vaping because of what they saw on the shows. A new analysis led by University of Pittsburgh School of Public Health scientists and published in the Journal of Health Communication examines the tweets for insights into the use of television shows to share public health messaging.
Following the January 2020 episodes of New Amsterdam, Chicago Med and Grey’s Anatomy that each included plots involving adolescents with vaping-associated lung-injury, also known as EVALI, at least 641 tweets commented on the shows and e-cigarettes. Nearly half the tweets commented on the storylines’ realism and 23.1% expressed enjoyment of the storyline, though a sizeable minority commented that the shows weren’t realistic in part because they didn’t involve cannabis oil-containing e-cigarettes. About 12% of the tweets expressed knowledge about vaping and 4.4% mentioned behavior, including intention to quit vaping.
“Given the rapid increase in e-cigarette use among U.S. adolescents, it is vital for public health professionals to develop ways in which to effectively communicate the harms of vaping to young people,” said lead author Beth Hoffman, Ph.D., M.P.H., postdoctoral researcher at Pitt Public Health’s Department of Behavioral and Community Health. “Our analysis suggests that primetime television may be a powerful way to positively shape viewers’ knowledge about the dangers associated with e-cigarette use.”
END
Medical dramas influence thoughts on dangers from vaping, new Twitter analysis reveals
2023-04-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
The Green Mediterranean / high polyphenols diet promotes dramatic proximal aortic de-stiffening, twice as much as the healthy Mediterranean diet
2023-04-17
BEER-SHEVA, Israel, April 17, 2023 – The green Mediterranean – high polyphenols diet substantially regresses proximal aortic stiffness (PAS), a marker of vascular aging and increased cardiovascular risk. The green Mediterranean diet was pitted against the healthy Mediterranean diet and a healthy guideline-recommended control diet in the DIRECT PLUS, a large-scale clinical intervention trial. Researchers found that the green Mediterranean diet regressed proximal aortic stiffness by 15%, the Mediterranean diet by 7.3%, and ...
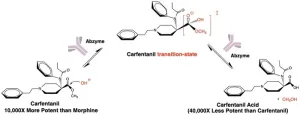
Therapeutic can seek and destroy potent opioid to treat overdoses
2023-04-17
LA JOLLA, CA—A new therapeutic designed by Scripps Research chemists can alter the molecular structure of the potent opioid carfentanil, inactivating the opioid and reversing a carfentanil overdose. The compound, which is described in an ACS Pharmacology & Translational Science paper published on April 17, 2023, and hasn’t yet been studied in humans, works in a fundamentally different way than existing treatments for opioid overdose.
Carfentanil is up to 10,000 times more potent than morphine and 100 times stronger than fentanyl, making it one of the deadliest opioids. It is typically only used as a tranquilizer ...
No magic number for time it takes to form habits
2023-04-17
Putting on your workout clothes and getting to the gym can feel like a slog at first. Eventually, you might get in the habit of going to the gym and readily pop over to your Zumba class or for a run on the treadmill. A new study from social scientists at Caltech now shows how long it takes to form the gym habit: an average of about six months.
The same study also looked at how long it takes health care workers to get in the habit of washing their hands: an average of a few weeks.
“There is no magic number for habit formation,” says Anastasia Buyalskaya (PhD ’21), now an assistant professor of marketing at HEC Paris. Other authors ...
Cai wins 2023 Gopal K. Shenoy Excellence in Beamline Science Award
2023-04-17
Cai from Argonne’s X-ray Science division recognized for his commitment and advances in beamline science, most notably X-ray diffraction.
Physicist Zhonghou Cai is the 2023 recipient of the Gopal K. Shenoy Excellence in Beamline Science Award. He is a beamline scientist at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory.
The annual award recognizes active beamline scientists at the Advanced Photon Source (APS), a DOE Office of Science user facility, for significant contributions to research or instrumentation and support of the beamline user community. The APS Users Office, which grants the award, renamed it ...
AACR: Mutations in three key genes associated with poor outcomes in lung cancer patients treated with KRAS G12C inhibitors
2023-04-17
ABSTRACT: 3431
ORLANDO, Fla. ― A new study led by researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center discovered that co-occurring mutations in three tumor suppressor genes – KEAP1, SMARCA4 and CDKN2A – are linked with poor clinical outcomes in patients with KRAS G12C-mutant non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) treated with the KRAS G12C inhibitors adagrasib or sotorasib.
The findings were presented today at the American Association for Cancer Research (AACR) Annual Meeting 2023 and published in Cancer Discovery, a journal of the AACR. This study, which encompasses the largest cohort to date of patients with KRAS G12C-mutant NSCLC treated with ...
Scientists create powerful, most-accurate tools to research deadliest blood cancer, study says
2023-04-17
New York, NY (April 17, 2023) — Tisch Cancer Center scientists have developed unique models of the deadliest blood cancer, acute myeloid leukemia (AML), creating a transformative resource to study this cancer and eventually its drug response and drug resistance. The models were described in a late-breaking abstract at the annual meeting of the American Association of Cancer Research and simultaneously published in Blood Cancer Discovery, a journal of the American Association for Cancer Research.
These are the first powerful models that are ...
EMBARGOED: Two brain networks are activated while reading, study finds
2023-04-17
When a person reads a sentence, two distinct networks in the brain are activated, working together to integrate the meanings of the individual words to obtain more complex, higher-order meaning, according to a study at UTHealth Houston.
The study, led by Oscar Woolnough, PhD, postdoctoral research fellow in the Vivian L. Smith Department of Neurosurgery with McGovern Medical School at UTHealth Houston, and Nitin Tandon, MD, professor and chair ad interim of the department in the medical school, was published ...
The surprising science behind long-distance bird migration
2023-04-17
AMHERST, Mass. – A team of scientists led by researchers at the University of Massachusetts Amherst has recently made a surprising discovery, with the help of a wind tunnel and a flock of birds. Songbirds, many of which make twice-yearly, non-stop flights of more than 1,000 miles to get from breeding range to wintering range, fuel themselves by burning lots of fat and a surprising amount of the protein making up lean body mass, including muscle, early in the flight. This flips the conventional wisdom ...
Fossils reveal the long-term relationship between feathered dinosaurs and feather-feeding beetles
2023-04-17
New fossils in amber have revealed that beetles fed on the feathers of dinosaurs about 105 million years ago, showing a symbiotic relationship of one-sided or mutual benefit, according to an article published in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America today*.
The main amber fragments studied, from the Spanish locality of San Just (Teruel), contain larval moults of small beetle larvae tightly surrounded by portions of downy feathers. The feathers belonged to an unknown theropod dinosaur, either avian (a term referring ...
Sea-level rise in southwest Greenland as a contributor to Viking abandonment
2023-04-17
Vikings occupied Greenland from roughly 985 to 1450, farming and building communities before abandoning their settlements and mysteriously vanishing. Why they disappeared has long been a puzzle, but a new paper from the Department of Earth and Planetary Sciences (EPS) determines that one factor – rising sea level – likely played a major role.
“There are many theories as to what exactly happened” to drive the Vikings from their settlements in Greenland, said Marisa J. Borreggine, lead author of the “Sea-Level ...