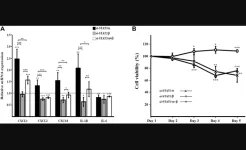
(Press-News.org) The World Health Organization’s draft drinking water guidance for the two most well-studied per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) exhibit a “striking and inappropriate disregard of the best available science,” according to former directors of the U.S. EPA’s Office of Science and Technology and the National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences (NIEHS). In a viewpoint for the peer-reviewed journal Environmental Science & Technology, Betsy Southerland and Linda Birnbaum strongly recommend the guidelines be “extensively revised” to adequately protect public health.
WHO’s draft recommends a limit of 100 ppt for PFOS and PFOA in drinking water—a level 25 times higher than that recently proposed by the U.S. EPA. This wide gap could hamper federal and state efforts to enact the EPA’s proposed standards.
The discrepancy between the two agency’s guidelines is largely because WHO eschewed calculating health-based values in favor of technology-based values. As a result, WHO’s draft ignores the large body of human and animal health studies—which contains robust evidence of cancer, liver damage, increased cholesterol, and immune system harms—to focus on remediation technology capabilities and costs. Moreover, the authors explain how the draft’s technological basis appeared to be “arbitrary” with no specific evidence that these levels are the lowest that can be reliably achieved.
Today’s article comes nearly six months after more than 100 scientists sent a letter to the WHO urging a complete overhaul or withdrawal of the draft guidance and requesting disclosure of its authorship and potential conflicts of interest. As a result of this letter and other calls for transparency, WHO published a list of contributors in January. However, it’s unclear if this list is comprehensive. During the public comment period, WHO received 25 sets of comments but has not yet disclosed them or announced when the guidelines will be finalized.
END
Former EPA and NIEHS directors urge overhaul of WHO’s draft PFAS drinking water guidance
2023-04-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Using microbes to get more out of mining waste
2023-04-27
Researchers have developed a new mining technique which uses microbes to recover metals and store carbon in the waste produced by mining. Adopting this technique of reusing mining waste, called tailings, could transform the mining industry and create a greener and more sustainable future.
Tailings are a by-product of mining. They are the fine-grained waste materials left after extracting the target ore mineral, which are then stacked and stored. This method is called dry-stack tailing.
Over time, mining practices have evolved and become more efficient. But the climate crisis and rising demand for critical minerals require the development of new ore removal and ...
Carnegie Mellon research aims to revive office chatter
2023-04-26
About one-third of our lives are spent at work, and the relationships we build there can have personal and professional benefits. But a majority of workers indicate difficulty connecting with co-workers socially, especially in the new landscape of remote and hybrid work arrangements.
To ease the friction caused by reduced in-person interaction, a team of researchers from Carnegie Mellon University's Human-Computer Interaction Institute created a Slack application that helps to initiate casual conversations and create affinity groups in an online workspace.
"We were freshly out of the pandemic, and we realized that everyone around us was complaining ...
Differential silencing of STAT3 isoforms leads to changes in STAT3 activation
2023-04-26
“Our study emphasizes the importance of distinguishing between STAT3α and STAT3β proteins and their active forms when discussing STAT3-related cancer diagnosis and therapy.”
BUFFALO, NY- April 26, 2023 – A new research paper was published in Oncotarget's Volume 14 on April 24, 2023, entitled, “Differential silencing of STAT3 isoforms leads to changes in STAT3 activation.”
Signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) is a transcription factor involved in ...
Terasaki Institute to celebrate grand opening of Woodland Hills Research Center with ribbon-cutting
2023-04-26
WOODLAND HILLS, Calif. – April 26, 2023 – The Terasaki Institute for Biomedical Innovation, a nonprofit dedicated to rapidly translating scientific knowledge into real-world solutions, will celebrate the grand opening of its latest biomedical research center with a ribbon-cutting ceremony on Saturday, April 29.
When: Saturday, April 29 at 11:30 a.m.
Where: 21100[ML1] Erwin St., Woodland Hills, Calif., 91367
What: ...
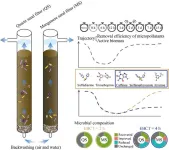
Backwashing affects the removal of micropollutants and the dynamic changes in the microbial community in sand filters
2023-04-26
Sand filters are commonly applied in drinking water treatment and can efficiently remove suspended solids, organic matter, and microorganisms from source water. During the process, particulate matter and microbes can attach to filter sands and develop a thick biofilm in both rapid and slow sand filters. To prevent clogging and restore pollutant removal efficiency, backwashing using air, water, or a combination of both is usually required for sand filters. However, backwashing can induce a loss in biomass, thus decreasing the pollutant ...
Researchers create antimicrobial ‘superfoam’
2023-04-26
A versatile new foam material developed by researchers at the University of Georgia could significantly reduce health care-related infections caused by implanted medical devices—or drastically improve cleanup efforts following environmental disasters like oil spills.
Like a spongy Swiss Army knife, the porous three-dimensional foam is water repellent—meaning it resists blood, microbes and proteins, while also exhibiting antimicrobial and oil-water separation properties. Its versatility, functionality and relatively inexpensive production costs could make it a valuable resource for future clinicians and environmental remediation professionals ...
Integrative neuro-oncology for brain tumor patients
2023-04-26
The University of Cincinnati's Soma Sengupta, MD, PhD, published an article in the Journal of Neuro-Oncology April 25 discussing her journey and approach to practicing integrative neuro-oncology.
Sengupta, associate professor in neurology, director of neuro-oncology clinical trials, associate director of the Brain Tumor Center and a UC Health neuro-oncologist, funded by the Harold C. Schott Endowed Chair in Molecular Therapeutics (Neurosurgery) and the Pam and Tom Mischell Funds, said she personally ...
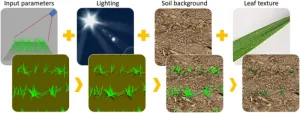
A high-throughput AI method for leaf counting
2023-04-26
In cereal crops, the number of new leaves each plant produces is used to study the periodic events that constitute the biological life cycle of the crop. The conventional method of determining leaf numbers involves manual counting, which is slow, labor-intensive, and usually associated with large uncertainties because of the small sample sizes involved. It is thus difficult to get accurate estimates of some traits by manually counting leaves.
Conventional methods have, however, been improved upon with technology. Deep learning has enabled the use of object detection and segmentation algorithms to estimate the number of plants (and ...
Humidity may increase heat risk in urban climates
2023-04-26
As temperatures across the globe reach record-level highs, urban areas are facing increased heat stress. Cities are generally warmer and dryer than adjacent rural land. But in the Global South, there is an additional complicating factor — urban humid heat.
A new study, led by Yale School of the Environment scientists and published in Nature, investigated the combined effect of temperature and humidity on urban heat stress using observational data and an urban climate model calculation. Researchers found that the heat stress burden is dependent on local climate and a humidifying effect can erase the cooling benefits that would come from trees and vegetation.
“A widely ...
Roadmap to fair AI: revealing biases in AI models for medical imaging
2023-04-26
Artificial intelligence and machine learning (AI/ML) technologies are constantly finding new applications across several disciplines. Medicine is no exception, with AI/ML being used for the diagnosis, prognosis, risk assessment, and treatment response assessment of various diseases. In particular, AI/ML models are finding increasing applications in the analysis of medical images. This includes X-ray, computed tomography, and magnetic resonance images. A key requirement for the successful implementation of AI/ML models in ...