(Press-News.org)
U.S. middle and high schools with the most students taking prescription stimulants to treat ADHD also had, overall, the highest percentage of students who misused prescription stimulants within the past year.
The University of Michigan-led study highlights a significant association between ADHD stimulant therapy in schools and prescription stimulant misuse, said Sean Esteban McCabe, U-M professor of nursing and principal investigator on the study.
At some schools, 25% or more of kids reported misusing prescription stimulants in the past year—meaning they used the medication without a doctor's orders or nonmedically, e.g., for recreation or to stay awake.
Key takeaway: Wide variation in stimulant misuse among schools
This is the first large study to examine the prevalence of prescription stimulant misuse and correlating factors in U.S middle and high schools, McCabe said. Stimulant misuse among schools ranged from 0% to 25%, with some outliers that were higher. Other findings include:
Students in schools with the highest rates of stimulant therapy for ADHD had a 36% higher risk of misusing prescription stimulants
In schools with 12% or more students treated with prescription stimulants for ADHD, 8% of students reported misusing prescription stimulants
In schools with 6% or fewer students taking prescription stimulants for ADHD, 0-4% reported misusing prescription stimulants.
Other characteristics of schools with higher misuse: higher proportion of highly educated parents; located in non-Northeastern regions and suburbs; more white students; medium levels of binge drinking; and schools surveyed from 2015-2020
"I can tell you that a student's experience will be different at a school with no peers who misuse stimulants versus a school where 1 in 4 peers misuse stimulants," said McCabe, director of the U-M Center for the Study of Drugs, Alcohol, Smoking and Health.
McCabe said the wide variation in misuse means individual schools should assess their own students for substance misuse behaviors rather than rely on existing data collected elsewhere.
Stimulant therapy is highly effective; risk for misuse can be reduced
Stimulant therapy for ADHD has increased in the last two decades. Prescription stimulants are one of the most widely shared prescription drugs among teens, and the most misused prescription drug among teens.
"Prescription stimulant therapy for ADHD does help millions of people, including in my own family, and students, friends and colleagues," McCabe said. "It's critical to balance the need for access to these medications while reducing the risk for misuse. This is more important than ever with the increases in prescribing."
Medication-sharing among teens is a big reason kids who aren't on stimulant therapy have access to prescription stimulants, but it's not the only factor, McCabe said. Some schools in the study with little or no stimulant therapy still had misuse. Parents can take steps to prevent medication sharing:
In middle school, start talking to kids about managing their medications
Role play so kids know how to respond if asked to share medications
Always store controlled substances in a lockbox and monitor pill counts
Make sure schools have safe storage and dispensing policies, and ask about prevalence of misuse
Contact prescriber immediately if you detect misuse
Other recent U-M studies show associations between stimulant therapy and misuse
One paper found that students who had used both stimulant and nonstimulant medications for ADHD were more likely to misuse prescription stimulants, or to use cocaine or methamphetamine, in the past year, compared to students who reported never using stimulant or non-stimulant therapy.
Another paper found that kids diagnosed early with ADHD, who started stimulant therapy early and were treated longer, had lower odds of later stimulant misuse compared to those who started therapy later and for a shorter duration.
These two studies and the current study used data collected between 2005 and 2020 by Monitoring the Future, a large survey of trends in legal and illicit drug use among American students in 8th, 10th and 12th grades. Not all studies used the same data sets.
The findings, appearing in JAMA Network Open, were supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse at the National Institutes of Health and the U.S. Food and Drug Administration.
Study (available when embargo lifts): Prescription stimulant medical and nonmedical use among US secondary school students (DOI: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.20238707)
END
In some US schools, 1 in 4 students report misusing prescription stimulants
2023-04-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
USPSTF statement on screening for skin cancer
2023-04-18
Bottom Line: The U.S. Preventive Services Task Force (USPSTF) concludes that the current evidence is insufficient to assess the balance of benefits and harms of visual skin examination by a clinician to screen for skin cancer in adolescents and adults. Skin cancer is the most commonly diagnosed cancer in the U.S. There are different types of skin cancer varying in disease incidence and severity. Basal and squamous cell carcinomas are the most common types of skin cancer but infrequently lead to death or substantial morbidity. Melanomas represent about 1% of skin cancer and cause the most skin cancer deaths. The USPSTF routinely ...
Association of COVID-19 infection with incident diabetes
2023-04-18
About The Study: In this study of more than 600,000 individuals, SARS-CoV-2 infection was associated with a higher risk of diabetes and may have contributed to a 3% to 5% excess burden of diabetes at a population level.
Authors: Naveed Z. Janjua M.B.B.S, Dr.P.H., of the British Columbia Centre for Disease Control in Vancouver, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.8866)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions ...
Factors associated with knowledge and experience of self-managed abortion among patients seeking care at abortion clinics
2023-04-18
About The Study: In this survey study of 19,000 patients attending 49 abortion clinics in 29 states, considering self-managed abortion was common before accessing in-clinic care, particularly among those on the margins of access or with a preference for at-home care. These findings suggest a need for expanded access to telemedicine and other decentralized abortion care models.
Authors: Abigail R. A. Aiken, Ph.D., of the University of Texas at Austin, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: ...
School prevalence of stimulant therapy for ADHD associated with higher rates of prescription stimulant misuse among teens
2023-04-18
Researchers have identified a strong association between prevalence of prescription stimulant therapy for attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and rates of prescription stimulant misuse (taken in a way other than as directed by a clinician) by students in middle and high schools. The study, which appeared today in JAMA Network Open, highlights the need for assessments and education in schools and communities to prevent medication-sharing among teens. This is especially important considering non-medical use of prescription stimulants among teens remains more prevalent than misuse ...
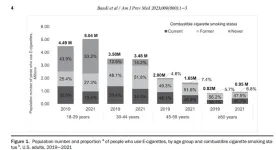
New research shows e-cigarette use up sharply among younger adults in U.S. during EVALI outbreak and COVID-19 pandemic
2023-04-18
ATLANTA, April 18, 2023 – A new study by researchers at the American Cancer Society (ACS) shows almost three-quarters of a million more adults in the United States, ages 18-29 years, used e-cigarettes between 2019-2021 during the period that spanned the EVALI outbreak (E-cigarette or vaping product use–associated lung injury) and COVID-19 pandemic. Scientists report the year-on-year increase was primarily among adults who never smoked cigarettes. The study was published today in the American Journal of Preventive Medicine (AJPM).
“Unfortunately, these numbers show we’re moving in the wrong direction concerning e-cigarette use in this vulnerable ...
Over half of top selling Medicare drugs have low added therapeutic benefit
2023-04-18
Brand-name drugs cost two to three times more in the U.S. than in other countries, but many of the top-selling brand name drugs may provide little added therapeutic benefit. A new study led by researchers at Brigham and Women’s Hospital, a founding member of Mass General Brigham, used public Medicare data to identify the 50 highest-selling brand-name drugs in 2020. The researchers evaluated their therapeutic benefit compared to existing standards of care, based on ratings from the national health technology assessment (HTA) organizations of Canada, France, and Germany. The team found that 27 of the 50 drugs received ...
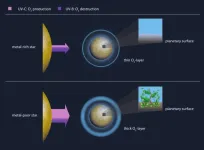
Metal-poor stars are more life-friendly
2023-04-18
Stars that contain comparatively large amounts of heavy elements provide less favourable conditions for the emergence of complex life than metal-poor stars, as scientists from the Max Planck Institutes for Solar System Research and for Chemistry as well as from the University of Göttingen have now found. The team showed how the metallicity of a star is connected to the ability of its planets to surround themselves with a protective ozone layer. Crucial to this is the intensity of the ultraviolet light that the star emits into space, in different wavelength ranges. The study provides scientists searching ...
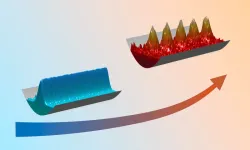
Quantum liquid becomes solid when heated
2023-04-18
Supersolids are a relatively new and exciting area of research. They exhibit both solid and superfluid properties simultaneously. In 2019, three research groups were able to demonstrate this state for the first time beyond doubt in ultracold quantum gases, among them the research group led by Francesca Ferlaino from the Department of Experimental Physics at the University of Innsbruck and the ÖAW Institute for Quantum Optics and Quantum Information (IQOQI) in Innsbruck.
In 2021, Francesca Ferlaino's team studied in detail the life cycle of supersolid states ...
Researchers ID gene that shapes heart attack, aneurysm risk
2023-04-18
University of School of Medicine researchers have identified a gene that plays a crucial role in determining our risk for heart attacks, deadly aneurysms, coronary artery disease and other dangerous vascular conditions.
The discovery advances our understanding of the underlying causes of a wide range of serious health conditions, including atherosclerosis (hardening of the arteries), and moves us closer to new treatments and preventive measures that could help people live longer, healthier lives.
“The first step towards translating the knowledge of population risk for vascular disease is disentangling the fundamental cellular ...
Extreme poverty a key driver for relapse in kids with ALL
2023-04-18
(WASHINGTON, DC, April 18, 2023) – Children with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) who live in extreme poverty and were undergoing maintenance therapy faced an almost two-fold greater risk of relapse compared with kids who weren’t as poor, according to a study published in today’s issue of Blood. Moreover, a higher proportion of these children had difficulty adhering to treatment, though researchers said this only partially explains the link between poverty and the risk of relapse.
“ALL is a curable disease, so while we observed relatively few relapses in total, children living in extreme poverty – those whose families were really stretched thin and not able ...