Characterization of the HDAC/PI3K inhibitor CUDC-907 as a novel senolytic
2023-04-26
(Press-News.org)
“The mechanisms of induction of senescent cell death by CUDC-907 remain to be fully elucidated.”
BUFFALO, NY- April 25, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 15, Issue 7, entitled, “Characterization of the HDAC/PI3K inhibitor CUDC-907 as a novel senolytic.”
The accumulation of senescent cells has an important role in the phenotypical changes observed in aging and in many age-related pathologies. Thus, the strategies designed to prevent these effects, collectively known as senotherapies, have a strong clinical potential.
Senolytics are a type of senotherapy aimed at specifically eliminating senescent cells from tissues. Several small molecule compounds with senolytic properties have already been identified, but their specificity and range of action are variable. Because of this, potential novel senolytics are being actively investigated.
Given the involvement of HDACs and the PI3K pathway in senescence, researchers Fares Al-Mansour, Abdullah Alraddadi, Buwei He, Anes Saleh, Marta Poblocka, Wael Alzahrani, Shaun Cowley, and Salvador Macip from the University of Leicester, Najran University and Universitat Oberta de Catalunya hypothesized that the dual inhibitor CUDC-907, a drug already in clinical trials for its antineoplastic effects, could have senolytic effects.
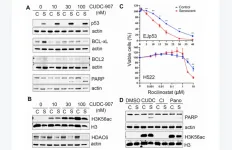
“Here, we show that CUDC-907 was indeed able to selectively induce apoptosis in cells driven to senesce by p53 expression, but not when senescence happened in the absence of p53.”
Consistent with this, CUDC-907 showed senolytic properties in different models of stress-induced senescence. Their results also indicate that the senolytic functions of CUDC-907 depend on the inhibitory effects of both HDACs and PI3K, which leads to an increase in p53 and a reduction in BH3 pro-survival proteins. Taken together, their results show that CUDC-907 has the potential to be a clinically relevant senolytic in pathological conditions in which stress-induced senescence is involved.
“According to our results, CUDC-907 could be an interesting drug to be used as a senolytic, alone or as part of a targeted approach.”
Continue Reading: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/aging.204616
Corresponding Author: Salvador Macip
Corresponding Email: sm460@le.ac.uk
Keywords: senescence, senolytics, HDAC, PI3K, CUDC-907
Sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article: https://aging.altmetric.com/details/email_updates?id=10.18632%2Faging.204616
About Aging-US:
Launched in 2009, Aging publishes papers of general interest and biological significance in all fields of aging research and age-related diseases, including cancer—and now, with a special focus on COVID-19 vulnerability as an age-dependent syndrome. Topics in Aging go beyond traditional gerontology, including, but not limited to, cellular and molecular biology, human age-related diseases, pathology in model organisms, signal transduction pathways (e.g., p53, sirtuins, and PI-3K/AKT/mTOR, among others), and approaches to modulating these signaling pathways.
Please visit our website at www.Aging-US.com and connect with us:
SoundCloud
Facebook
Twitter
Instagram
YouTube
LabTube
LinkedIn
Reddit
Pinterest
Click here to subscribe to Aging publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Aging (Aging-US) Journal Office
6666 E. Quaker Str., Suite 1B
Orchard Park, NY 14127
Phone: 1-800-922-0957, option 1
###
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2023-04-26
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — Showing users that visual data fed into artificial intelligence (AI) systems was labeled correctly might make people trust AI more, according to researchers. The findings also may pave the way to help scientists better measure the connection between labeling credibility, AI performance, and trust, the team added.
In a study, the researchers found that high-quality labeling of images led people to perceive that the training data was credible and they trusted the AI system more. ...
2023-04-26
25 April 2023
The Geological Society of America
Release no. 23-20
Contact: Justin Samuel
+1-303-357-1026
jsamuel@geosociety.org
For Immediate Release
A Meeting in the Mitten: Water, Rock, Wonderland
Boulder, Colo., USA: The 2023 Geological Society of America North-Central
Section Meeting will be held on 4–5 May in Grand Rapids, Michigan, USA. We
are pleased to announce a wide-ranging set of theme sessions, field trips,
and short courses aligned with our meeting theme: A Meeting in the Mitten:
Water, Rock, Wonderland.
...
2023-04-26
Mothers with the long term autoimmune disorder, systemic lupus erythematosus, or SLE for short, run more than double the risk of giving birth to a premature or growth restricted baby, finds a 10-year nationwide audit of hospital admissions records in the US and published online in the open access journal RMD Open.
And these mothers are nearly 4 times as likely to need a blood transfusion and 15 times as likely to develop kidney failure during delivery as mothers without the condition, the audit shows.
Rates of death and serious illness among new mothers are increasing in the USA, likely due to rising rates of obesity, underlying conditions, and older age ...
2023-04-26
Climate changes are conjuring a whirlwind ride that seems to present some creatures opportunities to thrive. Scientists scripting supercharged scenarios caution the difference between seasonal coping and long-term adaption is vast – and tricky to predict.
Michigan State University biologists have studied damselflies – which resemble dragonflies and are abundant as both predator and prey in wetlands – to understand what happens throughout their lifecycle from nymph to winged insect, along with what they eat when summers grow warmer and longer.
Their work in this week’s Proceedings of the Royal Society B has a twist – ...
2023-04-26
Press release: Under Embargo until Wednesday 26th April 2023, 12:05am BST
Higher rates of HIV diagnoses found amongst mental health service users
New National Institute for Health and Care Research Maudsley BRC supported research has found HIV is 2.5 times more frequent in people who use mental health services than the general population in South London. The paper was published today in BMJ Open.
HIV is 2.5 times more common in people who use mental health services than the general population in South London.
The researchers, at King’s College London, found that 2.5% of people who have had contact with mental health services had a recorded diagnosis of ...
2023-04-26
Even mild concussion can cause long-lasting effects to the brain, according to researchers at the University of Cambridge. Using data from a Europe-wide study, the team has shown that for almost a half of all people who receive a knock to the head, there are changes in how regions of the brain communicate with each other, potentially causing long term symptoms such as fatigue and cognitive impairment.
Mild traumatic brain injury – concussion – results from a blow or jolt to the head. It can occur as a result of a fall, a sports injury or from a cycling accident or car crash, ...
2023-04-26
**Strictly embargoed until 01:01 (BST) Wednesday 26 April 2023**
Astronomers solve the 60-year mystery of quasars – the most powerful objects in the Universe
First discovered 60 years ago, quasars can shine as brightly as a trillion stars packed into a volume the size of our Solar System, but until now it has remained a mystery what could trigger such powerful activity
By observing 48 galaxies that host quasars and comparing them to over 100 non-quasar galaxies, scientists discovered that the phenomenon is ignited by galaxies colliding
When two galaxies collide, gravitational forces ...
2023-04-26
Social media is fuelling eating disorders among female athletes who feel they must achieve the ‘ideal’ body, according to experts.
Dr Kathryn Vidlock and Catherine Liggett, who have both competed in collegiate athletics, and dietician Andrew Dole warn that nutrition ‘myths’ posted by fitness influencers, exercise-related ‘fitspiration’ images on Instagram, and photoshopping are having a direct impact on sportswomen.
Their new book Spring Forward: Balanced Eating, Exercise, and Body Image in ...
2023-04-25
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — People may appreciate online apps that provide advice on health and fitness, but they seem to draw the line when those apps use their social media networks for data, according to researchers.
In a study, users showed a strong preference for fitness recommendations that were personalized for them based on their self-reported preferences. They also liked systems that allowed users to choose among different recommendation approaches, which made them feel more in control.
“As big data gives people new opportunities to personalize their health and fitness routines, it also calls into question how ...
2023-04-25
(SACRAMENTO, Calif.) — One in five adults in California, or an estimated 6.5 million people, are concerned that someone they know, usually a friend or family member, is at risk of harming themselves or others, according to new research published in Preventive Medicine.
Alcohol and substance misuse, a history of violence, and firearm access were common reasons for concerns about potential violence.
Of the people perceived to be at risk for harming others, an estimated 19% were said to have access to firearms. For those perceived to be at risk of harming themselves, that number was approximately 11%.
Amanda J. Aubel, a research data analyst at the UC Davis Violence Prevention Research ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Characterization of the HDAC/PI3K inhibitor CUDC-907 as a novel senolytic