(Press-News.org) CRISPR claimed scientific fame for its ability to quickly and accurately edit genes. But, at the core, CRISPR systems are immune systems that help bacteria protect themselves from viruses by targeting and destroying viral DNA and RNA. A new study published in Science reveals a previously unrecognized player in one such system – a membrane protein that enhances anti-viral defense – simultaneously broadening our understanding of and raising more questions related to the complexities of CRISPR.
Uncovering New Clues about CRISPR
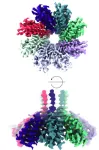
CRISPR systems consist of two major components – a guide RNA that targets a specific viral DNA or RNA sequence and a Cas enzyme that cuts the targeted DNA or RNA, preventing a virus from replicating and spreading. A team at the University of Rochester Center for RNA Biology found that a specific Cas protein (Cas13b) not only cuts viral RNA, but communicates with another protein (Csx28) to augment its anti-viral defense.
In partnership with scientists at Cornell, the team discovered that the Csx28 protein forms a pore-like structure (i.e. it has a big hole in it). When they infected E. coli with a phage (virus that attacks bacteria) and deployed the CRISPR-Cas13 system to target and halt infection, they found that Cas13 signals to Csx28 to affect membrane permeability. Once this happens, Csx28 wreaks havoc in the infected cell, discombobulating membrane potential, crushing metabolism and hindering energy production. A virus can’t replicate under such unhospitable circumstances, leading to the team’s conclusion that Csx28 enhances CRISPR-Cas13b’s phage defense.
“This finding upends the idea that CRISPR systems mount their defense only by degrading RNA and DNA in cells and really broadens our view of how CRISPR systems may be working,” said corresponding author Mitchell O’Connell, PhD, assistant professor of Biochemistry and Biophysics at the University of Rochester Medical Center (URMC) and a member of the UR Center for RNA Biology. “When we think about CRISPR, we see Cas proteins such as Cas9 or Cas13 as the big hammer doing all the damage, but that might not be the case; we found that Cas13 and Csx28 are working together to effectively extinguish a virus.”
“When you read this paper you think to yourself…‘what?’ This is such a weird mechanism and not the way I would have predicted that bacteria would work,” added John Lueck, PhD, assistant professor of Pharmacology and Physiology at URMC. “It is really impressive that the team identified this pore-like protein that doesn’t resemble anything else we’ve seen before, and now that we know that this mechanism exists people will start to look for it in other systems. This is exciting because in science, when you scratch the surface, you often find that there is an entirely new world behind it.”
More Questions than Answers
With the added knowledge of the structure of Csx28 through the use of high-resolution cryo-EM, the team is beginning to probe the function of the protein. Questions abound. If the goal is protection, why is there a giant hole in the membrane? The team found that when Cas13 isn’t around, Csx28 isn’t active. What makes it become active in defense? How long does it stay active and what does it let through the membrane? Understanding the biochemistry behind the opening and closing of the pore will shed light on how CRISPR-Cas13 uses it as part of its defense and provide a jumping off point for the study of membrane proteins across other CRISPR systems.
“This finding is unexpected and raises all kinds of new questions about how bacteria protect themselves and what they are doing to survive infection,” noted Mark Dumont, PhD, a professor of Biochemistry and Biophysics at URMC who has spent his career studying membrane proteins. “It is also a very interesting interface between RNA biology, CRISPR, structural biology and membrane biology. While there is no immediate medical relevance or application, the ideas that boil up from this could be very powerful.”
Lueck adds, “It is very rare for one study to have this many thought-provoking pieces that it brings several different fields together. And because the concepts are brand new, future work won’t be burdened by dogma. Any time people can bring fresh, unfettered ideas to the table it is really good for science.”
In addition to O’Connell, lead study author Arica VanderWal, PhD, a former graduate student in O’Connell’s lab who is now a postdoctoral researcher at UC San Diego, contributed to the research. Graduate students Julia K. Nicosia and Adrian M. Molina Vargas in the O’Connell lab, Bogdan Polevoda, PhD, research assistant professor of Biochemistry and Biophysics at URMC, and Elizabeth Kellogg, PhD, and Jung-Un Park from the department of Molecular Biology and Genetics at Cornell University also supported the research. The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health.
END
Pulling the plug on viral infections: CRISPR isn’t just about cutting
Study shows how a Cas protein partners with a unique membrane protein to stop viral infection in bacteria
2023-04-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Unraveling the mathematics behind wiggly worm knots
2023-04-27
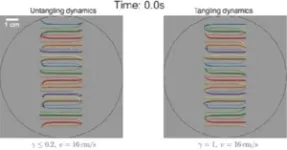
For millennia, humans have used knots for all kinds of reasons — to tie rope, braid hair, or weave fabrics. But there are organisms that are better at tying knots and far superior — and faster — at untangling them.
Tiny California blackworms intricately tangle themselves by the thousands to form ball-shaped blobs that allow them to execute a wide range of biological functions. But, most striking of all, while the worms tangle over a period of several minutes, they can untangle in mere milliseconds, escaping at the first sign of a threat from a predator.
Saad Bhamla, assistant ...
Information ‘deleted’ from the human genome may be what made us human
2023-04-27
New Haven, Conn. — What the human genome is lacking compared with the genomes of other primates might have been as crucial to the development of humankind as what has been added during our evolutionary history, according to a new study led by researchers at Yale and the Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard.
The new findings, published April 28 in the journal Science, fill an important gap in what is known about historical changes to the human genome. While a revolution in the capacity to collect data from genomes ...
Mammalian evolution provides hints for understanding the origins of human disease
2023-04-27
CHAPEL HILL, N.C. – Hundreds of scientific studies have been conducted over the years to find the genes underlying common human traits, from eye color to intelligence and physical and mental illnesses.
Patrick Sullivan, MD, FRANZCP, the Yeargan Distinguished Professor of Psychiatry and Genetics at the UNC School of Medicine, and the Psychiatric Genomic Consortium have produced a new packet for the journal Science, to give researchers another way to understand human disease, using the power of evolutionary genomics.
“This is a tool that can give us a lot of important hints about human disease,” ...
How dormant bacteria come back to life
2023-04-27
Solving a riddle that has confounded biologists since bacterial spores — inert, sleeping bacteria — were first described more than 150 years ago, researchers at Harvard Medical School have discovered a new kind of cellular sensor that allows spores to detect the presence of nutrients in their environment and quickly spring back to life.
It turns out that these sensors double as channels through the membrane and remain closed during dormancy but rapidly open when they detect nutrients. Once open, the channels allow electrically charged ions to flow out through the cell membrane, setting in motion ...
Collaborative and creative policies needed to maximize psychedelics’ therapeutic potential
2023-04-27
HOUSTON – (April 27, 2023) – Research supports the promise of psychedelics in treating conditions like depression and post-traumatic stress disorder, but the future regulatory landscape for these drugs remains unclear. Experts from Baylor College of Medicine, the University of Pennsylvania, American University and Harvard Law School call for creativity and collaboration at the federal and state levels in developing policies for the use and oversight of psychedelics and a commitment to developing a strong evidence base for efficacy and safety.
In a paper published in the journal Science, the authors, experts in bioethics, law and ...
Fish’s growth is not reduced by spawning
2023-04-27
Contrary to what is stated in biology textbooks, the growth of fish doesn’t slow down when and because they start spawning. In fact, their growth accelerates after they reproduce, according to a new article published in Science.
“Fish don’t have to choose between growth or reproduction because, in the real world, they don’t occur simultaneously but rather sequentially,” says University of British Columbia (UBC) fisheries researcher Dr. Daniel Pauly, co-author of ...
Local holographic transformations: tractability and hardness
2023-04-27
Counting problems arise in many different fields, e.g., statistical physics, economics and machine learning. In order to study the complexity of counting problems, several natural frameworks have been proposed. Two well studied frameworks are counting constraint satisfaction problems (#CSP) and Holant problems. For counting satisfaction problems over the Boolean domain, two explicit tractable families namely and , are identified; any function set which is not contained in these two families is proved to be #P-hard. Furthermore, counting CSPd is the counting constraint satisfaction problem restricted to the instances where every variable occurs a multiple of d times. The team ...
IVF procedures can be improved by combining genetic and clinical data to predict the number of eggs retrieved in patients undergoing ovarian stimulation
2023-04-27
IVF procedures can be improved by combining genetic and clinical data to predict the number of eggs retrieved in patients undergoing ovarian stimulation.
####
Article URL: https://journals.plos.org/ploscompbiol/article?id=10.1371/journal.pcbi.1011020
Article Title: Personalized prediction of the secondary oocytes number after ovarian stimulation: A machine learning model based on clinical and genetic data
Author Countries: Poland
Funding: The research was co-financed by the European Regional Development Fund under the ...
NRG Oncology study results confirm conventional external beam radiotherapy should remain standard of care in treating localized vertebral metastases of the spine
2023-04-27
Results from the NRG Oncology RTOG 0631 clinical trial comparing stereotactic vs. conventional radiotherapy for localized vertebral metastases of the spine did not meet its primary endpoint. Data from the study suggests that radiosurgery was not considered superior in terms of pain responses at 3 months following treatment, and even displayed worse pain response, than the conventional external beam radiotherapy (cEBRT). These results were recently published in the JAMA Oncology.
cEBRT is currently the standard of care for treating ...
Being hospitalized with acute kidney injury may increase risk for rehospitalization and death
2023-04-27
A study supported by the National Institutes of Health found that people who experienced acute kidney injury (AKI) during a hospitalization, including those admitted with AKI or who developed AKI in the hospital, were more likely to revisit the hospital or die shortly after discharge, compared to people hospitalized without AKI. AKI is a sudden loss of kidney function that usually lasts for a short time. The research, funded by NIH’s National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK), was ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Massive-scale spatial multiplexing with 3D-printed photonic lanterns achieved by researchers
Younger stroke survivors face greater concentration, mental health challenges — especially those not employed
From chatbots to assembly lines: the impact of AI on workplace safety
Low testosterone levels may be associated with increased risk of prostate cancer progression during surveillance
Analysis of ancient parrot DNA reveals sophisticated, long-distance animal trade network that pre-dates the Inca Empire
How does snow gather on a roof?
Modeling how pollen flows through urban areas
Blood test predicts dementia in women as many as 25 years before symptoms begin
Female reproductive cancers and the sex gap in survival
GLP-1RA switching and treatment persistence in adults without diabetes
Gnaw-y by nature: Researchers discover neural circuit that rewards gnawing behavior in rodents
Research alert: How one receptor can help — or hurt — your blood vessels
Lamprey-inspired amphibious suction disc with hybrid adhesion mechanism
A domain generalization method for EEG based on domain-invariant feature and data augmentation
Bionic wearable ECG with multimodal large language models: coherent temporal modeling for early ischemia warning and reperfusion risk stratification
JMIR Publications partners with the University of Turku for unlimited OA publishing
Strange cosmic burst from colliding galaxies shines light on heavy elements
Press program now available for the world's largest physics meeting
New release: Wiley’s Mass Spectra of Designer Drugs 2026 expands coverage of emerging novel psychoactive substances
Exposure to life-limiting heat has soared around the planet
New AI agent could transform how scientists study weather and climate
New study sheds light on protein landscape crucial for plant life
New study finds deep ocean microbes already prepared to tackle climate change
ARLIS partners with industry leaders to improve safety of quantum computers
Modernization can increase differences between cultures
Cannabis intoxication disrupts many types of memory
Heat does not reduce prosociality
Advancing brain–computer interfaces for rehabilitation and assistive technologies
Detecting Alzheimer's with DNA aptamers—new tool for an easy blood test
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal study develops radiomics model to predict secondary decompressive craniectomy
[Press-News.org] Pulling the plug on viral infections: CRISPR isn’t just about cuttingStudy shows how a Cas protein partners with a unique membrane protein to stop viral infection in bacteria