(Press-News.org) Sleep disturbances can be an early sign of Alzheimer’s disease. Many people eventually diagnosed with Alzheimer’s start experiencing difficulty falling and staying asleep years before cognitive problems such as memory loss and confusion emerge. It’s a vicious cycle: Alzheimer’s disease involves changes to the brain that disrupt sleep, and poor sleep accelerates harmful changes to the brain.
Researchers at Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis have identified a possible way to help break that cycle. A small, two-night study has shown that people who took a sleeping pill before bed experienced a drop in the levels of key Alzheimer’s proteins — a good sign, since higher levels of such proteins tracks with worsening disease. The study, which involved a sleeping aid known as suvorexant that is already approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for insomnia, hints at the potential of sleep medications to slow or stop the progression of Alzheimer’s disease, although much more work is needed to confirm the viability of such an approach.
The study is published April 20 in Annals of Neurology.
“This is a small, proof-of-concept study. It would be premature for people who are worried about developing Alzheimer’s to interpret it as a reason to start taking suvorexant every night,” said senior author Brendan Lucey, MD, an associate professor of neurology and director of Washington University’s Sleep Medicine Center. “We don’t yet know whether long-term use is effective in staving off cognitive decline, and if it is, at what dose and for whom. Still, these results are very encouraging. This drug is already available and proven safe, and now we have evidence that it affects the levels of proteins that are critical for driving Alzheimer’s disease.”
Suvorexant belongs to a class of insomnia medications known as dual orexin receptor antagonists. Orexin is a natural biomolecule that promotes wakefulness. When orexin is blocked, people fall asleep. Three orexin inhibitors have been approved by the FDA, and more are in the pipeline.
Alzheimer’s disease begins when plaques of the protein amyloid beta start building up in the brain. After years of amyloid accumulation, a second brain protein, tau, begins to form tangles that are toxic to neurons. People with Alzheimer’s disease start experiencing cognitive symptoms such as memory loss around the time tau tangles become detectable.
Lucey and colleagues were among the first to show in people that poor sleep is linked to higher levels of both amyloid and tau in the brain. The question remains as to whether good sleep has the opposite effect — a reduction in amyloid and tau levels, and a halt in or reversal of the progress of Alzheimer’s disease — but mouse studies with orexin inhibitors have been promising.
As a first step to assess the effect of orexin inhibitors on people, Lucey and colleagues recruited 38 participants ages 45 to 65 and with no cognitive impairments to undergo a two-night sleep study. The participants were given a lower dose (10 mg) of suvorexant (13 people), a higher dose (20 mg) of suvorexant (12 people) or a placebo (13 people) at 9 p.m. and then went to sleep in a clinical research unit at Washington University. Researchers withdrew a small amount of cerebrospinal fluid via spinal tap every two hours for 36 hours, starting one hour before the sleeping aid or placebo was administered, to measure how amyloid and tau levels changed over the next day and a half.
Amyloid levels dropped 10% to 20% in the cerebrospinal fluid of people who had received the high dose of suvorexant compared to people who had received placebo, and the levels of a key form of tau known as hyperphosphorylated tau dropped 10% to 15%, compared to people who had received placebo. Both differences are statistically significant. There was not a significant difference between the people who received a low dose of suvorexant and those who received the placebo.
By 24 hours after the first dose, hyperphosphorylated tau levels in the high-dose group had risen, while amyloid levels remained low compared to the placebo group. A second dose of suvorexant, administered on the second night, sent the levels of both proteins down again for people in the high-dose group.
“If we can lower amyloid every day, we think the accumulation of amyloid plaques in the brain will decrease over time,” Lucey said. “And hyperphosphorylated tau is very important in the development of Alzheimer’s disease, because it’s associated with forming tau tangles that kill neurons. If you can reduce tau phosphorylation, potentially there would be less tangle formation and less neuronal death.”
The study is preliminary, since it only looked at the effect of two doses of the drug in a small group of participants. Lucey has studies underway to assess the longer-term effects of orexin inhibitors in people at higher risk of dementia.
“Future studies need to have people taking these drugs for months, at least, and measuring the effect on amyloid and tau over time,” Lucey said. “We’re also going to be studying participants who are older and may still be cognitively healthy, but who already have some amyloid plaques in their brains. This study involved healthy middle-aged participants; the results may be different in an older population.
“I’m hopeful that we will eventually develop drugs that take advantage of the link between sleep and Alzheimer’s to prevent cognitive decline,” he continued. “We’re not quite there yet. At this point, the best advice I can give is to get a good night’s sleep if you can, and if you can’t, to see a sleep specialist and get your sleep problems treated.”
END
Sleeping pill reduces levels of Alzheimer’s proteins
More research needed to determine if sleep medications prevent, delay Alzheimer’s
2023-04-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
One-step solution-coating method to advance perovskite solar cell manufacturing and commercialization
2023-04-20
Perovskite solar cells (PSCs) are considered a promising candidate for next-generation photovoltaic technology with high efficiency and low production cost, potentially revolutionizing the renewable energy industry. However, the existing layer-by-layer manufacturing process presents challenges that have hindered the commercialisation of this technology. Recently, researchers from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) and the National Renewable Energy Laboratory (NREL) in the US jointly developed an innovative one-step solution-coating ...
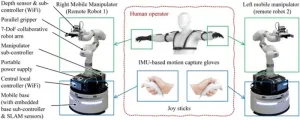
Body extension by using two mobile manipulators
2023-04-20
Imagine lying on a bed, you just have to move your fingers to guide a mobile robot to bring you a cup of water, open the door to fetch some deliveries, or even do some laundry. If you are interested, you may want to learn more about a new remotely operated robotic system based on two mobile manipulators. This system was developed by roboticists from Osaka University. They published a research paper describing this robotic system on Feb. 10 in the journal Cyborg and Bionic Systems.
Back in the year of 2013, Fukushima nuclear power plant witnessed a catastrophic radioactive leakage and contamination, which makes the surrounding area extremely dangerous for ...
Advance care planning produces trend toward less aggressive and more comfort- focused care for patients with cancer
2023-04-20
INDIANAPOLIS – A meta-analysis of studies involving 33,541 cancer patients evaluates the relationship between advance care planning and aggressive vs. comfort-focused end-of-life care. The study, led by Kristin Levoy, PhD, MSN, RN, of the Regenstrief Institute and Indiana University School of Nursing, found a general trend toward less aggressive and more comfort-focused end-of-life care among cancer patients who had engaged in advance care planning, compared to those who did not do so.
Advance care planning is a dynamic process to help prepare people for future decision-making with the goal of ensuring that individuals receive care at the end-of-life that is consistent ...
Ground reaction force and moment estimation through EMG sensing using long short-term memory network during posture coordination
2023-04-20
Imagine by only attaching a number of electromyography (EMG) sensors to your legs, your motion in the future several seconds can be predicted. Such a way of predicting motion via muscle states is an alternative to the mainstream visual cue-based motion prediction, which heavily relies on multi-view cameras to construct time-series posture. However, there is still a gap between muscle states and future movements.
Muscles act upon the ground, which induces ground reaction force. Together with muscle states and ground reaction force, body movements are produced. Therefore, estimating ...
ASBMB cautions against sacrificing science funds to make debt-ceiling deal
2023-04-20
The American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology released a statement this week calling on policymakers participating in debt-ceiling negotiations to preserve funding to major scientific agencies such as the National Institutes of Health, National Science Foundation and the Department of Energy.
In January, the United States reached its debt limit of $31.4 trillion. House Republicans are resisting raising the debt ceiling unless federal spending levels are reduced to fiscal year 2022 levels, which would reduce discretionary funding ...
Important role of intestinal immune cells in iron deficiency identified for the first time
2023-04-20
Iron deficiency is one of the five main causes of impaired health. It affects 30 percent of the world's population, particularly women. Why iron deficiency can occur, even if enough iron is supplied through the diet, has not yet been sufficiently clarified in scientific research. For the first time, a research team from MedUni Vienna has discovered that certain immune cells in the intestine play an important role in iron absorption in the body. The study results may provide a new approach for possible therapeutic measures and were recently published in the journal "Blood".
Approximately one to two milligrams of ...
Versatile, high-speed, and efficient crystal actuation with photothermally resonated natural vibrations
2023-04-20
Every material possesses a unique natural vibration frequency such that when an external periodic force is applied to this material close to this frequency, the vibrations are greatly amplified. In the parlance of physics, this phenomenon is known as “resonance.” Resonance is ubiquitous in our daily life, and, depending on the context, could be deemed desirable or undesirable. For instance, musical instruments like the guitar relies on resonance for sound amplification. On the other hand, buildings and bridges are more likely to collapse under an earthquake if the ground vibration frequency matches their natural frequency.
Interestingly, natural vibration has not received ...
Children’s language development doesn’t just happen through words
2023-04-20
Children learn to understand language and to speak largely independently of cognitive functions like spatial awareness, working (short-term) memory and perception (interpreting and organizing sensory impressions), according to established theory and tradition within linguistics.
Professor Mila Vulchanova at the Norwegian University of Science and Technology (NTNU) heads the university's language laboratory and studies language learning. Her findings over several years have challenged this linguistic assumption and demonstrated ...
Researchers identify a potential new therapeutic target in Parkinson’s disease
2023-04-20
TORONTO - In a study published in Nature Communications, a team led by Krembil Brain Institute Senior Scientists, Drs. Lorraine Kalia and Suneil Kalia, and University of Toronto (U of T) Professor, Dr. Philip M. Kim, identified a protein-protein interaction that contributes to Parkinson’s disease.
In the disease, a protein called α-synuclein (a-syn) accumulates in the brain and leads to cell death. Much research is currently focused on clearing a-syn with antibodies or using small molecules to prevent a-syn from aggregating. In this study, the researchers took an alternate approach by looking for protein-protein interactions that may be promoting ...
Dr. Natalya Chernichenko named site chief of otolaryngology at NewYork-Presbyterian Brooklyn Methodist Hospital
2023-04-20
Dr. Natalya Chernichenko, a leading otolaryngologist who specializes in tumors of the head and neck, has been named site chief of otolaryngology at NewYork-Presbyterian Brooklyn Methodist Hospital, effective May 1. Dr. Chernichenko was also recruited to Weill Cornell Medicine as an assistant professor of clinical otolaryngology and vice chair in the Department of Otolaryngology—Head and Neck Surgery.
In her new role, Dr. Chernichenko will lead a skilled team of specialists and surgeons providing comprehensive otolaryngology care, also known as ear, nose and throat, or ENT care, and further develop the hospital’s head and neck surgical oncology ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Public and patient involvement in research is a balancing act of power
Scientists discover “bacterial constipation,” a new disease caused by gut-drying bacteria
DGIST identifies “magic blueprint” for converting carbon dioxide into resources through atom-level catalyst design
COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy may help prevent preeclampsia
Menopausal hormone therapy not linked to increased risk of death
Chronic shortage of family doctors in England, reveals BMJ analysis
Booster jabs reduce the risks of COVID-19 deaths, study finds
Screening increases survival rate for stage IV breast cancer by 60%
ACC announces inaugural fellow for the Thad and Gerry Waites Rural Cardiovascular Research Fellowship
University of Oklahoma researchers develop durable hybrid materials for faster radiation detection
Medicaid disenrollment spikes at age 19, study finds
Turning agricultural waste into advanced materials: Review highlights how torrefaction could power a sustainable carbon future
New study warns emerging pollutants in livestock and aquaculture waste may threaten ecosystems and public health
Integrated rice–aquatic farming systems may hold the key to smarter nitrogen use and lower agricultural emissions
Hope for global banana farming in genetic discovery
Mirror image pheromones help beetles swipe right
Prenatal lead exposure related to worse cognitive function in adults
Research alert: Understanding substance use across the full spectrum of sexual identity
Pekingese, Shih Tzu and Staffordshire Bull Terrier among twelve dog breeds at risk of serious breathing condition
Selected dog breeds with most breathing trouble identified in new study
Interplay of class and gender may influence social judgments differently between cultures
Pollen counts can be predicted by machine learning models using meteorological data with more than 80% accuracy even a week ahead, for both grass and birch tree pollen, which could be key in effective
Rewriting our understanding of early hominin dispersal to Eurasia
Rising simultaneous wildfire risk compromises international firefighting efforts
Honey bee "dance floors" can be accurately located with a new method, mapping where in the hive forager bees perform waggle dances to signal the location of pollen and nectar for their nestmates
Exercise and nutritional drinks can reduce the need for care in dementia
Michelson Medical Research Foundation awards $750,000 to rising immunology leaders
SfN announces Early Career Policy Ambassadors Class of 2026
Spiritual practices strongly associated with reduced risk for hazardous alcohol and drug use
Novel vaccine protects against C. diff disease and recurrence
[Press-News.org] Sleeping pill reduces levels of Alzheimer’s proteinsMore research needed to determine if sleep medications prevent, delay Alzheimer’s