(Press-News.org) Running is one of the most accessible forms of exercise with an array of proven cardiovascular and musculoskeletal benefits, and an added bonus of increased mental health. Good quality running gear, such as the right pair of shoes, is vital to improve running performance and reduce injury risk. For women particularly, a well-designed sports bra protects from exercise-induced breast pain, which can be a significant barrier to practicing sports. Up to 72% of women experience breast pain while running.
Previous research has shown that the increased breast support sports bras offer not only influences breast movement but can also positively influence running performance. Greater breast support has been linked to lower oxygen consumption and better range of motion.
Dr Douglas Powell and Hailey Fong and colleagues at the Breast Biomechanics Research Center at the University of Memphis wanted to further investigate the effect of a good sports bra on running biomechanics, and have now published new findings in Frontiers in Sports and Active Living.
“The biomechanics underlying improved running performance with greater breast support are not well understood. Our study represents one of a series of research studies on the topic of breast support and whole body biomechanics,” explained Powell. “We wanted to identify strategies to reduce activity-induced breast pain for females, a group that makes up approximately 50% of the population.”
Biomechanics of running
Specifically, Powell and his colleagues looked at the influence of breast support on knee joint stiffness during treadmill running. Knee joint stiffness is a biomechanical measure that indicates how resistant the knee joint is to movement when force is applied. Knee joint stiffness has been associated with lower oxygen consumption, improved running performance, and running-related injury.
A sample size of 12 recreational runners, aged between 18 and 35 years, with a self reported B-, C-, or D-cup were professionally fitted with two different sports bras: a high support bra and a low support bra. For the control condition, the participants were asked to perform the experiment bare chested. Each participant then performed three-minute running bouts in each of the three randomized breast support conditions (high, low, bare/control).
To collect the data the researchers used a 10-camera motion capture system and instrumented treadmill. The movements of the participants were tracked using individual retroreflective markers fitted on different parts of their bodies. The researchers used Visual3D to calculate knee joint excursions, while custom software was used to calculate knee joint stiffness and breast displacements during the stance phase of running in each experimental condition.
The importance of good support
The experiment showed that increased levels of breast support were associated with greater knee joint stiffness due to smaller joint excursions. Compared to the control condition, the low and high support conditions were associated with 2% and 5% increases in knee joint stiffness respectively. Overall, taking into account these results and results from previous research by Powell and Fong, a high support sports bra can improve a female's running performance by 7%.
“The findings show that breast support not only influences movement of the breasts but that compensations occur across the entire body,” said Powell. These compensations can lead to reduced running performance, increased injury risk, and even the development of chronic pain such as back and chest pain.
Powell continued: “Over the past 50 years, limited evolution in bra design has occurred. Our findings, in conjunction with previous research studies, show that sports bras should be considered not only as apparel, but also as sports equipment that can both improve performance and reduce the risk of injury, playing a role in women’s health.”
END
The right sports bra may increase your running performance by 7%
A new study in Frontiers in Sports and Active Living found that greater breast support during running is associated with increased knee joint stiffness, altering the lower body biomechanics of female runners
2023-04-21
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
SwRI-led team successfully observes Australian eclipse in preparation for 2024 US eclipse
2023-04-21
SAN ANTONIO – 4.20.23 -Scientists from Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) led a team in the unique Citizen Continental-America Telescopic Eclipse (CATE) experiment to image the Sun’s outer atmosphere, the corona, during a short solar eclipse on the opposite side of the Earth. Using four platforms in the northwest corner of Australia, the team successfully observed the million-degree solar corona at the April 20 eclipse viewed from the Exmouth peninsula. The Australian eclipse serves both as a unique scientific opportunity and a training exercise for the program’s leadership in preparation ...
When an earthquake strikes, how do Mexico city hospitals respond?
2023-04-21
Staff in public and private hospitals in Mexico City are likely to follow well-established and reinforced earthquake early warning (EEW) protocols for evacuation, according to an ongoing study.
Overall, staff are likely to follow the protocols especially when they are “reinforced with drills that help practice the correct protective action,” said Sandra Vaiciulyte of Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México. She discussed her research at the Seismological Society of America (SSA)’s 2023 Annual Meeting.
In the study, there have been “no accounts of injuries of patients and staff because of the particular reaction by staff,” ...
The mental health of pediatric ICU teams: how has the pandemic affected these professionals?
2023-04-21
Concern about the mental health of hospital professionals has been increasing in recent years, and when, in early 2020, the Covid-19 pandemic was declared and rapidly spread, there was a large increase in the overload of workers in Intensive Care Units (ICUs). Given this, researchers from the D’Or Institute for Research and Education (IDOR) and other national institutions assessed the prevalence and extent of psychological disorders such as burnout, anxiety, depression, and post-traumatic stress disorder ...
Ridgecrest faults increasingly sensitive to solid Earth tides before earthquakes
2023-04-21
Faults in the Ridgecrest, California area were very sensitive to solid earth tidal stresses in the year and a half before the July 2019 Ridgecrest earthquake sequence, researchers reported at the Seismological Society of America (SSA)’s 2023 Annual Meeting.
“The signal of tidal modulation becomes extremely strong” after 2018, said Eric Beauce of Lamont-Doherty Earth Observatory, who noted that the signal was identified with seismicity that occurred around the faults that broke in the 2019 magnitude 7.1 earthquake.
The link ...
New study reveals that childhood adversity is linked to an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes as young adults
2023-04-21
A new study published in Diabetologia (the journal of the European Association for the Study of Diabetes [EASD])finds that individuals who experienced childhood adversity are at increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes (T2D) in early adulthood.
The research was conducted by Assistant Professor Leonie K. Elsenburg and colleagues at the Section of Epidemiology, Department of Public Health, University of Copenhagen, Copenhagen, Denmark and aimed to determine whether there was a link between childhood adversity and the development ...
Reducing fatigue and errors among nurses working night shifts
2023-04-21
Nurses exposed to 40 minutes of bright light before their night shifts feel less fatigued and make fewer errors at work, according to a study led by McGill University. The nurses also slept better after their shifts.
“Healthcare workers are experiencing high levels of fatigue due to staffing shortages, difficult schedules, and heavy workloads. Further, the cost of medical errors has been estimated at tens of billions of dollars per year in North America,” says Jay Olson, the senior author of the recent study in Sleep Health, ...
Surgery most effective treatment of metabolic liver disease
2023-04-21
Metabolic (bariatric) surgery is more effective than medications and lifestyle interventions for the treatment of advanced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease.
A new paper, published today in The Lancet by King’s College London and the Catholic University of Rome, is the first to compare three active treatments of non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) and to specifically investigate the effectiveness of metabolic surgery (weight loss surgery) in a randomised clinical trial.
Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) is the most common cause of chronic liver disease, globally affecting 55% of people with type 2 diabetes and 75% of those with obesity. Non-alcoholic ...
Whales stop by Gold Coast bay for day spa fix with full body scrubs
2023-04-21
A new Griffith University study has found that humpback whales will use sandy, shallow bay areas to ‘roll’ around in sandy substrates to remove dead skin cells on their return journeys south to cooler waters.
Marine ecologist Dr Olaf Meynecke, from the Griffith-led Whales and Climate Research Program and Coastal and Marine Research Centre, used suction cup tags to track southward migrating whales between August 2021 and October 2022.
The CATS tags are fitted with integrated high-definition video, magnesium release system, a VHF transmitter for retrieval, magnetometers, ...
Horodyskia is among the oldest multicellular macroorganisms: Study
2023-04-21
Horodyskia, characterized by a string of beads with uniform size and spacing, is a kind of macroscopic fossil with a record extending from the early Mesoproterozoic Era (~1.48 Ga) to the terminal Ediacaran Period (~550 Ma).
Now, researchers led by Dr. LI Guangjin and Prof. PANG Ke from the Nanjing Institute of Geology and Palaeontology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (NIGPAS) and Prof. CHEN Lei from Shandong University of Science and Technology have revealed that Horodyskia is among the oldest multicellular macroorganisms and may have attained its macroscopic ...
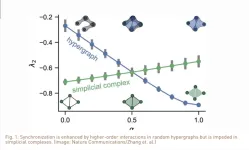
Study: Do higher-order interactions promote synchronization?
2023-04-20
APRIL 20, 2023
Researchers use networks to model the dynamics of coupled systems ranging from food webs to neurological processes. Those models originally focused on pairwise interactions, or behaviors that emerge from interactions between two entities. But in the last few years, network theorists have been asking, what about phenomena that involve three or more? In medicine, antibiotic combinations may fight a bacterial infection differently than they would on their own. In ecology, survival strategies may arise from ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
[Press-News.org] The right sports bra may increase your running performance by 7%A new study in Frontiers in Sports and Active Living found that greater breast support during running is associated with increased knee joint stiffness, altering the lower body biomechanics of female runners