(Press-News.org) About The Study: In this study of 436 cognitively normal older adults, unawareness, rather than heightened awareness, of memory decline was strongly associated with future clinical progression, providing further support that discordant self- and informant-reported cognitive decline may provide important information to practitioners.
Authors: Patrizia Vannini, Ph.D., of Brigham and Women’s Hospital in Boston, is the corresponding author.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.9964)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2023.9964?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=042523
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Self-awareness of memory function and clinical progression in cognitively normal older adults
JAMA Network Open
2023-04-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How to land on a planet safely
2023-04-25
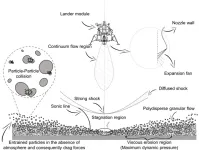
WASHINGTON, April 25, 2023 – When a lander descends toward the moon – or a rocky planet, asteroid, or comet – the exhaust plume of the rocket interacts with the surface, causing erosion and kicking up regolith particles. The resulting blanket of dusty debris can create a dangerous brownout effect, limiting visibility and potentially damaging the spacecraft or nearby equipment.
In Physics of Fluids, by AIP Publishing, researchers from Chungnam National University, the University of Edinburgh, Gyeongsang National University, and the Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information ...
Global research reveals countries where record-breaking heatwaves are likely to cause most harm
2023-04-25
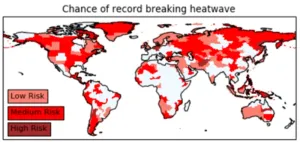
A new study has highlighted under-prepared regions across the world most at risk of the devastating effects of scorching temperatures.
The University of Bristol-led research, published today in Nature Communications, shows that unprecedented heat extremes combined with socioeconomic vulnerability puts certain regions, such as Afghanistan, Papua New Guinea, and Central America, most in peril.
Countries yet to experience the most intense heatwaves are often especially susceptible, as adaptation measures are often only introduced after the event. A high chance of record-breaking ...
Using artificial intelligence to create a tsunami early warning system
2023-04-25
Cardiff University media release/Datganiad i’r wasg gan Brifysgol Caerdydd
Under embargo until 16:00 BST/11:00 EST on Tuesday 25 April 2023/O dan embargo tan 16:00 BST/11:00 EST ddydd Mawrth 25 Ebrill 2023
Using artificial intelligence to create a tsunami early warning system
Real-time classification of underwater earthquakes enables earlier and more reliable tsunami alerts
An early warning system that quickly classifies submarine earthquakes and determines the risk of tsunami events has been developed by scientists at Cardiff ...
Researchers at Albert Einstein College of Medicine discover how long-lasting memories form in the brain
2023-04-25
April 25, 2023—(BRONX NY)—Helping your mother make pancakes when you were three…riding your bike without training wheels…your first romantic kiss: How do we retain vivid memories of long-ago events? As described in a paper published online on April 25 in Neuron, researchers at Albert Einstein College of Medicine have found the explanation.
“The ability to learn new information and store it for long periods is one of the brain’s most remarkable features,” said Robert H. Singer, Ph.D., ...
Researchers find rhythmic brain activity helps to maintain temporary memories
2023-04-25
New research shows that rhythmic brain activity is key to temporarily maintaining important information in memory. Researchers at the Del Monte Institute for Neuroscience at the University of Rochester published these findings today in Current Biology that found brain rhythms—or patterns of neuronal activity—organize the bursts of activity in the brain that maintain short-term connections.
“The thought has been that the temporary storage of important information is linked to neurons in the brain that just fire away, retaining that information until it is no longer needed. Recent research has shown that it might not be such persistent ...
Near-universal T cell immunity towards a broad range of bacteria
2023-04-25
Typically T cells of the immune system respond to a specific feature (antigen) of a microbe, thereby generating protective immunity. As reported in the journal Immunity, an international team of scientists have discovered an exception to this rule. Namely, a group of divergent bacterial pathogens, including pneumococci, all share a small highly conserved protein sequence, which is both presented and recognized by human T cells in a conserved population-wide manner.
The study set out to understand immune mechanisms that protect against pneumococcus, a bacterial pathobiont that can reside harmlessly in the upper respiratory mucosae but can also cause infectious ...
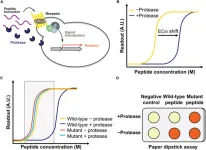
Novel living yeast-based dual biosensor for detecting peptide variants
2023-04-25
Biosensors—sensors that can detect biological samples—are powerful tools for understanding the function, composition, and structure of biochemical molecules. Biosensors are often applied for the detection of proteins and their subunits, called peptides, yielding a wide range of biomedical applications. In 2017, researchers from Columbia University in USA engineered a living yeast biosensor by rewiring pheromone-related signaling pathways used by yeast for mating. In the presence of the pheromone peptide, the G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) could detect the peptide, triggering a cascade that would eventually activate a ...
Sizing them up! An algorithm to accurately quantify rapeseed silique morphology
2023-04-25
Rapeseed or oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) is an important crop cultivated worldwide for its oil-rich seeds. The rapeseed silique is an organ that plays a role in photosynthesis, sends developmental signals to maturing seeds, and provides a capsule that harbors the seeds. High-yield rapeseed varieties have both a high number and optimal morphology–the form and structure–of siliques. In this regard, rapeseed genotype and cultivation method directly influence the number of siliques that a plant produces. Thus, accurately quantifying silique development parameters is critical for predicting ...
Columbia University launches Center for Precision Psychiatry & Mental Health with $75 million grant from the Stavros Niarchos Foundation
2023-04-25
NEW YORK, April 24, 2023—Columbia University today announced the establishment of the Stavros Niarchos Foundation (SNF) Center for Precision Psychiatry & Mental Health at Columbia University. The center will catalyze the scientific innovation and clinical implementation of precision medicine to advance the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of mental illness. The center is being established with a $75 million grant from the Stavros Niarchos Foundation (SNF), an international philanthropic organization, as part of SNF’s Global Health Initiative (GHI).
The SNF Center is a joint effort of the Department of Psychiatry at Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians ...
Research links common insecticide to neurodevelopmental disorders
2023-04-25
A new study from The University of Toledo suggests early exposure to a common class of insecticides called pyrethroids may increase the risk of autism and other developmental disorders, even at levels currently recognized as safe by federal regulators.
The findings, which come from a study of mice, were published today in the peer-reviewed journal PNAS Nexus.
Pyrethroids are some of the most widely used insecticides in the country, appearing in both consumer products and industrial preparations.
“If ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
Psilocybin trends in states that decriminalized use
New data signals high demand in aesthetic surgery in southern, rural U.S. despite access issues
$3.4 million grant to improve weight-management programs
Higher burnout rates among physicians who treat sickle cell disease
Wetlands in Brazil’s Cerrado are carbon-storage powerhouses
Brain diseases: certain neurons are especially susceptible to ALS and FTD
Father’s tobacco use may raise children’s diabetes risk
Structured exercise programs may help combat “chemo brain” according to new study in JNCCN
The ‘croak’ conundrum: Parasites complicate love signals in frogs
Global trends in the integration of traditional and modern medicine: challenges and opportunities
Medicinal plants with anti-entamoeba histolytica activity: phytochemistry, efficacy, and clinical potential
What a releaf: Tomatoes, carrots and lettuce store pharmaceutical byproducts in their leaves
[Press-News.org] Self-awareness of memory function and clinical progression in cognitively normal older adultsJAMA Network Open